* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 10.4 Practice with Examples
Problem of Apollonius wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Riemann–Roch theorem wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Brouwer fixed-point theorem wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
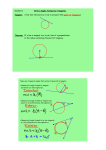
Chapter 10 LESSON 10.4 NAME _________________________________________________________ DATE ____________ Practice with Examples For use with pages 621–627 GOAL Use angles formed by tangents and chords to solve problems in geometry and use angles formed by lines that intersect a circle to solve problems VOCABULARY Theorem 10.12 If a tangent and a chord intersect at a point on a circle, then the measure of each angle formed is one half the measure of its intercepted arc. Theorem 10.13 If two chords intersect in the interior of a circle, then the measure of each angle is one half the sum of the measures of the arcs intercepted by the angle and its vertical angle. Theorem 10.14 If a tangent and a secant, two tangents, or two secants intersect in the exterior of a circle, then the measure of the angle formed is one half the difference of the measures of the intercepted arcs. EXAMPLE 1 Finding Angle and Arc Measures Line m is tangent to the circle. a. Find m1 b. mACB 90 B A 1 2 m SOLUTION 1 2 C a. m1 90 45 b. Because 1 and 2 are a linear pair, m2 180 m1 180 45 135. So, mACB 2135 270. 190 Geometry Practice Workbook with Examples Copyright © McDougal Littell Inc. All rights reserved. LESSON Practice with Examples Chapter 10 10.4 CONTINUED NAME _________________________________________________________ DATE ____________ For use with pages 621–627 Exercises for Example 1 Find the value of each variable. 1. 2. B 3. M m P x 156 z 2x C 1 EXAMPLE 2 x 2 x y A Q m m y N Using Theorem 10.13 Find the value of x. SOLUTION A 1 x mAB mCD 2 Apply Theorem 10.13. 60 B 1 x 60 20 Substitute. 2 x 40 x D 20 C Simplify. Exercises for Example 2 Find the value of x. 4. 5. A N 135 M 6. 30 P W x 2x 45 B C x D Copyright © McDougal Littell Inc. All rights reserved. 110 100 Y x Z X Q Geometry Practice Workbook with Examples 191 Chapter 10 LESSON 10.4 CONTINUED EXAMPLE 3 NAME _________________________________________________________ DATE ____________ Practice with Examples For use with pages 621–627 Using Theorem 10.14 Find the value of x. A D B x SOLUTION 85 E 1 x mBC mDE 2 Apply Theorem 10.14. 1 x 171 85 2 Substitute. x 43 171 C Simplify. Exercises for Example 3 Find the value of x. 7. 8. x 9. 30 136 60 38 x 2x 8x 170 192 Geometry Practice Workbook with Examples Copyright © McDougal Littell Inc. All rights reserved.