* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download multifocal maximizing full spectrum
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
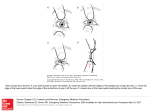
featuring the MULTIFOCAL solution for MAXIMIZING correction & comfort across the FULL SPECTRUM of vision needs Indicated Corneal Types: • Spherical • Regular Astigmatic • Irregular Astigmatic • Keratoconic • Post-Surgical • Trauma Maximizing Correction & Comfort Indications The InSight® Scleral can be used on virtually anyone. It works equally well on normal corneas as it does on compromised corneas. It provides a stable and comfortable fit while maximizing visual potential in cases where soft lenses and intra-corneal rigid lenses cannot provide acceptable vision and/or comfort. InSight Scleral® can also deliver multifocal correction up to 3 diopters of add power. This innovative feature now allows both normal and compromised cornea patients to experience excellent distance and reading correction in a remarkably comfortable lens. Indicated Corneal Types: • Spherical • Regular Astigmatic • Irregular Astigmatic • Keratoconic • Post-Surgical • Trauma Including optional Multifocal The theory behind HHM Technology began with the study of the human cornea, limbus and sclera to maximize patients’ optimal visual performance while maintaining best ocular health, vision, and comfort. HHM Technology uses patient experiences, expectations, and physical parameters to develop a theoretical and practical model for contact lens success. Attention to the theoretical model has brought about practical changes in design that will exceed both patient and practitioner expectations. HHM technology develops a physiologically safe contact lens modality that will compensate visual impairment for the near-sighted, far-sighted, astigmatic, presbyopic, ocular surface diseased, and irregular cornea patient. The innovation and technology behind HHM Technology will continue to push boundaries on large diameter rigid contact lens designs so that all refractive errors and corneal conditions will be fit successfully with one lens modality. Available Parameters: BASE CURVEUNLIMITED SPHERE POWERUNLIMITED CYLINDER POWER -0.25 to -8.00 in 0.25D STEPS AXIS 0˚ to 180˚ in 5˚ STEPS DIAMETER STANDARD: 15.2mm or 15.6 mm CUSTOM: 13.5mm to 20.0mm PERIPHERYSTANDARD FLAT1, FLAT2, FLAT3, Description STEEP1, STEEP2, STEEP3 The InSight Scleral Lens is a versatile design addressing a virtually unlimited range of vision correction needs. It also features a unique design approach we like to call HHM Technology which refers to the way this lens was developed. HHM Technology stands for the collaboration of custom contact lens industry professionals and clinical practitioners in the development of optical devices that substantially improve the world of sight for those in need of visual compensation. HHM includes the expertise of over 80 years of work in the field of contact lenses and optics. It blends characteristics of optics, physiology, theory, and practicality to develop a contact lens that is optimal to the wearer for both vision and comfort; and reduces chair time for the clinical practitioner. TORIC Fitting Approach Empiric fitting is easily achieved on Spherical, Regular Astigmatic and Corneal Surface Disease cases having spherical or regular astigmatic corneas. Empiric fitting is described in a separate fitting guide accompanying this guide. Diagnostic fitting is recommended on all irregular cornea cases including Keratoconus, Trauma, Post Surgery and other related irregular corneas. Lens Evaluation Examples a. Central Clearance - An ideal fit will have 150-300 microns of clearance Too Steep Ideal Too Flat Diagnostic Fitting Approach 1. Base Curve Selection Working from Keratometry or Corneal Topography readings: FOR - Standard Cornea or Corneal Surface Disease Corneal Cylinder a. Less than 2.50 Diopters Select Base Curve .40mm Steeper than Flat K b. Greater than 2.50 Diopters Select Base Curve .30mm Steeper than Steep K Tear pool is greater than 300 microns. Thicker than the lens. Tear pool is between 100 & 300 microns. Equal to lens thickness. Tear pool is less than 100 microns. Barely visible. b. Limbal Clearance - An ideal fit will have slightly less clearance than observed in the central portion Too Steep Ideal Too Flat FOR - Corneal Ectasia or Post-Surgery Select Base Curve .30mm Steeper than Steep K Note: If Keratometry readings are unobtainable select Base Curve 7.20mm as a starting point. 