* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Breast Cancer Intra-tumour Heterogeneity
Survey
Document related concepts
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
The eclipse of Darwinism wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
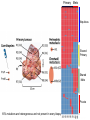
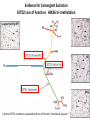
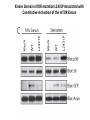
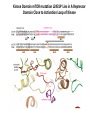
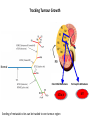
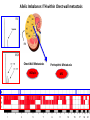
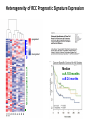
Predictive Biomarkers and Drug Resistance • Acquisition of tumour multidrug resistance inevitable in most advanced solid tumours – – • Drug resistance highly complex: – • Failing to cure the majority of advanced solid tumours Declining therapeutic benefits at higher drug cost Approx 10% of kinases alter resistance to one or more drugs (Swanton et al 2007 Cancer Cell ; Swanton et al 2007 Cell Cycle) Failure of Biomarker Validation – 150,000 biomarkers only 100 for clinical use Intratumour Heterogeneity • Evidence of intratumour heterogeneity • Possible Implications for biomarker studies • Practical approaches to address heterogeneity Breast Cancer Intra-tumour Heterogeneity Sector Ploidy Profiling and DNA Copy Number Analysis • Multiple intermixed cell subpopulations within one tumour differ by large genomic events/focal amplifications/ deletions Navin N, et al. Genome Res 2010 Navin N, et al Nature 2011 Geyer and Reis-Filho J Path 2010 Shah and Aparicio Nature 2012 Does a Single Tumour Biopsy: Represent the tumour somatic/transcriptomic landscape ? Provide robust biomarkers of outcome ? Demonstrate that all mutations are ubiquitously present in every region of a tumour Predicted by a linear/clonal sweep model of tumour evolution Provide reliable data following Deep Sequencing Analysis to stratify patients for trials ? Primary Mets Ubiquitous Shared Primary Shared Mets Private 65% mutations are heterogeneous and not present in every biopsy Re-construct Phylogenetic Evolution of Tumour Evidence for Convergent Evolution SETD2 Loss of Function: H3K36 tri-methylation Normal 3 distinct SETD2 mutations associated with loss of function: Mutational capacity? Evidence intratumour heterogeneity may impact upon drug response? 6 weeks of Everolimus therapy Assess status of mTOR pathway across different regions of the tumour Evidence of Differential Pathway Activity post-Everolimus exposure? mTOR active in all primary regions except R4 and metastases Heterogeneous Kinase Domain mTOR mutation L2431P mTOR mutation L2431P Kinase Domain mTOR mutation L2431P Associated with Constitutive Activation of the mTOR Kinase Kinase Domain mTOR mutation L2431P Lies in A Repressor Domain Close to Activation Loop of Kinase Tracking Tumour Growth R9 Normal Chest Wall Metastasis M2a,b Seeding of metastatic sites can be tracked to one tumour region Perinephric Metastasis M1 Primary TumourRegions Regions Primary Tumour Metastatic Sites Metastatic Sites Allelic Imbalance: ITH within Chest wall metastasis R9 Chest Wall Metastasis M2a,b Perinephric Metastasis M1 Onlysomatic somatic mutations with >20x>20x coverage Only mutations with coverage wereincluded included were Primary TumourRegions Regions Primary Tumour Metastatic Sites Metastatic Sites Genes upregulated in ccA Genes in ccB Heterogeneity of RCC Prognostic Signature Expression Median ccA 103 months ccB 24 months Onlysomatic somatic mutations with >20x>20x coverage Only mutations with coverage wereincluded included were Darwin and cancer branched evolution Relevance of ITH and Cancer Branched Evolution Tumour Diversity Supports Evolutionary Fitness (Maley et al 2006) Tumour Adaptation and Selection for • Drug resistance (Su et al 2012; Lee et al 2011) • Metastatic growth (Yachida and Campbell 2010, Shah 2009) Tumour Sampling Bias • Different tumour biopsies different results • Sites of disease evolve independently Clonal Dominance and Actionable Mutations? • Mutations present at one site but not another Patient 1