* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Simulation Techniques for Operations Management
Strategic management wikipedia , lookup
Project management wikipedia , lookup
High-commitment management wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem-based management wikipedia , lookup
Environmental resource management wikipedia , lookup
Investment management wikipedia , lookup
Management consulting wikipedia , lookup
International Council of Management Consulting Institutes wikipedia , lookup
Opportunity management wikipedia , lookup
Operations research wikipedia , lookup
Operations management wikipedia , lookup
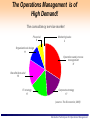
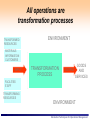
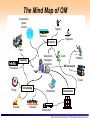
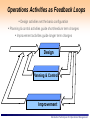
Erasmus Intensive Programme “SINTROME 2012” Simulation Techniques for Operations Management – An Introduction Dr. Vasiliki Kazantzi Assistant Professor, Dept. of Project Management 16-29 September 2012 TEI of Larissa, Greece Responsible for the Academic Part of SINTROME: Dr. Vasiliki Kazantzi – Educational Background: » B.Sc. in Chemical Engineering, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, » M.Eng. and PhD in Chemical Engineering, Texas A&M University, USA – Academic Experience: » Assistant Professor, Department of Project Management, Technological Education Institute of Larissa, Greece » Lecturer, Texas A&M University, USA – Professional Experience: » Environmental Project Consultant, Project Manager (EU funded R&D projects) – Tel. +30-2410-684545 Mobile: 6940617693 – e-mail: [email protected] – Web: http://dde.teilar.gr/main.aspx?category=338&UICulture=el-GR Simulation Techniques for Operations Management Outline Motivation for Studying OM What is Operations Management (OM) and What Do Operations Managers Do? OM activities and challenges Heritage of OM OM through Simulation Techniques What is Simulation? Advantages and Disadvantages of Simulation Techniques Monte Carlo Simulation Technique Simulation Techniques for Operations Management The Operations Management is of High Demand! The consultancy service market Financial 6 Marketing/sales 2 Organizational design 11 Operations and process management 31 Benefits/Actuarial 16 IT strategy 17 Corporate strategy 17 (source: The Economist, 2005) Simulation Techniques for Operations Management OM is Management Management is the process of • • • • • achieving organisational objectives within a changing environment, by balancing efficiency, effectiveness and equity, obtaining the most from limited resources, and working with and through people Simulation Techniques for Operations Management Operations Management Management Operations Principles Management which are in fact highly “symbiotic”: Management Operations Principles Management Simulation Techniques for Operations Management Four Common Attributes: 1. ‘Important’ ‘Management Principles’: • intellectual foundation of management thought and innovation for more than 100 years ‘Operations’: design & creation of products and services upon which we all depend the only rationale for an organisation existence (business objectives: reduce costs, increase revenue, reduce amount of investment, provide innovation) ‘operations function’ is the area where most of the organisations financial resources are spent Simulation Techniques for Operations Management Four Common Attributes: 2. ‘Exciting’ ‘Management Principles’: provides the “Vision” ‘Operations’: is at the very centre of changes affecting the Business world Simulation Techniques for Operations Management Four Common Attributes: 3. ‘Challenging’ ‘Operations’: creativity is the prime task of Operations Managers: they (have to) respond to global competition, environmental challenges, customer pressure etc. ‘Management Principles’: the essential intellectual underpinning for balancing the ‘3 Es’: Simulation Techniques for Operations Management Four Common Attributes: 4. ‘Ubiquitous ’ Oxford Illustrated Dictionary (1962) defines ubiquity as “omnipresence, being everywhere or in many places at the same time” ‘Operations’: Operations processes can be found everywhere ‘Management Principles’: cover developments in HR management, chaos theory, game theory, business strategy, change management, ‘ethics’ and so on Simulation Techniques for Operations Management What is Operations Management? Operation function: arrangement of organization resources to produce products and services Operations management: set of activities, decisions and responsibilities that creates value in the form of goods and services by transforming inputs into outputs Operations managers task: – managing (both effectively and efficiently) resources comprising operations function – managing processes transforming “inputs” into “outputs” » design processes, products and services » monitor processes » seeking ways of improvement Simulation Techniques for Operations Management All operations are transformation processes TRANSFORMED RESOURCES ENVIRONMENT MATERIALS INFORMATION CUSTOMERS INPUT TRANSFORMATION PROCESS GOODS OUTPUT AND SERVICES FACILITIES STAFF TRANSFORMING RESOURCES ENVIRONMENT Simulation Techniques for Operations Management Look Around You … Everything you can see around you has been processed by an operation Every service you receive (radio station, bus service, lecture, library etc.) has also been produced by an operation Operations Managers are responsible to manage the creation process of everything you buy, sit on, wear, eat, throw at people, and throw away Simulation Techniques for Operations Management Back office operation in a bank Kitchen unit manufacturing operation They are all operations Retail operation Take-out / restaurant operation Simulation Techniques for Operations Management An Operations Manager could be called… “fleet manager”, in a distribution company “administrative manager”, in a hospital “store manager”, in a supermarket and so on ..... ..... Simulation Techniques for Operations Management The Mind Map of OM Competitive global context Targets Measure Regulate Control Plant Operations manager’s decisions Capacity Processes Costs Models OM concepts Theory Timing