* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Law of Demand
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
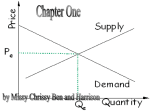
Lecture - SS 2015 Prof. Dr. K.J. Bernhard Neumärker Matthew Bonick Principles of Economics 4th Class: Supply and Demand. 1 Today’s Concepts • • • • • Market Forces Types of Markets Law of Demand Law of Supply Market Equilibrium Market Forces • Market : a group of buyers and sellers of a particular good or service. Groups of buyers determine demand and groups of sellers determine supply • Supply: The quantity of a good that sellers are willing and are able to sell • Demand: The quantity of a good that buyers are willing and are able to purchase Competitive Markets • Market in which there are many buyers and sellers so that each has a negligible impact on the market • Sellers have little control over the prices • Sellers: They know that if they raise their prices to much, buyers will move to their competitors • Buyers : Have little control over the market price because each buyer as a whole only purchases a small amount of good in comparison to the whole market of buyers. • Can you think of example where this is not the case? Perfect Markets • In this section we assume markets are perfectly competitive – Goods being offered for sale are all the same – Buyer and sellers are numerous and thus cannot influence the price. The market determines the price and buyers and sellers are prices takers • Examples: Wheat markets Types of Markets • Auctions • Competitive Markets – Monopoly – Monopolistically Competitive – Oligopoly – Perfect competition Demand • Demand: The quantity of a good that buyers are willing and are able to purchase . • Law of Demand : Other things equal when the price of a good rises, the quantity demanded of the good falls, and when the price falls the quantity demanded rises P↑ Q↓ or P↓ Q↑ • Price and quantity demanded are negatively related. Demand Curves • Demand Schedule: A table that shows the relationship between price of a good and the quantity of goods demanded • Demand Curve: Graphical representation of relationship between price of a good and the quantity Demanded • Example: Ice-cream Demand Curve Demand • From the previous graph please create a demand schedule • What is the slope of the demand curve? What does this indicate? • How do you think we determine overall market demand? Market Demand Demand Curve • Changes to the demand curve – Price change • Movement along the Demand curve – Quantity change: • Shift of the demand curve, which indicates a change in quantity demanded at every price • Income • Prices of related goods • Preferences change • Expectations • Number of buyers Why do demand curves shift? • Income: Increase in income changes quantity of demanded – Normal good : Others things being held equal. A good in which an Increase in income will increase quantity demanded – Example? – Inferior good: Other things being equal an increase in income will lead to a decrease in demand Why do demand curves shift? • Price of related goods: The effect of changes in prices of related goods. – Substitutes: two good for which and increase in the prices of one leads to an increase in the demand of another – Example? – Complements: two goods for which an increase in the price of one will decrease the demand for another Why do demand curves shift? • Tastes : Changes in tastes effect demand • Expectations: Expectations about the future may effect demand – Why is this the case? • Number of buyers: Higher number of buyers increase total demand Shifts in Demand Policy Supply • Supply: The quantity of a good that sellers are willing and are able to sell • Law of supply : Other things equal when the price of a good rises the quantity supplied also rises, and when the price falls the quantity provided falls as well P↑ Q ↑ or P↓ Q ↓ • Price and quantity supplied are positively related. Supply • Supply Schedule: A table that shows the relationship between price of a good and the quantity of goods supplied • Supply Curve: Graphical representation of relationship between price of a good and the quantity supplied • Given the quantity and price relationship how will the curve slope? Supply Curve Market Supply Why does the supply curve shift? • Price changes: Movement along the supply curve • Quantity changes: Shifts of the curve – Input Prices – Technology – Expectations – Number of Sellers Why does the supply curve shift? • Input prices: – To produce a good inputs are necessary – Ice cream: sugar, flower, ice-cream maker, and labor – When the price of one of these good rises, producing ice-cream is less profitable – Inputs and supply are negatively related • Technology: – Better technology can increase the efficiency of inputs and thus the profitability of supplying a good. – Example? – Technology and Supply have a positive relationship Why does the supply curve shift? • Expectations: Future expectations will effect the supply – Example? • Number of Sellers: Increasing number of sellers will increase overall supply. Shifts in Supply Now lets combine… • Law of Supply and Demand: The price of any good adjusts to bring the quantity supplied and quantity demanded for that good into balance • Equilibrium: The situation in which the price has reached the level where quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded. Now lets combine…2 • Market Clearing Price: The price of the good when everyone in the market has been satisfied • Equilibrium Price: The price that balances quantity demanded and quantity supplied • Equilibrium Quantity: The quantity demanded and quantity supplied at the equilibrium price Equilibrium Equilibrium • Market forces in general drive prices to the equilibrium point • Surplus: A situation in which quantity supplies is greater that demand • Shortage: A situation in which the quantity demanded is greater than supplies Equilibrium Shifts – Demand Shifts – Supply Example • Draw a supply and demand curve in equilibrium. • In the example of ice-cream – What happens if a new and better ice-cream machine is created – What happens if the price of frozen yogurt ( substitute good) rises. • Things to look for: – What curves shifts? And in which direction – How will this effect the equilibrium price and quantity The Words of the day! • Supply, Demand, Law of Supply, Law of Demand, Change along the demand curve, change in demand, Equilibrium, Equilibrium Price, Equilibrium Quantity, Surplus, Shortage, Change in supply, Change of the quantity demanded, comparative statics Exercise • Try to formulate sentences where these words make sense. • If you have doubts about your formulation do not hesitate to contact me. 34