* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mesonet, Plant Available Water - No-Till
Survey
Document related concepts
Weed control wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Crop rotation wikipedia , lookup
Soil compaction (agriculture) wikipedia , lookup
Surface runoff wikipedia , lookup
No-till farming wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Soil salinity control wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
Plant Available Water Monitoring with the Oklahoma Mesonet
2013 No Till Oklahoma Conference, Norman, OK, Feb. 19‐20, 2013 Tyson Ochsner Plant and Soil Sciences, Oklahoma State University
Funding provided by the Oklahoma Water Resources Research Institute, the Oklahoma Water Resources Board, and the Oklahoma Agricultural Experiment Station.
Drought classifications
• Severe impacts begin during agro‐ecological drought
• Agro‐ecological drought often foreshadows hydrologic drought
• Agro‐ecological drought is defined by soil moisture
Pocasset, OK, Aug. 22, 2012 (Sue Ogrocki) Texas Co., OK, Aug. 2012 (Mark Mabry)
Meteorological
Agro‐ecological
Hydrological
• Precipitation deficits
• Precipitation measurements
• Soil moisture deficits
• Soil moisture measurements
• Surface water and groundwater deficits
• Surface and groundwater measurements
Luther, OK, Aug. 4, 2012. (Jim Beckel)
Kay Co., OK, Oct. 18, 2012. (AP)
Large‐Scale Soil Moisture Monitoring
• Automated monitoring networks first emerged in late 1990’s – Oklahoma Mesonet
– NRCS SCAN
(
!
( !
# !(
!
(
!
(
# !(
!
(
#
#
!
(
!
(
!
(
!
(
!
(
#!(
(
#
!
(!
!
(
#
!
(
!
(
!
(
!
(
#
(
!
(!
!
(
#
!
(
!
(
!
!
(
!
((
!
(
!
(
!
(
## #
(!
(
!
(!
( !
!
(!
(
(!
!
(
!
(
(
!
(
!
( !
(
!
( !
!
(( !
(
!
( !
( !
!
(
!
( !
(!
(!
!
(
(
!
(
!
(
!
(
!
(
!
(!
!
(
!
(
(
!
(( !
#
#
!
(
!
(!
(
! !
(
(
!
(
#
#
!
(
!
(
!
(
!
(
!
(
!
(
!
(
(
!
( !
#
!
(
!
(
##
!
(
!
(
!
(
#
!
(
#
!
(
!
(
!
(
(!
(
(!
!
(!
(!
##
!
(
#
#
#
!
(
!
(
!
(
!
(
#
!
(!
(
(
!!
(
!
(
!
(
#
!
(
!
(
#!(
!
(
#
#
!
(
!
(
!
(
!
(
#
#
#
!
(
!
(
!
(
!
(
(
!
!
(
(!
!
(!
(
!
!
(
(
!
(
!(!
(
(!
!
( (!
#!(
#
!
(
!
( !
(!
(
! !
!
( (
!
!
( ((
!
(
!
(!
(
!
(
!
(!
(
(!
!
(
!
(
!
(
!
"
!
(
!
(
!
(
!
(
!!
(
!
( (
!(
!
(
!
(
#
"
"
""""
#
!
(
!
(
#
!
(
!
(
##
#!(
Legend
!
(
("
"
"
""
"
" " """ ""
" "!
"
(
""
""
"
" "
"
"
""
"
!
( " "
!
(
COSMOS
Illinois Water Survey
!
(
!
(
!
(
USDA SCAN
NOAA CRN
#
#!(
ARM SGP Sites
#!(
OK Mesonet
"
NC EcoNET
West Texas Mesonet
!
(
NE High Plains Climate Center
Georgia WeatherNet
USDA ARS Watersheds
Station locations (>700) for some of the in situ soil moisture monitoring networks currently operational in the US. (Mike Cosh)
• Today there is a large and growing system of networks around the world
• Transformative approaches are emerging, e.g.:
– Cosmic rays
– GPS receivers
Soil moisture stations currently contained in the ISMN. Green dots show the stations that are still measuring soil moisture, red dots the stations that were imported from the Global Soil Moisture Data Bank. (Wouter Dorigo)
Large‐Scale Soil Moisture Monitoring
•
Soil Moisture and Ocean Salinity mission (ESA)
– Launched 2009
– Surface soil moisture, 25 mile resolution
•
Soil Moisture Active Passive mission (NASA)
Artist’s rendition of the ESA Soil Moisture and Ocean Salinity (SMOS) satellite (courtesy of Yann Kerr).
– Schedule launch 2014
– Surface soil moisture, 6 mile resolution
•
Problem #1: In situ soil moisture measurements have not been used in any operational drought monitoring system Artist’s rendition of the NASA Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) satellite (courtesy of Eni Njoku).
Plant Available Water (PAW)
• Problem #2: Soil moisture alone does not indicate the water available for plant uptake
0
10
20
30
0
4
8
Soil depth (in)
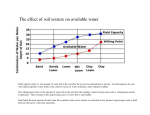
• “Plant available water” is the amount of water stored in the soil and available for plant uptake.
Soil moisture (% by vol.)
Plant available water (3.2 in)
12
16
20
24
28
• We developed an operational, PAW‐based drought monitoring system for Oklahoma.
32
Wilting point
Actual soil moisture
The Oklahoma Mesonet
“…the ‘gold standard’ for statewide mesoscale surface networks…” (National Research Council, 2009)
The 16‐inch Plant Available Water map is based on the 24‐hour‐averaged plant available water for the top 16 inches (40 cm) of soil under the existing vegetation at each Mesonet site for the previous day. Plant available water under other vegetation types may differ. Plant available water is the amount of water in the soil that is potentially available for plant uptake. Technically, it is calculated as the amount of soil water at matric potentials above ‐1500 kPa. The maximum possible plant available water varies between sites due to soil differences. Most plants experience water stress when less than 50% of the maximum plant available water remains in the active root zone. This map is updated once each day between 7 and 8 AM
How can we use this information?
• Soil moisture (and related variables) are key indicators of agro‐
ecological drought.
?
• Availability of soil moisture measurements is rapidly increasing.
• Problem #3: The science required to use these measurements within the context of drought is not well developed.
Pocasset, OK, Aug. 22, 2012 (Sue Ogrocki) Texas Co., OK, Aug. 2012 (Mark Mabry)
Luther, OK, Aug. 4, 2012. (Jim Beckel)
Kay Co., OK, Oct. 18, 2012. (AP)
2008 wheat crop (the good)
• 167 million bushels
• 37 bushels/ac
2006 wheat crop (the bad)
• 82 million bushels
• 24 bushels/ac
2011 wheat crop (the ugly)
• 70 million bushels
• 22 bushels/ac
2013 wheat crop (the ?)
• 69% poor or very poor
• 22% of wheat grazed
– 36% is 5‐yr average
Summary
• Soil moisture is a key drought indicator that has not been used for systematic drought monitoring.
• We are just beginning to develop the science needed to make use of these data within the context of drought.
• “Departure from average” tools can help you interpret Mesonet plant available water.
[email protected]
http://soilphysics.okstate.edu/