* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download virulence factors
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
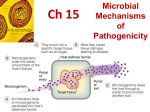
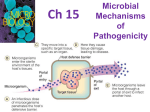
BACTERIAL VIRULENCE FACTORS The ability to: • 1. Adherence • To host surfaces and not be washed off • 2. Avoid phagocytosis • Prevent host defenses from destroying • 3. Penetrate • Get into host and spread • 4. Produce Enzymes • Spread, prevent host defenses and cause damage at or near site of infection • 5. Produce Toxins • Cause damage at distant site Virulence Factors • 1. Adherence • 2. Capsule • 3. Enzymes • leukocidins • Hemolysins • Coagulase • Kinases • Hyaluronidase • Collagenase • Necrotizing Factor 4. Toxins Adherence • Adhesions/ligands bind to receptors on host cells so won’t get flushed off. • Mechanisms to adhere and avoid host defenses: • Glycocalyx Streptococcus mutans Dextran (plaque) • Waxes Mycobacteria • Fimbriae Escherichia coli • M protein Streptococcus pyogenes • Tapered end w/ hooks Treponema pallidum Capsules Prevent phagocytosis and help with attachment (adherence) • Streptococcus pneumoniae • Klebsiella pneumoniae • Haemophilus influenzae • Bacillus anthracis • Streptococcus mutans • Yersinia pestis Enzymes to help penetration Many pathogens secrete enzymes that contribute to their pathogenicity: • Increase virulence by use of enzymes • And avoid phagocytosis • Coagulase Coagulate blood - wall off from host make boil • Kinases Digest fibrin clot - allow spreading streptokinase and staphylolinase • Hyaluronidase Hydrolyses hyaluronic acid connective tissue • Collagenase Hydrolyzes collagen • IgA proteases Destroy IgA antibodies • Hemolysins lyse RBC’s Hemolysins Alpha Hemolytic Streptococci - secrete hemolysins that cause the incomplete lysis or RBC’s Beta Hemolytic Streptococci - secrete hemolysins that cause the complete lysis of RBC’s Leukocidins • Enzymes that attack certain types of WBC’s • 1. Kills WBC’s which prevents phagocytosis • 2. Releases & ruptures lysosomes • lysosomes - contain powerful hydrolytic enzymes which then cause more tissue damage Enzymes: Necrotizing Factor “Flesh Eating Bacteria” Necrotizing fasciitis causes death (necrosis) to tissue cells Toxins Provide properties to spread and cause damage to the host. Compare endotoxins and exotoxins • Endotoxins from inside the cell. Released upon cell lysis. • Exotoxins are secreted out of the cell during cell life. • Toxin Substances that contribute to pathogenicity • Toxigenicity Ability to produce a toxin • Toxemia Presence of toxin the host's blood • Toxoid Inactivated toxin used in a vaccine • Antitoxin Antibodies against a specific toxin Exotoxins Seen in both Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria Figure 15.4a Exotoxin Exotoxin Source Metabolic product Chemistry Fever? Neutralized by antitoxin LD50 Mostly Gram positive By-products of growing cell Protein Water soluble No Yes Small - Very potent 1 mg of Clostridium botulinum toxin can kill 1 million guinea pigs Exotoxins - three types • 1. Cytotoxins • kill cells • 2. Neurotoxins • interfere with normal nerve impulses • 3. Enterotoxins • effect cells lining the G.I. Tract Many toxins have A-B subunit toxins or type III toxins • A - active • Causes change in host • B - binding Figure 15.5 Exotoxins • Superantigens or type I toxins • Cause an intense immune response due to release of cytokines from host cells • Fever, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, shock, death Exotoxins • Membrane-disrupting toxins or type II toxins • Lyse host’s cells by: • Making protein channels in the plasma membrane (e.g., leukocidins, hemolysins) • Disrupting phospholipid bilayer Cholera enterotoxin •Vibrio cholerae •Gram (-) comma shaped rods Exotoxins Exotoxin Lysogenic conversion A-B toxin type III. Inhibits protein synthesis. + • Streptococcus pyogenes Membrane-disrupting. Type II Erythrogenic. + • Clostridium botulinum A-B toxin. Neurotoxin - flaccid paralysis + • Corynebacterium diphtheriae • C. tetani • Vibrio cholerae • Staphylococcus aureus A-B toxin. Neurotoxin - prevents CNS inhibition - spastic paralysis A-B toxin. Enterotoxin. Stimulates cAMP to cause severe diarrhea Superantigen. Type I. Enterotoxin. + Botox • Botulism • Clostridium botulinum • Gram (+), anaerobic, spore-forming rod, found in soil • works at the neuromuscular junction • prevents impulse from nerve cell to muscle cell • results in muscle paralysis • Botulus – latin word for sausage (first known as sausage disease) C. botulinum does not grow in sausage today mainly due to nitrites added. Infant botulism 250 per yr., most associated with honey due to little microbial flora in G.I. Tetanus (Lock Jaw) • Clostridium tetani • Gram (+), spore-forming, anaerobic rod • neurotoxin acts on nerves, resulting in the inhibition of muscle relaxation • Tetanospasmin “spasms” or “Lock Jaw” Endotoxin Figure 15.4b Endotoxins Source Gram negative Metabolic product Present in LPS of outer membrane Chemistry Lipid Fever? Yes Neutralized by antitoxin No LD50 Relatively large Endotoxins - part of the Gram (-) Bacterial cell wall • LPS (Lipopolysaccharides) • O Antigen • Lipid A • Heat Stable (exotoxins are typically heat liable) • Lipid A - Toxin portion of the LPS • responsible for Fever that is associated with many Gram (-) Bacterial infections • Gram (-) cells are “digested” endotoxins are released – fever Endotoxins Figure 15.6