* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Guided notes part 1 - Duplin County Schools
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
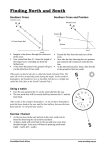
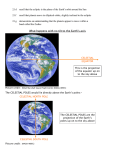
22.2 Part 1 Note Guide The Earth-Moon-Sun System People have always been fascinated by the changing positions of the ____________________________________ in the sky Prehistoric people, for example, built __________________________________ The structure known as ___________________________________ was probably an attempt to better solar predictions At the beginning of ________________________________ in the Northern Hemisphere (the summer solstice on June 21 or 22), the _________________________________________ comes up directly above the heel stone of Stonehenge Besides keeping this calendar, Stonehenge may also have provided a method of determining ________________________________ Motions of Earth The two main motions of Earth are _____________________________________________________________ Rotation is the ___________________________, or _______________________________, of a body on its axis Revolution is the motion of a body, such as a _________________________________________________, along a path around some point in space For example, ___________________________ revolves around the sun, and the __________________________ revolves around Earth Earth also has another very slow motion known as _________________________________, which is the slight movement, over a period of __________________________________, of Earth’s axis Rotation The main results of Earth’s rotation are ___________________________________________________ Earth’s rotation has become a standard method of measuring _____________________________ because it is so dependable and easy to use Each rotation equals about ___________________________________ We can _______________________________ Earth’s rotation in two ways, making two kinds of days Most familiar is the ________________________________________________, the time interval from one noon to the next, which averages about ______________________________ Noon is when the sun has reached its _________________________________, or highest point in the sky The _____________________________________, on the other hand, is the time it takes for Earth to make one complete rotation (_________________________________) with respect to a star other than our sun The sidereal day is measured by the time required for a star to _________________________________ at the identical position in the sky where it was observed the _______________________________________ The sidereal day has a period of ______________ hours, ______________ minutes, and _____________seconds (measured in solar time), which is almost 4 minutes shorter than the mean solar day This difference results because the direction to distant _________________________ barely changes because of Earth’s slow _____________________________ along it orbit The direction to the sun, on the other hand, changes by almost ________________________________ each day In sidereal time, “_______________________” occurs four minutes earlier each day Therefore, after six months, “_______________________” occurs at “_________________________” Astronomers use sidereal time because the ____________________________ appear in the same position in the sky every 24 _____________________________ hours Usually, an observatory will begin its sidereal day when the position of the _______________________________ is directly overhead Revolution Earth revolves around the sun in an elliptical orbit at an average speed of _______________________ kilometers per hour Its average ______________________________ from the sun is 150 million kilometers But because its orbit is an ellipse, Earth’s distance from the sun ___________________________ At _________________________________, Earth is closest to the sun—about ______________ million kilometers away Perihelion occurs about _______________________________ each year At _________________________________, Earth is farthest from the sun—about ___________ million kilometers away Aphelion occurs about __________________________ So Earth is __________________________ from the sun in July and ___________________________ to the sun in January Because of Earth’s ________________________________________________ around the sun, each day the sun appears to be displaced among the constellations at a distance equal to about twice its width, or __________________ The apparent annual path of the sun against the backdrop of the celestial sphere is called the ____________________________ Generally, the ____________________________________________________ travel in nearly the same plane as Earth So their paths on the celestial sphere lie near the ____________________________ Earth’s Axis and Seasons The ______________________________________________ that connects Earth’s orbit with the celestial sphere is called the plane of the ecliptic From the reference plane, Earth’s axis of rotation is tilted about _________________________________ Because of Earth’s _____________________, the apparent _______________________ of the sun and the _____________________________ equator intersect each other at an angle of 23.5 degrees This angle, 23.5 degrees, is very important to Earth’s _________________________________ Because of the inclination of Earth’s axis to the plane of the ecliptic, Earth has its yearly cycle of ___________________________ When the apparent position of the ______________________ is plotted on the celestial sphere over a period of a year’s time, its path intersects the celestial equator at ______________________ points From a ____________________________ Hemisphere point of view, these intersections are called the spring equinox (March ___________________) and autumn equinox (September ___________________) On June 21 or 22, the date of the __________________________________________, the sun appears 23.5 degrees north of the celestial equator Six months later, on December 21-22, the date of the _______________________________________________, the sun appears 23.5 degrees south of the celestial equator Precession A third and ________________________________________________________ of Earth is called precession Earth’s ____________________________ maintains approximately the same angle of tilt But the direction in which the axis ____________________________ continually changes As a result, the axis traces a ____________________________ on the sky This movement is very similar to the wobble of a __________________________________________ At the present time, the axis points toward the bright star ______________________________ In the year ________________________, it will point toward the bright star _______________________, which will then become the North Star The period of precession is ______________________________________ By the year _______________________, __________________________ will once again be the North Star Precession has only a minor effect on the ________________________________, because the angle of tilt changes only slightly It does, however, cause the positions of the seasons (________________________________________________) to move slightly each year among the stars Earth-Sun Motion In addition to its own movements, ___________________________ accompanies the sun as the entire solar system speeds in the direction of the bright star ______________________ at 20 kilometers per second Also, the sun, like other nearby stars, revolves around the ____________________________ This trip takes _________________________________ years to traverse at speeds approaching ______________ kilometers per second The galaxies themselves are also in ______________________________ Earth is presently approaching one of its nearest galactic neighbors, the Great Galaxy in _______________________________ The motions of Earth are _______________________________________________________, and its speed in space is very great