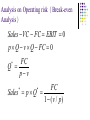* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Capital Structure II:
Moral hazard wikipedia , lookup
Present value wikipedia , lookup
Debt settlement wikipedia , lookup
Debt collection wikipedia , lookup
Debt bondage wikipedia , lookup
Global saving glut wikipedia , lookup
Financial economics wikipedia , lookup
Debtors Anonymous wikipedia , lookup
Business valuation wikipedia , lookup
First Report on the Public Credit wikipedia , lookup
Household debt wikipedia , lookup
Financialization wikipedia , lookup
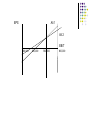
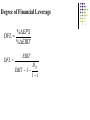
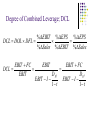
Capital Structure II: Limits to the Use of Debt Costs of Financial Distress Bankruptcy risk versus bankruptcy cost. The possibility of bankruptcy has a negative effect on the value of the firm. However, it is not the risk of bankruptcy itself that lowers value. Rather it is the costs associated with bankruptcy. It is the stockholders who bear these costs. Description of Bankruptcy Costs Direct Costs Legal and administrative costs (tend to be a small percentage of firm value). Indirect Costs Impaired ability to conduct business (e.g., lost sales) Agency Costs Selfish strategy 1: Incentive to take large risks Selfish strategy 2: Incentive toward underinvestment Selfish Strategy 3: Milking the property Balance Sheet for a Company in Distress Assets BV MV Cash $200 $200 Fixed Asset $400 $0 Total $600 $200 Liabilities BV MV LT bonds $300 $200 Equity $300 $0 Total $600 $200 What happens if the firm is liquidated today? The bondholders get $200; the shareholders get nothing. Selfish Strategy 1: Take Large Risks The Gamble Win Big Lose Big Probability 10% 90% Payoff $1,000 $0 Cost of investment is $200 (all the firm’s cash) Required return is 50% Expected CF from the Gamble = $1000 × 0.10 + $0 = $100 $100 NPV = –$200 + (1.50) NPV = –$133 Selfish Stockholders Accept Negative NPV Project with Large Risks Expected CF from the Gamble To Bondholders = $300 × 0.10 + $0 = $30 To Stockholders = ($1000 – $300) × 0.10 + $0 = $70 PV of Bonds Without the Gamble = $200 PV of Stocks Without the Gamble = $0 $30 (1.50) PV of Stocks With the Gamble: $47 = $70 (1.50) PV of Bonds With the Gamble: $20 = The value of firm becomes: 67 = 20 + 47 = 200 - 133 Selfish Strategy 2: Underinvestment Consider a government-sponsored project that guarantees $350 in one period Cost of investment is $300 (the firm only has $200 now) so the stockholders will have to supply an additional $100 to finance the project Required return is 10% $350 NPV = –$300 + (1.10) Should we accept or reject? NPV = $18.18 Selfish Stockholders Forego Positive NPV Project Expected CF from the government sponsored project: To Bondholder = $300 To Stockholder = ($350 – $300) = $50 PV of Bonds Without the Project = $200 PV of Stocks Without the Project = $0 PV of Bonds With the Project: PV of Stocks With the Project: $300 $272.73 = (1.10) $50 – $100 $-54.55 = (1.10) The value of firm = 272.73 – 54.55 = 218.18=200 + 18.18 Selfish Strategy 3: Milking the Property Liquidating dividends Suppose our firm paid out a $200 dividend to the shareholders. This leaves the firm insolvent, with nothing for the bondholders, but plenty for the former shareholders. Such tactics often violate bond indentures. Increase perquisites to shareholders and/or management Integration of Tax Effects and Financial Distress Costs There is a trade-off between the tax advantage of debt and the costs of financial distress. It is difficult to express this with a precise and rigorous formula. Integration of Tax Effects and Financial Distress Costs Value of firm under MM with corporate taxes and debt Value of firm (V) Present value of tax shield on debt VL = VU + TCB Present value of financial distress costs Maximum firm value V = Actual value of firm VU = Value of firm with no debt 0 Debt (B) B* Optimal amount of debt Signaling The firm’s capital structure is optimized where the marginal subsidy to debt equals the marginal cost. Investors view debt as a signal of firm value. Firms with low anticipated profits will take on a low level of debt. Firms with high anticipated profits will take on high levels of debt. A manager that takes on more debt than is optimal in order to fool investors will pay the cost in the long run. Shirking, Perquisites, and Bad Investments: The Agency Cost of Equity An individual will work harder for a firm if he is one