* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Volcanic ash filter testing experiments for EDF
Silverthrone Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Cascade Volcanoes wikipedia , lookup
1257 Samalas eruption wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pinatubo wikipedia , lookup
Nevado del Ruiz wikipedia , lookup
Mount Vesuvius wikipedia , lookup
Mount St. Helens wikipedia , lookup
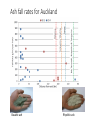
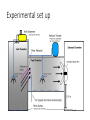
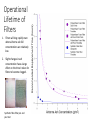
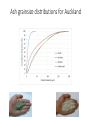
Volcanic ash fall impacts to diesel generators – results from the lab George Williams and Thomas Wilson Volcanic Ash Testing Lab, University of Canterbury [email protected] [email protected] Overview 1. Why is this important? o Ash hazard in New Zealand o Vulnerability of electricity supply to ash o Case study from Argentina 2. What did we do? o Test set up o Test results 3. Implications o Best-practice mitigation and preparedness measures o International interest in further testing • Cordon Caulle volcano erupting in 2011 • Clean and ash clogged filters from a hospital’s HVAC system in Villa la Angostura, Argentina NZ ash sources Tongariro Last eruption 2012 Mayor Island Last eruption ~7,000 a Ruapehu Last eruption 2007 Okataina Last eruption 1886 Taranaki Last eruption ~1854 Taupo Last eruption ~1800 a Volcanic ash impacts to electricity supplies • Impact: Volcanic ash can cause outages on both electrical distribution and transmission networks. High voltage flashover experiments in the Volcanic Ash Testing Laboratory at UC New Zealand transmission network Volcanic ash impacts to GenSets Air Intake Volcanic ash impacts to GenSets Air Intake Engine Air Intake Air flow Radiator Impacts to GenSets - Case study from Argentina The 2011 eruption of Cordon Caulle, Argentina Impacts to GenSets - Case study from Argentina The 2011 eruption of Cordon Caulle, Argentina Impacts to GenSets - Case study from Argentina The 2011 eruption of Cordon Caulle, Argentina Impacts to GenSets - Case study from Argentina Towns receiving ash following the 2011 Cordon Caulle eruption 90 km from Cordon Caulle in the town of Bariloche, 45 mm of ash fell within 24 hours Impacts to GenSets - Case study from Argentina Bariloche • Population: 113,000 (2010) • Latitude: 41° S (the same as Wellington) • Tourism town Impacts to GenSets - Case study from Argentina Electricity supply to Bariloche disrupted • Transmission feed from national grid experienced flashover during the ashfall causing disruption for ~10 days Impacts to GenSets - Case study from Argentina 5MW emergency power generation facility • Ash rapidly clogged air intakes within 12 hours leading to suffocation of generator engines and overheating of radiators • Lead to electricity disruption to key facilities (e.g. hospital, water supply, wastewater treatment facility) Impacts to GenSets - Case study from Argentina Newly built 20 MW generation farm • Modern generator farm set up to provide power to the town • Experienced ongoing issues related to ash ingress following intermittent ash falls <1 mm and remobilised ash Lessons from Argentina – potential mitigation strategies • Deflection hoods installed GenSet air intakes. • Large stocks of filters kept on site to allow for heightened filter replacement frequency post-eruption. Lessons from Argentina – potential mitigation strategies Despite these mitigation measures, a fine layer of ash was still be found within the GenSet’s casing Overview 1. Why is this important? o Vulnerability of electricity supply to ash o Case study from Argentina 2. What did we do? o Test set up o Test results 3. Now what do we do next? o Implications of testing o Best-practice mitigation and preparedness measures o International interest in further testing • Cordon Caulle volcano erupting in 2011 (top) • Clean and ash clogged filters from a hospital’s HVAC system in Villa la Angostura, Argentina What did we do? Filter performance testing Experiments focussed on answering three key questions: 1. Determine ash concentration and volume that will be ingested prior to filtration 2. How effective are a range of standard GenSet filters at filtering ash under different ashfall scenarios? 3. Is there an optimal time to replace filters and how often might this be? Ash fall rates for Auckland Basaltic ash Rhyolitic ash Experimental set up Filter Efficiency 1. Up to 90% of airborne ash immediately outside a GenSet can be ingested into contact with the filters. Irrespective of ash concentration 2. All filters provide a tradeoff between % of ash filtered and airflow rate 3. The percentage of ash filtered varied between different ash types despite similar grainsizes being used – particle mass appears to be an important ash characteristic Operational Lifetime of Filters 1. Filters will clog rapidly even when airborne ash fall concentrations are relatively low. 2. Slight changes in ash concentration have a large effect on the time it takes for filters to become clogged. Synthetic fibre filter pre and post test Take home messages • The test results suggest GenSet operators should plan for replacing filters at much higher frequency during ashfalls. • Even exposure to relatively low ash concentrations may require hourly filter replacement. Facilities which rely on GenSets for emergency power should: 1. have access to a large stock of filters 2. develop filter monitoring and replacement procedures 3. ensure sufficient resources to effect the procedure are available (e.g. maintenance staff and additional generators). • When replacing GenSets, we recommend purchasing those that use high spec filtration. Variety within GenSet filters implies that mitigation measures will need to be determined on a case by case basis Broader resilience considerations • These results need to be taken with broader resilience considerations in mind • fuel supply • staff making it to site: health concerns Future work Currently carrying out tests for a large European nuclear power plant operator who are interested in investigating possible ash impacts to air-handling systems following eruptions from distal volcanoes. Investigate the feasibility of using cyclonic filters versus conventional filters Eruption scenarios for Auckland Basaltic ash Rhyolitic ash Impacts to GenSets - Case study from Argentina Ash travelled around the southern hemisphere having impacts on aviation in NZ Ash grainsize distributions for Auckland