Projects Scheduling Information Inventories Queues Distribution Simulation Techniques for Operations Management Operations Provide Advantages to Business reduce costs of producing products/services by being efficient increase revenue by increasing customer satisfaction through good quality & service reduce amount of investment by increasing effective capacity provide basis for innovation Simulation Techniques for Operations Management Why Study OM? OM is one of three major functions (marketing, finance, and operations) of any organization We want (and need) to know how goods and services are produced We want to understand what operations managers do OM is such a costly part of an organization Simulation Techniques for Operations Management Critical Decisions in OM 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Service, product design Quality management Process, capacity design Location Layout design Human resources, job design Supply-chain management Inventory management Scheduling Maintenance Simulation Techniques for Operations Management Operations Activities as Feedback Loops Design activities set the basic configuration Planning & control activities guide short/medium term changes Improvement activities guide longer term changes Design Planning & Control Improvement Simulation Techniques for Operations Management Broader Scope of OM Activities How do OM cope with Globalization? Environmental Protection Social Responsibility Technology Awareness etc. Simulation Techniques for Operations Management Where are the OM Jobs ? Simulation Techniques for Operations Management The Heritage of OM - 1 Division of labor (Adam Smith 1776 and Charles Babbage 1852) Standardized parts (Whitney 1800) Scientific Management (Taylor 1881) Coordinated assembly line (Ford/Sorenson/Avery 1913) Gantt charts (Gantt 1916) Motion study (Frank and Lillian Gilbreth 1922) Quality control (Shewhart 1924; Deming 1950) Computer (Atanasoff 1938) CPM/PERT (DuPont 1957) 23 Simulation Techniques for Operations Management The Heritage of OM - 2 Material requirements planning (Orlicky 1960) Computer aided design (CAD 1970) Flexible manufacturing system (FMS 1975) Baldrige Quality Awards (1980) Computer integrated manufacturing (1990) Globalization(1992) Internet (1995) 24 Simulation Techniques for Operations Management New Challenges in OM From Local or national focus Batch shipments Lengthy product development Standard products Job specialization To Global focus Just-in-time (pull systems) Supply chain partnering Rapid product development, alliances Mass customization Empowered employees, teams Simulation Techniques for Operations Management Operations Management through Simulation Simulation is a considerably powerful, yet simple, tool for an experiential understanding of any operational system’s behaviour Presents complex abstract models of reality in experientially rich and concrete forms Simulation training: a ‘learning by doing’ educational approach Simulation games: facilitate a better understanding of the implementation of organizational changes and new processes, as well as the benefits, difficulties, people management and information system needs Simulation Techniques for Operations Management Simulation Numerical technique of experimentation Attempts to duplicate a system – Features – Behavior Requires description of system Many application areas – Operations management – Finance & economics Simulation Techniques for Operations Management Simulation Imitate a real world situation Study its properties and operating characteristics Draw conclusions and make action decisions Simulation Techniques for Operations Management The Process of Simulation Define the Problem Introduce important variables Construct simulation model Specify values of variables to be tested Conduct the simulation Examine the results Select best course of action Simulation Techniques for Operations Management Some Applications of Simulation Ambulance location and dispatching Bus scheduling Assembly-line balancing Design of library operations Parking lot and harbor design Taxi, truck, and railroad dispatching Distribution system design Production facility scheduling Scheduling aircraft Plant layout Labor-hiring decisions Capital investments Personnel scheduling Production scheduling Traffic-light timing Sales forecasting Voting pattern prediction Inventory planning and control Simulation Techniques for Operations Management Advantages of Simulation flexible, straightforward can analyze large, complex real-world problems for which no closed-form analytical solutions exists can include real-world complications which most other techniques cannot enables “time compression” allows “what if” type questions does not interfere with the real-world system allows study of relationships Simulation Techniques for Operations Management Disadvantages of Simulation Can be expensive and time consuming Does not yield optimal solution Requires good managerial input Results not generalizable to other situations Simulation Techniques for Operations Management The Monte Carlo Simulation Technique The MC Simulation technique applies in systems which contain elements that are probabilistic in nature MC Simulation steps: Setup probability distribution for important variables Build cumulative distribution for each variable Establish interval of random numbers for each variable Generate random numbers Simulate a series of trials Simulation Techniques for Operations Management Real World Variables Which Are Probabilistic in Nature Inventory demand Lead time for orders to arrive Time between machine breakdowns Times between arrivals at a service facility Service times Times to complete project activities Number of employees absent from work each day Simulation Techniques for Operations Management Simulation and Inventory Analysis - the Basic Model demand > begin inv? Begin end inv = begin-demand Order arrived? Increase current inv by qty order End inv < reorder point? random # for today's demand # of lost sales End inv = 0 Order placed & not arrived? Enough Days in simulation? Place order Generate Random lead time Compute averages Simulation Techniques for Operations Management