* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Wave Nature of Light
Bicycle lighting wikipedia , lookup
Architectural lighting design wikipedia , lookup
Daylighting wikipedia , lookup
Light pollution wikipedia , lookup
Photopolymer wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Gravitational lens wikipedia , lookup
Bioluminescence wikipedia , lookup
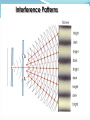
So far, we’ve studied some elements of the nature of light: reflection, refraction Isaac Newton In his day, Newton was most famous for his work on light. He described light as a beam of ultra-tiny particles. This could explain reflection and refraction, but couldn’t explain others. In the following centuries, light began to be thought of as a WAVE. Huygen’s Principle Christian Huygens – Dutch mathematician/scientist Described light waves spreading out from a point source as the overlapping of tiny secondary wavelets. Saw this with Ripple Tank Wide opening in barrier Wave goes right through, Bending around corners With narrow opening, More pronounced bending On Ripple Tank, we saw Diffraction and Interference Diffraction – bending of wave by anything other than reflection or refraction Interference – overlapping of waves, producing areas of constructive and destructive interference. Interference Patterns We saw that increasing the frequency longer wavelength, wider pattern We saw that bringing sources together wider also Do we see these things with light? Diffraction – laser on razor blade edge Light bends around edges Send light through tiny slit Do we see interference pattern? What happens if we narrow the slit width? Patterns Different wavelengths of light produce different patterns. Longer wavelengths, wider pattern. (So red wider pattern than green) White Light Separates Send white light through diffraction grating, get separation of colors according to wavelength. Compact Discs/DVDs The tracks of a CD or DVD act as a diffraction grating, producing a separation of the colors of white light. Opals, too! Doppler Effect with Light Like with sound waves, if a light source is moving towards an observer, they would experience a higher frequency (shift to blue end of spectrum) Likewise, a light source moving AWAY would be shifted to red end of spectrum. Red Shift of Stars The fact that light from ALL distant stars and galaxies is red-shifted is convincing evidence that the universe is expanding. Evidence that Light is a WAVE Light shows diffraction Light shows interference patterns Light shows Doppler effect Huygens, Young experiments Maxwell’s Theory (electromagnetic wave theory)