* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 29, World War II and its aftermath 1931-1955
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Role of music in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of the Winter War wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
War Front: Turning Point wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
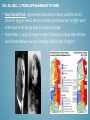
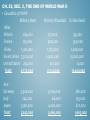
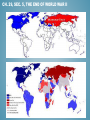
CH. 29, WORLD WAR II AND ITS AFTERMATH 1931-1955 Focus Question: How did aggressive world powers emerge, and what did it take to defeat them during World War II ? CH. 29, SEC. 1, FROM APPEASEMENT TO WAR • - Aggression Goes Unchecked: Japan overruns Manchuria in 1931 and Eastern China in 1937 Italy Invades and conquered Ethiopia in 1935-1936 Hitler Remilitarizes Germany in 1930s Hitler moves troops into the “demilitarized” Rhineland bordering France • Appeasement: policy of giving in to an aggressor’s demands in order to keep the peace. Western democracies adopted this policy. • Pacifism: opposition to all war. Western democracies adopted this policy after the Great Depression. CH. 29, SEC. 1, FROM APPEASEMENT TO WAR • Neutrality Acts: a series of acts passed by the U.S. Congress from 1935 to 1939 that aimed to keep the U.S. from becoming involved in WWII. • Spain Collapses into Civil War in 1936, started by conservative General Francisco Franco. - Fascists, Nationalists, Germany. And Italy helped Franco - Loyalists, Communists, Socialists, and Russia opposed him - 1939 Franco wins and he creates a Fascist dictatorship CH. 29, SEC. 1, FROM APPEASEMENT TO WAR • German Aggression Continues: Hitler declares “Aryan race” superior to all others. - Anschluss: union of Austria and Germany, Hitler annexes Austria, in 1938. - Sudetenland: a region of western Czechoslovakia, September 1938 to appease Hitler ,British and French leaders agree to let him annex it provided he agrees to go no further, Hitler agrees. - March 1939, Hitler breaks his promise takes the rest of Czechoslovakia. Allies finally react promise to protect Poland. CH. 29, SEC. 1, FROM APPEASEMENT TO WAR • Nazi-Soviet Pact: agreement between Germany and the Soviet Union in 1939 in which the two nations promised not to fight each other and to divide up land in Eastern Europe. • September 1, 1939 Germany invades Poland, two days later Britain and France declare war on Germany. World War II begins! CH. 29, SEC. 2, THE AXIS ADVANCES • Blitzkrieg: Hitler’s “lightning war”, using improved tank and airpower technology. • Luftwaffe: German air force. CH. 29, SEC. 2, THE AXIS ADVANCES • Allied Aircraft: CH. 29, SEC. 2, THE AXIS ADVANCES • Improved German Tanks: CH. 29, SEC. 2, THE AXIS ADVANCES • Allied Tanks: CH. 29, SEC. 2, THE AXIS ADVANCES • April 1940 Hitler invades Norway, Denmark • May 10,1940 Hitler invades France bypasses the Maginot Line! • June 22, 1940 France surrenders! CH. 29, SEC. 2, THE AXIS ADVANCES • Dunkirk: port in France from which 300,000 Allied troops were evacuated when their retreat by land was cut off by the German advance. May 27 to June 4 1940. CH. 29, SEC. 2, THE AXIS ADVANCES • Vichy: city in central France where a puppet state governed unoccupied France and the French colonies. • Operation Sea Lion: Hitler’s plan for the invasion of Britain. • Germany launches the Blitz, for 57 straight nights, Hitler’s Airforce bombed Britain. Much of London is destroyed but the Germans fail to take Britain. CH. 29, SEC. 2, THE AXIS ADVANCES • General Erwin Rommel: “Desert Fox” placed in charge of German troops in Africa, after Italy’s troops beaten by British. Rommel has a string of successes in 1941 and 1942. • June 1941 Germany invades the Soviet Union, with force of 3 million men. Soviet army fights delaying action and waits