* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Year-Long Expense Budget Plan
Pensions crisis wikipedia , lookup
Debtors Anonymous wikipedia , lookup
Business valuation wikipedia , lookup
Household debt wikipedia , lookup
Federal takeover of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac wikipedia , lookup
Present value wikipedia , lookup
Conditional budgeting wikipedia , lookup
Continuous-repayment mortgage wikipedia , lookup
Mark-to-market accounting wikipedia , lookup
Securitization wikipedia , lookup
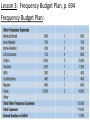
Date: 11.4 Notes: Lesson Objective: Develop and interpret a cash flow chart, frequency budget plan and a year-long expense budget plan. CCSS: A.SSE.1, F.BF.1 You will need: your book This is Jeopardy!!!: John makes $11 per hour. He makes time and a half on the hours he works beyond 40 hours in a week. His income tax withholdings are 20%. What would his net pay be if he works 46 hours in one week? Lesson 1: Not-So-Quick Write A. What is cash flow and a cash flow analysis? B. What is included in income? C. What are fixed expenses? Variable expenses? D. Why should savings be considered as an expense? Explain your rationale. E. What does it mean to prorate, and why would you need to do this? Lesson 1: Not-So-Quick Write F. What are assets and liabilities? G. What is net worth, and what does this tell you about your financial situation? H. What is debt-to-income ratio, and how/when should you use it? I. When do you need to create a debt reduction plan? Lesson 2: Cash Flow Analysis A. What is cash flow and a cash flow analysis? Lesson 2: Cash Flow Analysis, p. 691 Lesson 2: Creating, Using & Modifying a Budget Envelope Accounting System: Frequency Budget Plan: Year-Long Expense Budget Plan: Lesson 3: Frequency Budget Plan, p. 694 Frequency Budget Plan: Lesson 3: Frequency Budget Plan, p. 694 Frequency Budget Plan: Lesson 3: Frequency Budget Plan, p. 694 Frequency Budget Plan: Lesson 3: Frequency Budget Plan, p. 694 Frequency Budget Plan: Lesson 4: Year-Long Expense Plan, p. 695 Year-Long Expense Budget Plan: Lesson 4: Year-Long Expense Plan, p. 695 Year-Long Expense Budget Plan: Lesson 4: Year-Long Expense Plan, p. 695 Year-Long Expense Budget Plan: Lesson 4: Year-Long Expense Plan, p. 695 Year-Long Expense Budget Plan: Lesson 5: Assets and Liabilities Decide whether the following are an asset or a liability. Lesson 5: Assets and Liabilities Decide whether the following are assets or a liabilities. A. B. C. D. E. Balance in checking account Current value of home Remaining balance on mortgage of home Current value of computer Amount of love of money Lesson 5: Assets and Liabilities Decide whether the following are an asset or a liability. F. The difference between total assets and total liabilities G. Combined credit card balance H. Current value of retirement account I. Current value of video equipment J. Remaining balance on car loan Lesson 6: Net Worth Liam Brown is single, in his mid-20s, and owns a condo in a big city. He has calculated the following assets and liabilities. Lesson 6: Net Worth Assets: Current value of condo: $580,000 Current value of car (as listed in Kelley Blue Book): $17,000 Balance in checking account: $980 Combined balance in all savings accounts: $22,500 Current balance in retirement account: $24,800 Current value of computer: $2,900 Current value of collector bass guitar: $6,700 Current value of stocks/bonds: $18,300 TOTAL ASSETS: Lesson 6: Net Worth Liabilities: Remaining balance owed on home mortgage: $380,000 Remaining balance owed on student loans: $51,000 Combined credit card debt: $1,600 TOTAL LIABILITIES: Lesson 6: Net Worth Calculate Liam’s net worth. Last year at this time, he calculated his net worth as $205,780. Compare both values. What do the changes mean? Lesson 6: Net Worth Calculate Liam’s net worth. Last year at this time, he calculated his net worth as $205,780. Compare both values. What do the changes mean? TOTAL ASSETS: TOTAL LIABILITIES: NET WORTH: – _____________ Lesson 6: Net Worth Calculate Liam’s net worth. Last year at this time, he calculated his net worth as $205,780. Compare both values. What do the changes mean? TOTAL ASSETS: TOTAL LIABILITIES: NET WORTH: Previous Net Worth: Change in Net Worth: – _____________ _____________ ============= Lesson 7: Debt Debt-to-Income Ratio: Lesson 7: Debt Debt-to-Income Ratio: Liam’s Liabilities: Remaining balance owed on home mortgage: $380,000 Remaining balance owed on student loans: $51,000 Combined credit card debt: $1,600 TOTAL LIABILITIES: Lesson 7: Debt Liam’s Monthly Liability: Mortage: $ 2,500 Student Loan: 510 Credit Card Payment: 150 Total Monthly Liability: $ Liam’s Total Monthly Income: Gross Salary: $ 7,000 Investment Income 500 Total Monthly Income: $ Debt-to-Income Ratio: 11.4: DIGI Yes or No 1. The frequency budget from p. 694 states that Dave and Joan have an annual surplus of $1,284. How does this relate to the monthly positive cash flow from p. 691? 2. In Example 5, what would Liam’s net worth be if the current value of his condo increased by 10%, he paid down his student loan $5,000 and he paid off his credit card debt? Continued on next slide 1.2: DIGI Yes or No 3. Thome anticipates that next year, his car and student loans will have been paid off and he will have received a 10% salary increase. If everything else remains the same, calculate the debt-to-income ratio in Example 6.