* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 8.4 Similar Triangles
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Penrose tiling wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
Brouwer fixed-point theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Apollonian network wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
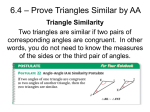
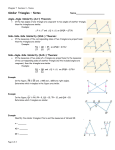
10.2 Proving Triangles Similar Geometry Mr. Calise Objectives/Assignment Identify similar triangles. Use similar triangles in real-life problems such as using shadows to determine the height of the Great Pyramid Identifying Similar Triangles In this lesson, you will continue the study similar polygons by looking at the properties of similar triangles. Ex. 1: Writing Proportionality Statements In the diagram, ∆BTW ~ ∆ETC. a. Write the statement of proportionality. b. Find mTEC. c. Find ET and BE. T E 34° C 3 20 79° B 12 W Ex. 1: Writing Proportionality Statements In the diagram, ∆BTW ~ ∆ETC. a. Write the statement of proportionality. ET BT = TC TW = T E 34° C 3 20 CE WB 79° B 12 W Ex. 1: Writing Proportionality Statements In the diagram, ∆BTW ~ ∆ETC. Find mTEC. B TEC, SO mTEC = 79° b. T E 34° C 3 20 79° B 12 W Ex. 1: Writing Proportionality Statements In the diagram, ∆BTW ~ ∆ETC. c. Find ET and BE. CE ET = WB BT Write proportion. 3 ET = 12 20 Substitute values. 3(20) = ET 12 5 = ET T E C 3 20 Multiply each side by 20. Simplify. 34° 79° B 12 W Because BE = BT – ET, BE = 20 – 5 = 15. So, ET is 5 units and BE is 15 units. Postulate 25 Angle-Angle Similarity Postulate If two angles of one triangle are congruent to the two angles of another triangle, then the two triangles are similar. If JKL XYZ and KJL YXZ, then ∆JKL ~ ∆XYZ. K L Y J X Z Ex. 2: Proving that two triangles are similar Color variations in the tourmaline crystal shown lie along the sides of isosceles triangles. In the triangles, each vertex measures 52°. Explain why the triangles are similar. Ex. 2: Proving that two triangles are similar Solution. Because the triangles are isosceles, you can determine that each base angle is 64°. Using the AA Similarity Postulate, you can conclude the triangles are similar. Side-Angle-Side Similarity Theorem If an angle in one triangle is congruent to an angle in another triangle, and the sides including the two angles are proportional, then the two triangles are similar. (SAS Similarity Thm.) USING SIMILARITY THEOREMS THEOREM S THEOREM 10.1 Side-Angle-Side (SAS) Similarity Theorem If an angle of one triangle is congruent to an angle of a second triangle and the lengths of the sides including these angles are proportional, then the triangles are similar. If X P XY M and ZX = PM then XYZ ~ MNP. M X MN Z Y N Side-Side-Side Similarity Theorem If the corresponding sides of two triangles are proportional, then the two triangles are similar. (SSS Similarity Thm.) USING SIMILARITY THEOREMS THEOREM S THEOREM 10.2 Side-Side-Side (SSS) Similarity Theorem If the corresponding sides of two triangles are proportional, then the triangles are similar. P A Q R If AB = BC = CA PQ QR RP then ABC ~ PQR. B C Using the SSS Similarity Theorem Which of the following three triangles are similar? 12 A 6 C E 6 9 F 14 G J 4 8 6 10 D B H SOLUTION To decide which of the triangles are similar, consider the ratios of the lengths of corresponding sides. Ratios of Side Lengths of ABC and DEF AB = 46 = 32 , DE Shortest sides CA 3 = 12 = , 8 2 FD Longest sides BC = 69 = 32 EF Remaining sides Because all of the ratios are equal, ABC ~ DEF Finding Distance Indirectly ROCK CLIMBING are at an indoor climbing wall. To estimate of SimilarYou triangles can be used to find distances thatthe areheight difficult the wall, youto place a mirror on the floor 85 feet from the base of the wall. Then measure directly. you walk backward until you can see the top of the wall centered in the mirror. You are 6.5 feet from the mirror and your eyes are 5 feet above the ground. Use similar triangles to estimate the height of the wall. D B 5 ft Not drawn to scale A 6.5 ft C 85 ft E Finding Distance Indirectly Use similar triangles to estimate the height of the wall. SOLUTION Due to the reflective property of mirrors, you can reason that ACB ECD. D Using the fact that ABC and EDC are right triangles, you can apply the AA Similarity Postulate to conclude that these two triangles are similar. B 5 ft A 6.5 ft C 85 ft E Finding Distance Indirectly Use similar triangles to estimate the height of the wall. SOLUTION DE EC Ratios of lengths of = corresponding sides are equal. BA AC So, the height of the wall is about 65 feet. DE = 85 Substitute. 5 6.5 D Multiply each side by 5 and simplify. 65.38 DE B 5 ft A 6.5 ft C 85 ft E Note: If two polygons are similar, then the ratio of any two corresponding lengths (such as altitudes, medians, angle bisector segments, and diagonals) is equal to the scale factor of the similar polygons. Ex. 5: Using Scale Factors Find the length of the altitude QS. Solution: Find the scale factor of ∆NQP to ∆TQR. NP = TR 12+12 8+8 = QS 3 = 2 Substitute 6 for QM and solve for QS to show that QS = 4 12 M 24 = 3 16 2 Now, because the ratio of the lengths of the altitudes is equal to the scale factor, you can write the following equation: QM 12 N P 6 Q R 8 S 8 T Homework Finish The Worksheets from Thursday DUE on Monday!