2. Prepare lens and insert a. Holding the lens base curve up, place on large suction cup and over-fill the lens with saline b. Add fluorescein c. Apply the lens: Have the subject tilt their head down, looking at a tabletop. Place the lens directly on the cornea so that the solution stays in the lens. For more details, see Insertion and Removal Tips on the back page. 3. Evaluate lens fit Tear pool is greater than 100 microns. Greater than 1/4 of lens thickness. Tear pool is between 50 & 80 microns. Approximately 1/4 of lens thickness. Tear pool is less than 50 microns. Barely visible. c. Edge alignment - An ideal fit will land squarely and evenly on the sclera not having any stand off or blood vessel blanching in the full circumference of the lens. An uneven fit may require a toric periphery which should be designed with the assistance of a consultant. Too Steep Ideal Too Flat Clearance Evaluation is done using a white light, slit-lamp optic section technique. Using the lens thickness as a reference, central clearance will generally be a 1 to 1 relationship. Limbal clearance will generally be 1/2 of lens thickness. Edge Landing The lens edge should land squarely and evenly on the sclera and must be evaluated 360 degrees. Be sure to lift upper and lower lids to evaluate the edge hiding beneath. Note any blanching or edge standoff. Depending on clock position and severity, the lens edge may require adjustment. This should be discussed with a consultant. 4. Determine lens power Perform a sphere-cylinder over-refraction 5. Configure Add Power Option For the needs of the presbyope, InSight Scleral can be ordered with an add power of up to 3.00 diopters. Specify the spectacle add requirement and pupil width measurement taken in normal room illumination. Edge is too steep and is pinching into sclera. Evidenced by blanching of underlying blood vessels. Edge is landing evenly and squarely on the sclera and is an ideal fit. Edge is too flat and is standing off sclera allowing air to accumulate under lens edge. Insertion and Removal Tips When handling the InSight Scleral lens, always wash your hands and follow the lens care instructions provided by your eye care practitioner. Insertion Before INSERTION, it is best to rinse the lens and use a non-preserved or sensitive-eye saline rinsing solution to apply the lens. Tear circulation is less with a scleral lens than with a smaller corneal lens. Therefore, preservatives in the soaking solution remain in contact with the cornea longer and this increases the chance of a reaction to these solutions. Step 1 Place the lens on suction cup and fill with non-preserved saline so that the lens is over-filled like the Example photo. Removal Since the InSight Scleral® lens is large, the capillary forces which hold the lens on the eye can be rather strong. Instilling several drops of contact lens rewetting solution or non-preserved saline before lens removal is beneficial. A DMV Contact Lens Remover is the recommended tool for lens removal. Step 1 Instill several drops of contact lens rewetting solution or non-preserved saline in the eye from which the lens is to be removed. Step 2 Position the DMV Contact Lens Remover on the lower portion of the lens as shown in the Example photo. Step 3 Gently lift the lens away from the eye with the suction cup attached to the lens. Example show best position of DMV on lens for removal. Step 2 Using your fingers, pull both eye lids back to expose a large enough area of the eye to allow easy insertion of the lens. Step 3 Insert lens while facing downward over a table or counter top so that the lens remains filled with saline. Step 4 Observe lens on eye by looking into a mirror looking for bubbles that may be trapped under the lens. If bubbles are present, remove the lens and repeat insertion steps. Proper position of DMV on lens being removed from eye. Lens properly filled with saline. Note that the saline level extends above lens edge. Apply DMV to lower portion of lens. Gently lift lens away using the remover. Eye properly opened with head tilted downward for easiest lens insertion. © 2015 Contamac US Inc. - 1000 - 12/15 ®/™ denote trademarks of Contamac US Inc. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.