* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EcoSystem_Exgroup_Mindmap
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
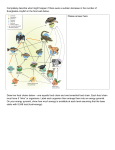
Name: _______________________ Expert Group 1: Desert Resources: A desert is an arid or dry area where the amount of water that evaporates is greater than the rainfall. Rainfall in a desert is usually less than 10 inches a year. Deserts are harsh environments with extreme temperatures. In tropical deserts, summer temperatures often exceed 120o F. Most deserts have cool to cold nights. Most desert soils contain little to no organic matter and have hard windblown surfaces with rocks and sand. Examples from Around the World: Tropical deserts, such as the Sahara and Namib in northern Africa, are warm to hot year round. Temperate deserts, such as the Mojave in southern California, are hot in the summer and cool in the winter. Cold deserts such as the Gobi in China, have cold winters and warm to hot summers. The coldest place in the world, Antarctica, is also a desert where the temperature can fall to -130o F in the winter. Producers: The dry soil, results in scarce or limited plant growth. The two main types of plants found in deserts are shrubs, such as sagebrush, creosote bush, mesquite, agave, prickly pear and tamarisk and small trees such as Joshua tree, Saguaro cactus. Many have adaptations such as waxy or oily covered small to no leaves to reduce loss of water, fleshy stems to store water, deep roots to tap into groundwater, and wide shallow roots which capture and conserve the scarce water. Some desert soils are rich in nutrients and have been converted to farmland with irrigation. An oasis is a fertile place in the desert with a lot of plant and animal growth due to ground water that reaches the surface. Consumers, Scavengers, & Decomposers: Animals that live in the desert have adaptations allowing them to survive the extreme temperatures, lack of water, and shortage of food. Some are nocturnal or active at night and rest in the shade during the hot day. Small desert animals get all the moisture they need from their food, reducing the need to drink. Some examples of plant eating animals, also called herbivores or primary consumers are the kangaroo rat, insects such as locusts, and quail. Some examples of carnivores (animals that eat other animals) or consumers are roadrunner, fringe-toed lizard, black widow spider, red-tailed hawk and diamondback rattlesnake. Scavengers are coyote, and vultures. Decomposers are dung beetles, fungi and bacteria. Name: _______________________ Expert Group 2: Grassland Resources: Grasslands are areas that have enough precipitation each year to allow grass and a few small trees to grow but periods of drought and fires prevent large groups of trees from growing. Annual precipitation is between 10-30 inches. The winters are wet and the summers are dry. Temperature varies with location. Soil is rich and fertile. Examples from Around the World: Grasslands are found in the middle on all continents except Antarctica. They can be hot year round such as the tropical African savannahs, hot in the summer and cold in the winter, such as the temperate North American prairies, Australian rangelands, and the pampas of South America or cold year round such as the arctic tundra. Grasslands are often referred to as a “sea of grass”. Nearly one fourth of the Earth’s land area is grassland. Producers: Plant growth is limited by the amount of rainfall. Grasslands often separate forests from deserts. Deep rooted grasses are the dominant plant life. Some grasslands have scattered shrubs or small trees. Because grasses grow from the bottom of their stems they can grow back after grazing and fire consumes the tops. Grasses vary in height from a few inches to several feet. Grasslands are used as farmland and for grazing. Consumers, Scavengers, & Decomposers: Animals of grasslands are adapted to dry windy conditions. Grazing and burrowing animals are dominant as well as insects. Plant eating animals, also called herbivores or primary consumers, include antelope, prairie dogs, rabbits, zebras and insects such as grasshoppers. Carnivores (animals that eat other animals) are sparrows, coyote, eagle, and cheetahs (cats). Scavengers are vultures, dingo, and insects. Decomposers are bacteria, fungi, earthworms, and insects. Grasslands carry a moderate amount of animal diversity. Name: _______________________ Expert Group 3: Temperate Forest Resources: Temperate forests are areas with high amounts of precipitation (30-60 inches) spread fairly evenly throughout the year. The average temperature is moderate (75o F) with significant changes with the seasons. Summers are long and the winters are cold but not extreme. The soil in a temperate forest is very fertile, enriched by the decomposition of leaves, twigs, logs and dead organisms. Examples from Around the World: Temperate forests are found in North America, eastern Asia, Europe and the southern tips of Chile and Australia. Producers: Large, broadleaf, deciduous trees, such as oak, maple, beech, sycamore, and hickory, are the dominant plant life. Smaller trees, shrubs, and ground cover are also present. Deciduous trees lose their leaves in the fall. This helps conserve water, which is often frozen and unavailable in the winter. In the fall, as the number of hours of daylight and temperature decrease, the leaves turn brilliant colors of red, orange and yellow and then fall to the ground. Unfortunately, most of the original temperate forests have been cleared for farmland and urban development. Consumers, Scavengers, & Decomposers: These forests provide food and shelter for many species of animals. The European Oak can support more than 300 animal species. Animal life is abundant and include the following: plant eating animals, also called herbivores or primary consumers, such as white tailed deer, rabbits, and insects. Carnivores (animals that eat other animals) or secondary consumers include songbirds, foxes, brown bear, wolves and raccoons. Scavengers include vultures and insects. Bacteria, fungi and earthworms are some decomposers found in this ecosystem. Name: _______________________ Expert Group 4: Tundra Resources: Tundras are areas with low amounts of precipitation (less than 5 inches) which is mostly frozen. The average temperature is low (10-21o F) with no significant changes with the seasons. The soil in the tundra has low nutrients due to the cold temperatures. Examples from Around the World: Tundra is found in extreme northern latitudes. They are found in Greenland, Northern Alaska, Northern Canada, Scandinavia, and Siberia. Producers: Due to the year-round low temperatures and low nutrient soil, there are few producers in the tundra. The main producers that survive in this environment are lichens and mosses. Dwarfed shrubs also survive the harsh climate as producers. Consumers, Scavengers, & Decomposers: Animal life in the tundra is not as abundant as other ecosystems. The main consumers include the following: plant eating animals, also called herbivores or primary consumers, such as musk ox and lemmings. Carnivores (animals that eat other animals) or secondary consumers include Artic fox and snowy owl. Scavengers include vultures and insects. Bacteria, fungi, nematodes, and earthworms are some decomposers found in this ecosystem. Name: _______________________ Ecosystem