* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Attitudes
Mentalism (discrimination) wikipedia , lookup
White nationalism wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom employment equality law wikipedia , lookup
Aversive racism wikipedia , lookup
Racial segregation in the United States Armed Forces wikipedia , lookup
Racial stereotyping in advertising wikipedia , lookup
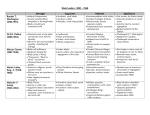
Racial Attitudes Concepts, Trends, and Explanations Prejudice • Definition • Components • Determinants • New Research on Racial Attitudes Questions • How would you define prejudice? • What are some parts of prejudice? • What factors are associated with being prejudiced? Definition A negative attitude toward an entire group of people, such as a racial or ethnic minority. • Discrimination: behavior • Homophobia • Anti-Semitism Components • Cognitive • Conative • Affective (Emotions: difficult to study) Cognitive Elements: Stereotyping • College Student Perceptions: • Thought Black Americans were lazy: 1932 1982 1993 75% 18% 5% Thought Jewish Americans were shrewd 79% 15% --- Devine and Elliot • It is important to distinguish between stereotypes and personal beliefs • Personal beliefs have improved • Stereotypes persist • Stereotypes can come into play even when they conflict with personal beliefs Conative Elements: Social Distance • Range: 1(marriage) - 7(exclude from U.S.) Group Irish Jews Turks 1926 1.30 2.39 3.30 Year 1966 1.40 1.97 2.48 1991 1.30 1.84 2.23 Some Examples of Prejudice(with thanks to the SPLC) • Madison - Feb. 2, 2001 Ying Vang, 23, Kao Vue, 24, and John Yang, 20, were convicted of battery as a hate crime for beating a black student at a local university • Madison - Feb. 26, 2001 A swastika, the word “die,” followed by a racial slur and the word “Jew,” were written at a local elementary school and targeted a fourth-grade teacher. Examples, continued • Madison - - Sept. 1, 2001 Two white men allegedly used racist epithets and assaulted two Asian students. Adam Coplien, and Carl Elam-Bishop, both 21, were charged with substantial battery with intentional bodily harm, one felony and one misdemeanor charge of a hate crime and battery in connection with the incident • Examples, continued • Madison - Nov. 6, 2001 Jeremy A. Giese, 21, was charged with a hate crime, criminal damage to property and disorderly conduct for allegedly smashing the window of a bar because Giese saw two men who appeared to be of Middle Eastern descent. Determinants Of Prejudice Individual Attributes • Sex • Education • Age(Cohort Effect) • Income Structural Factors • Region • Rural/Urban • Size of Group • Intensity of Competition • Contact – Common Goal – Equal Status New Research on Racial Attitudes James Kluegel, “Trends in Whites’ Explanations of the black/white gap in SES,” American Sociological Review 55 (1990): 512-526. • Paradox in Racial Attitudes • Explanations Black Perceptions Jaynes, Gerald D. and Robin M. Williams, Jr. (Eds), A Common Destiny: Blacks and American Society. Washington, D.C.: National Academy Press, 1989. • increasing skepticism • distrust • frustration A Comprehensive Review • Schuman, Howard, Charlotte Steeh, Lawrence Bobo, and Maria Krysan. 1997. Racial Attitudes in America: Trends and Interpretations. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. – The authoritative guide to racial attitudes; thorough, careful, and complete. Trends in White Attitudes 1. Strong and steady trend toward endorsement of equal treatment. 2. No trend in endorsement of policies to achieve equal treatment if they conflict with other values (e.g., neighborhood schools or merit). 3. Social distance varies depending on proportions of out-group involved. White Trends, cont. 4. The majority of whites do not believe that discrimination is still a major factor. 5. Support for principles of equality varies directly with income, while support for affirmative action varies inversely with income. 6. Education continues to have its traditional liberalizing effects. Black Trends 1. Blacks feel discrimination has declined, but still see it as a major problem in American society. 2. Blacks are much more supportive of affirmative action. 3. Blacks and whites agree in seeing the lack of educational opportunities as a barrier. Black Trends, Cont. 4. Among blacks, the perception that current discrimination is a problem increases with education. 5. Since middle class blacks are subject to extra police attention, occasional rude treatment, and occasional insults based on race, they sometimes have trouble distinguishing between racial discrimination and plain rude behavior. Conclusions 1. Blacks and whites agree on the principle of racial equality. 2. Blacks and whites disagree on the major causes of inequality. 3. We know very little about how groups other than blacks and whites view these issues.