* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Animal Structure and Function
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
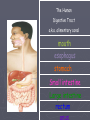
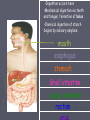
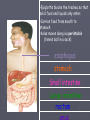
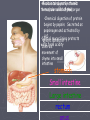
Animal Structure and Function Thermoregulation ► Ectotherms Obtain body heat from the environment. Poikilotherms ►Invertebrates, ►“cold amphibians, reptiles and fish. blooded” ► Endotherms Generate their own body heat. Homeotherms ►Mammals ►Warmblooded Temperature Regulation ► Cooling evaporation Sweating Panting ► Warming by metabolism Shivering ► Adjusting surface area Changing the volume of blood flow Countercurrent Exchange The Respiratory System ► Direct contact with the environment Cells have large surface areas with which they can have exchange with the environment. ► Gills Evaginated structures that create large surface areas. ► Tracheae Chitin lined tubes that permeate the body. Oxygen enters the tracheae through opening called spiracles. ► Lungs Invaginated structures which allow gas exchange Human Respiration ► Nose, pharynx, larynx ► Trachea ► Bronchi, bronchioles ► Alveolus ► Diffusion between alveolar chambers and blood. ► Bulk flow of O2 ► Diffusion between blood and cells ► Bulk flow of CO2 Circulatory System ► Open Circulatory Systems Blood is pumped into an internal cavity-hemocoel The tissues and organs are bathed in hemolymph. Hemolymph returns to the heart through holes called ostia. ► Mollusks, ► Closed insects Circulatory Systems Blood is confined to vessels. ► Annelida Octopuses, Squid, Vertebrate Human Circulatory System ► Basics: Arteries arterioles Capillaries Gas and waste exchange Venules Veins Heart Pumping Blood Through the Heart ► Right Atrium Deoxygenated blood enters via the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava ► Right Ventricle Blood moves through the tricuspid valve (right atrioventricular valve or AV valve) to the right ventricle. Right ventricle pumps the blood to the pulmonary artery through the pulmonary semilunar valve to the lungs. ► Left Atrium Oxygenated blood returns to the left Atrium through the pulmonary vein. ► Left Ventricle Blood moves through the bicuspid (mitral or left AV valve) to the left ventricle. The blood is then pumped from the heart via the aorta through the aortic semilunar valve and to the body. The Cardiac Cycle ► The rhythmic contraction and relaxation of heart muscles. ► Regulated by auto rhythmic cells which are selfexcitable. SA node, pacemaker ► Upper wall of the right atrium ► Initiates the cycle by contracting both atria AV node ► Lower half of the right atrium ► Receives a delayed impulse from the SA node then contracts the ventricles. Systole Phase ► Blood is forced through the pulmonary arteries and aorta and the AV valves are forced to close. Blood ► RBC, erythrocytes Transport oxygen ► WBC, leukocytes Disease fighting cells ► Platelets Cell fragements Blood clotting ► Plasma Liquid The Excretory System ► The excretory systems help maintain homeostasis in organisms by regulating water balance. Osmoregulation ► The absorption and excretion of water and dissolved substances so that proper water balance is maintained between the organism and its surroundings. Marine fish ►Hypoosmotic ►Drink lots, pee little Fresh water fish ►Hyperosmostic ►Drink little, pee lots Excretory Mechanisms ► Contractile ► Flame Vacuoles Cells ► Nephridia ► Malpighian tubules ► Kidney Contractile Vacuole ► Vacuole accumulates water and then merges with the plasma membrane to release the water Flame Cells ► An internal cilia that moves wastes out of the cell. Nephridia ► Fluids are concentrated as they pass through a collecting tubule. ► Blood capillaries that surround the tubule reabsorb necessary materials. ► The concentrated waste materials are excreted through an excretory pore. ► Early tubular excretory system Malpighian Tubules ► Tubes attached to the midsection collect body fluids from the hemolymph. ► Wastes are deposited into the midgut and out the anus Kidney ► Nephrons filter blood. ► Waste is collect and excreted through the ureters to the bladder. ► Urine is excreted through the urethra. Nephron Parts ► Bowman’s capsule ► Convoluted Tubule ► Collecting Tubule Bowman’s Capsule ► Bulb-shaped body. ► Renal artery (afferent arteriole) enters into the Bowman’s capsule to form a dense ball of capillaries Glomerulus ► Then exits the capsule (efferent arteriole) Convoluted Tubule ► Begins with the proximal convoluted tubule at Bowman’s capsule. ► Ends with the distal convoluted tubule where it joins with the collecting duct. ► Middle: Loop of Henle Descending and ascending limb Collecting Duct ► Descends to the center of the kidney. ► Shared by multiple nephrons ► Empties