* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ExamView - geometry review for final chapters 5 and 6 .tst
Survey
Document related concepts
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Atiyah–Singer index theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Riemann–Roch theorem wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Brouwer fixed-point theorem wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
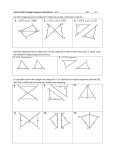
Name: ______________________ Class: _________________ Date: _________ Geometry - Review for Final Chapters 5 and 6 ____ 1. Classify a. b. ____ PQR by its sides. Then determine whether it is a right triangle. scalene ; right isoceles ; not right c. d. scalene ; not right isoceles ; right c. d. 101° 5° 2. Find m∠KMN . a. b. 20° 79° 1 ID: A Name: ______________________ ____ 3. A ramp is designed with the profile of a right triangle. The measure of one acute angle is 2 times the measure of the other acute angle. Find the measure of each acute angle. a. b. ____ ID: A 45°, 45° 11.25°, 78.75° c. d. 22.5°, 67.5° 30°, 60° c. d. QRP ≅ QRP ≅ 4. Write a congruence statement for the triangles. a. b. PRQ ≅ PRQ ≅ TUV UTV 2 TUV UTV Name: ______________________ ____ 5. In the diagram, a. b. ____ y = 51 y = 54 CDE ≅ ID: A GHI . Find the value of y. c. d. y = 42 y = 64 c. d. 56° 112° 6. Find m∠BDC . a. b. 68° 84° 3 Name: ______________________ ____ 7. Find the value of x. a. b. ____ ID: A 10 4 c. d. 5 6 8. In the diagram, M is the midpoint of BC . Find the coordinates of M. a. b. ÁÊÁ 3 ˜ˆ˜ ÁÁ ,2 ˜˜ Á2 ˜ Ë ¯ ÁÊÁ 3 4 ˜ˆ˜ ÁÁ , ˜˜ Á4 3˜ Ë ¯ c. d. 4 ÁÊÁ 4 3 ˜ˆ˜ ÁÁ , ˜˜ Á3 4˜ Ë ¯ ÁÊÁ 3 ˜ˆ˜ ÁÁ 2, ˜˜ Á 2˜ Ë ¯ Name: ______________________ ____ ID: A 9. Which statements about the diagram are true? a. b. c. BDE is obtuse. ABC is scalene. The value of x is 18. d. e. f. ____ 10. What additional information is needed to prove that a. b. ∠BNA ≅ ∠COD and CO ≅ BN AN ≅ DO and ∠ABN ≅ ∠DCO c. d. ABC is obtuse. BDE is right. The value of y is 113. ABN ≅ DCO using the SAS Congruence Theorem? ∠ABN ≅ ∠DCO and CO ≅ BN AN ≅ DO and ∠BAN ≅ ∠CDN ____ 11. In a coordinate plane, PQR has vertices P(0, 0) and Q(3a, 0). Which coordinates of vertex R make an isosceles right triangle? Assume all variables are positive. ÊÁ ˆ ÊÁ ˆ ÁÁ ÁÁ 3a 2 3a 2 ˜˜˜ 3a 3 ˜˜˜˜ Á Á ˜˜ a. ÁÁ 3a, ˜ d. ÁÁ , 2 ˜˜˜ 2 ˜˜˜ ÁÁ ÁÁ 2 Ë ¯ Ë ¯ ÁÊÁ 3a 3a ˜ˆ˜ ˜˜ , b. ÁÁÁ e. ÊÁË 3a, 3a ˆ˜¯ ˜ 2 2 Ë ¯ Ê ˆ Á ˜ c. Ë 0, 3a ¯ 5 PQR Name: ______________________ ID: A 12. Find the measure of each acute angle. ____ 13. In the diagram of the basketball hoop below, can you use the Hypotenuse-Leg Congruence Theorem to prove that WXY ≅ WZY ? a. yes b. no ____ 14. Are the triangles shown in the Brazilian flag congruent by the ASA Congruence Theorem? a. yes b. 6 no Name: ______________________ ID: A ____ 15. Are the triangles shown in the four-sided die congruent by the AAS Congruence Theorem? a. yes b. no Can the triangles be proven congruent with the information given in the diagram? If so, state the theorem you would use. ____ 16. a. b. c. yes; AAS Congruence Theorem yes; ASA Congruence Theorem no a. b. c. yes; AAS Congruence Theorem yes; ASA Congruence Theorem no ____ 17. 7 Name: ______________________ ID: A ____ 18. a. b. c. yes; AAS Congruence Theorem yes; ASA Congruence Theorem no ____ 19. Which reason is not necessary to explain how you can find the distance across the lake? a. b. c. d. e. ASA Congruence Theorem Right Angles Congruence Theorem SAS Congruence Theorem Corresponding parts of congruent triangles are congruent. Vertical Angles Congruence Theorem ____ 20. Which reason is not used in a plan to prove that XW ≅ ZY ? a. b. HL Congruence Theorem Reflexive Property of Congruence c. d. 8 Base Angles Theorem Corresponding parts of congruent triangles are congruent. Name: ______________________ ID: A ____ 21. Which reason is not used in a plan to prove that ∠1 ≅ ∠2? a. b. SAS Congruence Theorem Alternate Interior Angles Theorem c. d. Vertical Angles Congruence Theorem Corresponding parts of congruent triangles are congruent. Find the coordinates of vertex C for the figure placed in a coordinate plane. ____ 22. a rectangle with width m and length twice its width a. b. C(2m, m) C(m, m) c. d. C(m, 2m) C(2m, 2m) c. d. C(8, 0) C(4, 0) ____ 23. an isosceles triangle a. b. C(3, 0) C(6, 0) 9 Name: ______________________ ID: A ____ 24. In the diagram, AB passes through the center C of the circle and DC ⊥AB. Name two triangles that are congruent. a. b. DCA ≅ DAC ≅ ACD CBD c. d. DCA ≅ CBD not enough information ____ 25. Use the information in the diagram to determine which statements are true. a. b. c. d. You can use the Vertical Angles Congruence Theorem to prove that ABC ≅ DEC . ∠CAB ≅ ∠CDE because corresponding parts of congruent triangles are congruent. Point C is the midpoint of AD. You cannot make a conclusion using congruent triangles. ____ 26. Which statements are true for ABC with vertices A(0, 0), B(m, m), and C(2m, 0)? (Assume m is positive.) c. a. The slope of AC is undefined. ABC is a right triangle. ÊÁ 3m m ˆ˜ , ˜˜˜˜ . b. The midpoint of BC is ÁÁÁÁ d. ABC is isosceles. 