* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download T.Saginata. Gravid segment
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
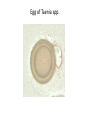
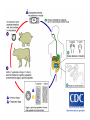
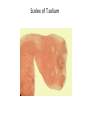
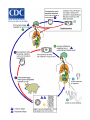
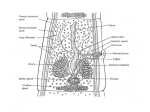
Phylum:Platyhelminths(flat worm) Class:Cestoidea(Tapeworms) Subclass:Cestoda General characters: -Flattened and segmented worms -Size from few mm to several meters -No digestive system,no body cavity. -Body is divided into 3 parts: A-Scolex: -suckers -rostellum -hooks B-Neck C-Strobila-proglottids(segments):a chain of progressively developing segments:immature, mature and gravid segment -Adults are hermaphrodites as cuch segment contains both male and female genital organs. Classification of cestodes according to habitat in man: 1-Intestinal:present as adults: -Diphyllobothrium latum( fish tapeworm) -Taenia saginata(Beef tapeworm) -Taenia solium(Pork tapeworm) -Hymenolepis nana(Dwarf tapeworm) -Hymenolepis diminuta(Rat tapeworm) -Dipylidium caninum(Dog tapeworm) 2-Exta-intestinal or tissue cestodes:these are present as larvae: -Sparganum-plerocercoides of Spirometra. -Hydatid cyst of Echinococcus granulosis. -Cesticercus cellulosae of Taenia solium. -Cysticercoid of Hymenolepis nana. -Coenurus cyst of Multiceps multiceps. There are 2 medically important orders: Pseudophyllidea and Cyclophyllidea: Pseudophyllidea Size Few meters Cyclophyllidea Few mms to several meters Scolex shape Suckers Rostellum Common genita pore Almond Pseudo(2 grooves) Absent Globular True 4 suckers Present or absent Venteral Lateral Vitelline glands Small follicles on the sides Mass behind the ovary Uterus With pores Blind sac Egg shape Operculated Non-operculated No.of I.H 2 1 or 0 Examples -Dyphyllobothrium latum. -Spirometra spp. -T.saginata -T.solium -Hymenolepis nana -Hymenolepis diminuta -Dipylidium caninum -Echinococcus granulosus Order cyclophyllidea Genus Taenia Taenia saginata (Beef tapeworm) Host: Man Habitat: Small intestine Intermediate host: cattle Geographical distribution:- world wide. Morphology : Size:- about 4 – 10 meters long. Scolex:-Globular in shape with 4 cup shaped suckers. No rostellum. Mature segment:- Slightly broader than long (nearly squarish) -Bilobed ovary -Uterus: simple tube in the median plane. -Compact vitelline glands. -Vagina: opens in the genital atrium. -Numerous testes. Gravid segment:-Uterus consists of median longitudinal stem with 15- 30 main uterine branches ( on each side). Egg:-30 × 40 µ in diameter. -Spherical, with an outer brownish, redially striated embryophore which surrounds a hexacanth embryo or onchosphere. -Color: yellowish brown. -Contents: hexacanth embryo (onchosphere). Scolex of T.saginata Egg of Taenia spp. Cysticercus bovis:-is the larval stage . Life cycle:-Mature eggs and gravid segments are detached separately and disintegrate liberating eggs. Sometimes these segments creep out of the anus by their own activity. -Cattle is the intermediate host within it cysticercus bovis develop. 4-The final host (man) is infected by ingestion of undercooked beef containing viable cysticercous bovis (the infective stage). Pathogensis:-Most infected individuals are asymptomatic. -Other cases show intestinal disorders, hunger feeling, diarrhea, loss of weight and weakness. -Appendicitis and intestinal obstruction. -Moderate eosinophilia (20- 30 %) -Segments of Taenia saginata migrating out of the anus cause worry and anexiety. This may be the first clue that the patient has tape worm infection. Diagnosis: ●Examination of stool to detect:-Eggs :- but rare and indistinguishable from T.solium egg. -Gravid segment Control:1-Treatment of infected persons. 2-meat inspection in slaughter-houses. 