of the owners than if he is one of the “hired help”. While managers may have motive to partake in perquisites, they also need opportunity. Free cash flow provides this opportunity. The free cash flow hypothesis says that an increase in dividends should benefit the stockholders by reducing the ability of managers to pursue wasteful activities. The free cash flow hypothesis also argues that an increase in debt will reduce the ability of managers to pursue wasteful activities more effectively than dividend increases. The managers may decide to pursue a capital structure which is less levered than that implied by maximized value, trying to reduce the risk in bankruptcy, thus the risk in losing his own job. The Pecking-Order Theory Theory stating that firms prefer to issue debt rather than equity if internal finance is insufficient. Rule 1 Use internal financing first. Rule 2 Issue debt next, equity last. The pecking-order Theory is at odds with the trade-off theory: There is no target D/E ratio. Profitable firms use less debt. Companies like financial slack Growth and the Debt-Equity Ratio High growth firms face high operating risk; so they adopt less risky financial strategy. Growth implies significant equity financing, even in a world with low bankruptcy costs. Thus, high-growth firms will have lower debt ratios than low-growth firms. Growth is an essential feature of the real world; as a result, 100% debt financing is sub-optimal. Capital Structure and Operating Risk Operating risk: a firm’s facing uncertainty in product prices, variable and fixed costs. This risk does not involves with debt financing. We can measure operating risk by standard deviation of operating income, i.e. EBIT. Financial risk: a firm facing uncertainty resulted from debt financing. Using debt increases uncertainty in EPS (and ROE). Analysis on Operating risk(Break-even Analysis) Sales VC FC EBIT 0 p Q v Q FC 0 FC Q pv * FC Sales p Q 1 ( v / p) * * Break-even Analysis One firm could have two ways to produce the same product. The first is to employ $20,000 fixed cost and thus incurs $1.50 variable cost per unit. The second is to employ $60,000 fixed cost and incurs $1.00 variable cost per unit. What are the breakeven volume for each production method? On what level of production volume that both ways will produce the same level of EBIT? The price for the product is $2.00. The first method FC 20, 000 Q 40, 000units p v 2 1. 5 * The second method Q* FC 60, 000 60, 000units pv 2 1 On what level of production volume that both ways will produce the same level of EBIT? Sales 20, 000 1. 5Q 60, 000 Q Q 80, 000 Sales $2 80, 000 $160, 000 EBIT 1st 40,000 2nd 60,000 80,000 Sales/Quantity Financial Break-even Analysis A firm currently has $2,000,000 bond outstanding, which has 8% coupon rate, in addition to its 100,000 shares common stock. The firm is consider to undertake $1,000,000 expansion plan, which could be financed by either of two alternatives: (1)100% debt financed which is issued on par and 10% coupon rate (2)100% equity financed with issuance of new stock, and at a price of $10. The firm expects its operating income (EBIT) to be $800,000, and corporate income tax rate is 25%. What will be the financial break-even points for both alternatives? What will be the EBIT/EPS indifferent point? Which financing alternative leads to higher EPS if the expected EBIT is $800,000? EPS E PS 1 ( EBIT I ) (1 t ) Dpf n ( E B IT I ) (1 t ) D n ( E B IT $260,000) (1 0.25) 0, 100,000 E B IT $260,000 EPS2 ( EBIT I ) (1 t ) Dpf n ( EBIT $160, 000) (1 0. 25) 0, 200, 000 EBIT $160, 000 ( EBIT * $260, 000) (1 0. 25) ( EBIT * $160, 000) (1 0. 25) EPS1 EPS2 100, 000 200, 000 EBIT * $360, 000 EPS Alt 1 Alt 2 EBIT 160,000 260,000 360,000 800,000 Degree of Operating Leverage %EBIT DOL %Sales Sales VC Sales VC EBIT FC DOL Sales VC FC EBIT EBIT Degree of Financial Leverage %EPS DFL %EBIT DFL EBIT EBIT I D pf 1 t Degree of Combined Leverage; DCL %EBIT %EPS %EPS DCL DOL DFL %Sales %EBIT %Sales EBIT FC DCL EBIT EBIT FC D pf D pf EBIT I EBIT I 1 t 1 t EBIT Integrate operating and financial risk with financing alternatives Firms try to manage total risk (financial and operating) to an acceptable level. Firms with high operating risk, tend to adopt less financial risk financing (equity financing dominant) alternatives, to avoid high interest payment. Firms with low operating risk, tend to adopt more financial risk financing (debt financing dominant) alternatives, to increase ROE.