for “General Winter.” Thousands of German soldiers froze to death. CH. 29, SEC. 2, THE AXIS ADVANCES • Hitler’s “New Order” • Concentration Camps: detention center for civilians considered enemies of the state. Nazis send Jewish people, and millions of Polish and Soviet Slavs to work as slave laborers. • Holocaust: the systematic genocide of about six million European Jews by the Nazis during WWII. Nearly six million other people are killed also. Hitler opens Death Camps! CH. 29, SEC. 2, THE AXIS ADVANCES • Japan’s Brutal Conquest: attacks China, Malaysia, Philippines. • Lend-Lease Act: act passed by the U.S. Congress in 1941 that allowed the president (FDR) to sell or lend war supplies to any country whose defense was considered vital to the United States. CH. 29, SEC. 2, THE AXIS ADVANCES • Pearl Harbor: Dec. 7, 1941 8:00 am. Japanese surprise attack, 2400 people killed, and battleships and aircraft destroyed. United States declares war on Japan. December 11, Germany and Italy declare war on United States. CH. 29, SEC. 2, THE AXIS ADVANCES • Japanese Weapons: CH. 29, SEC. 2, THE AXIS ADVANCES • Japanese victories continue! - Japan captures Philippines - Japan captures Hong Kong, Burma, and Malaya. CH. 29, SEC. 3, THE ALLIES TURN THE TIDE • Rosie the Riveter: popular name for women who worked in war industries/factories during WWII. • - Allies turn to total war: Factories switch from cars to tanks or airplanes Ration food and vital consumer goods Selling of war bonds Prices and wages regulated Censored the press Limited the rights of citizens CH. 29, SEC. 3, THE ALLIES TURN THE TIDE • Aircraft Carriers: ships that accommodate the taking off and landing of airplanes, and transport aircraft. CH. 29, SEC. 3, THE ALLIES TURN THE TIDE • Midway and Coral Sea: Major Naval battles in the Pacific, both key American victories over Japan. Coral Sea first serious loss for Japanese, 1 Japanese Carrier sunk, plus several cruisers and destroyers. Midway, 4 Japanese carriers sunk plus 250 planes destroyed, ends japans offensive action in Pacific. CH. 29, SEC. 3, THE ALLIES TURN THE TIDE • Big Three: Roosevelt (USA), Churchill (Britain), Stalin (USSR), in 1942 they plot a strategy to focus on finishing the war in Europe before trying to end the war in Asia. • General Dwight Eisenhower: USA took command of a joint British and American force in North Africa. In May 1943 German Army is trapped and surrenders to the Allies. CH. 29, SEC. 3, THE ALLIES TURN THE TIDE • Stalingrad: now Volgograd, a city in SW Russia that was the site of a fierce battle during WWII. January of 1943 German Army at Stalingrad surrendered to Soviet Troops, Red Army able to take offensive after this key battle and drive last of German troops out of Soviet Union. CH. 29, SEC. 3, THE ALLIES TURN THE TIDE • D-Day: code name for June 6, 1944, the day that Allied forces invaded France during WWII. The attack began on the beaches of Normandy. CH. 29, SEC. 3, THE ALLIES TURN THE TIDE • Battle of the Bulge: a massive German counterattack against the Allies, Dec. 16, 1944- Jan. 25, 1945. Location Ardennes Forested mountain region of Belgium. Last major German offensive of the Western front. Germans suffered between 60,000-100,000 casualties, Americans 89,500 casualties, British 1408 casualties. General George S. Patton and his third Army rescued the surrounded 101st Airborne Division at Bastogne. CH. 29, SEC. 3, THE ALLIES TURN THE TIDE • Yalta Conference: meeting between Churchill, Roosevelt, and Stalin in February 1945 where the three leaders made agreements regarding the end of World War II. An atmosphere of growing mistrust between the Soviet Union and Britain and the United States would later cause a split between the Allies. CH. 29, SEC. 4, VICTORY IN EUROPE AND THE PACIFIC • V-E Day: (Victory in Europe) Germany surrenders May 