4-Through cooking of beef. Taenia solium (Pork tapeworm) Host: Man Habitat: Small intestine Intermediate host: Pig and accidentally man Geographical distribution:- found in many parts of the world where raw or poorly cooked pork is eaten. Morphology:Size:- about 2 – 4 meters long. Scolex:-With 4 cup-shaped suckers and rostellum armed with 2 crowns of hooks . Mature segment:-Similar to that of T.Saginata. Gravid segment:-Resembles that of T.Saginata but differs in :1)Smaller in size. 2)Number of main uterine branches are 713 on each of the uterine tube. Scolex of T.solium Egg:-Similar to that of T.Saginata. Cysticercus cellulosae:-It is larval stage T.solium. Life cycle:-Similar to that of T.Saginata -Infection with the adult worm is initiated by ingestion of raw or poorly cooked pork containing encysted T.solium larvae. -Man, the final host, may be also infected with cysticerci so act as intermediate and definitive host. More importantly a human who carries an adult T.solium in the intestine is liable to ingest eggs passed in its own faeces. This type of self infection is called external auto-infection which is common. Also regurgitation of gravid segments or eggs to the stomach exposes them to gastric juice and may result in hatching of onchosphere on return to the intestine. This type is called internal auto-infection cysticercosis . ●Which is more dangerous, T.solium or T.saginata ? • Pathology:- Presence of the adult worm usually causes no problems other than:-Intestinal disorders, hunger pain, weakness. -Diarrhea alternating with constipation usually accompanies with increased appetite. -Anaemia, eosinophilia may reach 25-30%. Diagnosis:1-Examination of stool to detect gravid segments 2-Eggs rarely present in stool and are similar to those of T.Saginata. Control: 1)Treatment of infected patients. 2)Meat inspection in slaughter houses. 3)Avoid eating insufficiently cooked pork Cysticercosis Definition:- This is the invasion of human tissues by the larval stage of Taenia solium (cysticercus cellulosae). Mode of infection:- Man acquires infection on ingestion of T.solium egg by one of the following ways:1-Ingestion of raw vegetables or water contaminated by infected faeces containing eggs of T.soluim. 2-Auto infection:-Internal auto-infection as a result of regurgitation of eggs released by disintegration of gravid segment into the stomach by reverse peristalsis. -External auto infection as a result of hand to mouth way. 3-Infected food handlers may disseminate the eggs to food. Pathogenesis: 1-The cyst produces a foreign body inflammatory reaction which usually ends in fibrosis and calcification. 2-Manifestations depend upon the tissue invaded and the number of cysticerci. 3-The commonest sites are subcutaneous tissues, muscles, brain, heart, liver, lung and peritoneum. 4-The number of cysticerci vary from one to several thousands. 5-Most seriously neurocysticercosis may develop when the cysticerci localize in central nervous system producing mental disturbances or clinical signs of epilepsy or intracranial hypertension. Diagnosis:1-Biopsy. 2-X-ray may show calcifications later in the course of the disease. 3-CT (computerized tomography) scans and ultrasound may be helpful in identification. 4-Serological methods as IHA and ELISA may be of help. Prevention: 1- Human faeces should not be used as manure. 2-Proper washing of raw vegetables 3-Prompt treatment of infected persons to eliminate the danger of auto infection with cysticerci. 4-Infected persons should not take emetics or nauseating drugs. Cysticercus racemosus:Refer to an aggregate of cysts formed near the base of the brain looks like a bunch of grapes and may represent special type of cysticercosis. Treatment: 1-Praziquantel: 5-10mg ∕ kg in both adults and children. 2-Niclosamide:2g chewed thoroughly in adults. In children 50mg/kg. Treatment kills adult worms but NOT eggs. This is fine for T.saginata but may not for T.solium in which the praziquantel is the drug of choice. 3-Nitazoxanide is effective in praziquantel and niclosamide resistant strains. 4-Cysticerci in some parts of the body may be surgically removed. Also, care must be taken during treatment for adults so that vomiting is not included which may cause reverse peristalsis. N.B: T. saginata differ from T. solium in that: 1-Egg of T. saginata is more elliptic while egg of T. solium is spherical. 2-Gravid segment oT.saginata is opaque while that of T. solium is transparent (this can differentiate between them without staining). 3-Scolex of T.saginata is without rostellum or hooks. 4-Staining of the mature segment of T.saginata will show: - testis more numerous and none of them present posterior to the vitelline gland. -ovary has two lobules. -cirrus sac is small. -the vagina has a sphincter.