into the renal pelvis Drains into the ureter How does the Nephron Work ► Filtration Blood enters the glomerulus Filtrate that enters flows into the convoluted tube. ► Secretion Filtrate passes through the proximal tubule and distal tubule. Interstitial fluids join the filtrate from the capillary network. ► Reabsorption Filtrate moves down the loop of Henle water moves out. Filtrate moves up the loop of Henle and salts are removed. Filtrate descends through the collecting duct toward the renal pelvis as concentrated urine. Hormones ► Influence osmoregulation by regulating salts concentration Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) ►Increases reabsorption of water by the body. ►Increasing the permeability of the collecting duct to water. Aldosterone ►Increases the reabsorption of water and sodium. ►Increasing the permeability of the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct to sodium. Nitrogen Waste ► Toxic ammonia is the result of amino acids and nucleic acids. Mechanisms to rid the body ►Aquatic animals excrete NH3 directly into the surrounding water. ►Mammals convert NH3 to urea in the liver. ►Birds, insects and reptiles convert urea to uric acid. Concentrated precipitate The Human Digestive Tract a.k.a. alimentary canal mouth esophagus stomach Small intestine Large intestine rectum •Ingestion occurs here •Mechanical digestion via teeth and tongue; formation of bolus •Chemical digestion of starch begins by salivary amylase. mouth esophagus stomach Small intestine Large intestine rectum •Epiglottis blocks the trachea so that solid food and liquids only enter. •Carries food from mouth to stomach •bolus moves along via peristalsis (tennis ball in a sock) esophagus stomach Small intestine Large intestine rectum •Mechanical •Food is temporarily digestion stored thanks to here muscular (now called walls of chyme) this organ •Chemical digestion of protein begins by pepsin. Secreted as pepsinogen and activated by HCl mucus lining protects •Special •pyloric sphincter walls from acidity controls movement of chyme into small intestine stomach Small intestine Large intestine rectum •Remainder of Smalldigestion Intestine: •Duodenum: •Liver: Mechanical proteases digest of •Pancreas: produces enzymes monosachharides, amino acids, proteins, lipid thanks maltase to bile and (made lactase in proteases, lipase, and and nucleotides are absorbed digest liver/stored disaccharides in gall bladder) and pancreatic amylase into bloodfats vessels inand villianand phosphateases emulsify digest alkaline solution. microvilli nucleotides Small intestine (small diameter, long length) Large intestine rectum •Appendix is found at the junction of the small and large intestine (called a cecum in herbivors and larger) •Contains helpful bacteria which make some vitamins we need •Absorbs water and vitamins Large intestine (large diameter, short length) rectum •stores feces until egestion rectum •egestion occurs here Hormones ► Gastrin Produced in the stomach Enters the blood stream to stimulate the cells of the liver to produce gastric juices. ► Secretin Produced by the duodenum when food enters. Stimulates production of bicarbonate which neutralizes the acid. ► Cholecystokinin Produced by the small intestine. Stimulates the gallbladder to release bile and the pancreas to release enzymes Nervous System ► Basic structural Unit: Neuron ► 3 Parts: Cell Body Dendrite Axon ►Dendrite Axon Cell Body Axon Branches of the 3 Neuron Groups ► Sensory Neurons (afferent neurons) Receive the initial stimulus ► Motor Neurons (efferent neurons) Stimulate target cells (effectors) that produce some type of response. ► Association Neurons (interneurons neurons) Located in the spinal chord or brain. Receive impulses from sensory neurons or send impulses to motor neurons. Intergrators: Evaluate impulses for appropriate responses. How does it work? ► Overview Is the result of chemical changes across the membrane of the neuron. Unstimulated neuron is polorized ► The inside of the cell is negative with respect to the outside. Polarization is established by maintaining an excess of sodium on the outside and an excess of potassium on the inside. Other negatively charged ions such as protiens and nucleic acids reside inside the cell resulting in the overall negative charge on the inside of the cell membrane. Events of Nerve Impulse Transmission ► Resting potential ► Action potential ► Repolarization ► Hyperpolarization ► Refractory period Resting potential ► Unstimulated polized state. Action potential ► Stimulus ► Gated ion channels in the membrane suddenly open and permit the sodium on the outside to rush into the cell. ► The mebrane becomes depolarized. If the stimulus is strong enough (above the threshold level) more sodium gates open. The action potential continues down the