7th, May 8th, 1945 war in Germany officially over, Allies win. • Bataan Death March: during WWII, the forced march of Filipino and American prisoners of war under brutal conditions by the Japanese military, as many several hundred American soldiers and as many as 10,000 Filipino soldiers. CH. 29, SEC. 4, VICTORY IN EUROPE AND THE PACIFIC • Island-hopping: during WWII, Allied strategy of recapturing some Japanese-held islands while bypassing others. • General Douglas MacArthur: American commander of Pacific region responsible for retaking Philippines CH. 29, SEC. 4, VICTORY IN EUROPE AND THE PACIFIC • Kamikaze: Japanese pilot who undertook a suicide mission, crashing their explosive-laden airplanes into American warships. CH. 29, SEC. 4, VICTORY IN EUROPE AND THE PACIFIC • Manhattan Project: code name for the project to build the first atomic bomb during WWII, July 1945 first successful test of an atomic bomb at Alamogordo, New Mexico. CH. 29, SEC. 4, VICTORY IN EUROPE AND THE PACIFIC • Hiroshima and Nagasaki: United States drops two atomic bombs, Little Boy Aug. 6th, 1945 on Hiroshima, and Fat-Man Aug. 9th 1945 on Nagasaki. 70,000 people die instantly at Hiroshima, 70,000 later from radiation. 40,000 die at Nagasaki. August 10th Japan surrenders. CH. 29, SEC. 4, VICTORY IN EUROPE AND THE PACIFIC • September 2, 1945: formal peace treaty signed on board American Battleship Missouri, anchored in Tokyo Bay. CH. 29, SEC. 5, THE END OF WORLD WAR II • Casualties of WWII: Military Dead Allies Britain 264,000 France 213,000 China 1,310,000 Soviet Union 7,500,000 United States 292,000 Total: 9,579,000 Axis Germany Italy Japan Total: 3,500,000 242,000 1,300,000 5,042,000 Military Wounded 277,000 400,000 1,753,000 14,012,000 672,000 17,114,000 5,000,000 66,000 4,000,000 9,066,000 Civilian Dead 93,000 350,000 1,000,000 15,000,000 6,000 16,449,000 780,000 153,000 672,000 1,605,000 CH. 29, SEC. 5, THE END OF WORLD WAR II • Nuremberg: German city where Nazi war crimes trials were held after WWII. Nearly 200Germans and Austrians were tried, most were found guilty. CH. 29, SEC. 5, THE END OF WORLD WAR II • United Nations: (UN) international organization established after WWII with the goal of maintaining peace and cooperation in the international community. Each UN member nation has one vote in the General Assembly, with the five permanent members- the United States, Soviet Union, Britain, France, and China having the right to veto any council decision. April 1945, 50 nations joined , today 193 nations belong. CH. 29, SEC. 5, THE END OF WORLD WAR II • Cold War: state of tension and hostility between nations aligned with the United States on one side and the Soviet Union on the other that rarely led to direct armed conflict. • Truman Doctrine: United States policy, established in 1947, of trying to contain the spread of communism. CH. 29, SEC. 5, THE END OF WORLD WAR II • Marshall Plan: massive aid package of food and economic assistance offered by the U.S. to Europe to help countries rebuild after WWII. CH. 29, SEC. 5, THE END OF WORLD WAR II • Berlin Airlift: June 1948, Stalin seals off every railroad and highway into the western sectors of Berlin to try to force the Western allies out of Berlin. Western Allies led by U.S. mount a round-the-clock airlift of supplies for more than a year. Soviets finally end the blockade. CH. 29, SEC. 5, THE END OF WORLD WAR II • North Atlantic Treaty Organization: (NATO),1949, a military alliance between several North Atlantic states to safeguard them from the presumed threat of the Soviet Union’s communist bloc; countries from other regions later joined the alliance. CH. 29, SEC. 5, THE END OF WORLD WAR II • Warsaw Pact: mutual-defense alliance between the Soviet Union and seven satellites in Eastern Europe set up in 1955. CH. 29, SEC. 5, THE END OF WORLD WAR II