2 2¯ Ë 10 Name: ______________________ ID: A Match the numbered statement below with its reason to prove that the sides of the flag are parallel. Given QP ≅ RS , QP Ä RS Prove QR Ä SP a. b. c. d. e. f. SAS Congruence Theorem Converse of Alternate Interior Angles Theorem Corresponding parts of congruent triangles are congruent. Given Reflexive Property of Congruence Alternate Interior Angles Theorem ____ 27. 2. ∠QPR ≅ ∠SRP ____ 28. 3. QP ≅ RS ____ 29. 4. PR ≅ RP ____ 30. 5. QPR ≅ SRP ____ 31. 7. QR Ä SP Write a proof. 32. Given J is the midpoint of KM ,JL⊥KM Prove JKL ≅ JML 11 Name: ______________________ ID: A 33. Given DF ≅ DH ,FG ≅ HG Prove DFG ≅ DHG 34. Given B is the midpoint of AE , AC Ä DE Prove ABC ≅ EBD 35. Given ST ≅ UV , RS Ä TU , ∠RTS and ∠TVU are right angles. Prove RST ≅ TUV 12 Name: ______________________ ID: A Decide whether there is enough information given in the picture to prove that the triangles are congruent using the SAS Congruence Theorem. Explain your reasoning. 36. ABD, CBD 37. KLN, MNL 38. In the diagram of the house, the length of AB is 15 feet. Explain why the length of BC is the same. 39. Find PF. Explain your reasoning. 13 Name: ______________________ ID: A 40. A sandwich cut diagonally forms two right triangles, with JK ≅ LM . Prove that the two triangles are congruent. 41. Determine whether each statement is true or false. If true, explain your reasoning. If false, give a counterexample. a. If two triangles are congruent, then their perimeters are the same. b. If two triangles have the same perimeter, then the triangles are congruent. Write a coordinate proof. 42. Given Prove Coordinates of vertices of 1 MP = BC 2 ABC , M is the midpoint of AB, P is the midpoint of AC . 14 Name: ______________________ ID: A ____ 43. Find BC. a. b. BC = 15 BC = 30 c. d. BC = 24 BC = 9 c. d. m∠BAD = 23° m∠BAD = 67° ____ 44. Find m∠BAD. a. b. m∠BAD = 46° m∠BAD = 11.5° 15 Name: ______________________ ID: A → ____ 45. In the diagram, AD bisects ∠BAC. Find BD . a. b. BD = 12 BD = 1 c. d. BD = 9 BD = 18 ____ 46. Write an equation of the perpendicular bisector of the segment with endpoints G ÊÁË −2,0 ˆ˜¯ and H ÊÁË 8,−6 ˆ˜¯ . a. b. 5 34 x+ 3 3 5 y= x−8 3 y= ____ 47. Find the coordinates of the circumcenter of a. ÊÁË 6,−14.5ˆ˜¯ b. ÁÊË 0,1.5 ˜ˆ¯ c. d. 16 5 y=− x− 3 3 5 y=− x+2 3 ABC with vertices A ÊÁË −4,0ˆ˜¯ , B ÊÁË 8,3ˆ˜¯ , and C ÊÁË 4,3 ˆ˜¯ . c. ÊÁË 2,1.5 ˆ˜¯ d. ÁÊË 6,1.1 ˜ˆ¯ 16 Name: ______________________ ID: A In MNQ, BP = 5x + 4 , AP = 7x − 11, MP = 6x − 6, and QP = 8x − 15. Match the point of concurrency P below with its value of x in the diagram. a. x = 10 b. x= c. 9 2 x=4 15 2 19 e. x = 3 f. x = 5 d. x= ____ 48. incenter P ____ 49. circumcenter P Is there enough information given in the diagram to conclude that point P lies on the perpendicular bisector of LM ? Explain your reasoning. 50. 17 Name: ______________________ ID: A 51. ← → 52. The diagram shows fire hydrants located at points A and B. Line PQ coincides with Pont Road and is the perpendicular bisector of AB. Will a firefighter at the scene of the car fire have to walk farther to connect the hose to fire hydrant A or fire hydrant B? Explain your reasoning. 53. A pet owner plans to tie up the dog so it can reach the places shown in the diagram. Explain how the owner can determine where to place a stake so that it is the same distance from the dog’s food, the doghouse, and the door to the owner’s house. 18 Name: ______________________ ID: A 54. You are drilling a hole in the triangular birdhouse shown. You want the hole to be the same distance from all three sides. Where should you drill the hole? Explain your reasoning. 55. The diagram shows a piece of wood for one side of a shelf. Point P is the center of a hole for a dowel rod that is to be drilled 5 centimeters from sides AB and BC . You draw segment BP . Can you conclude that the segment bisects ∠ABC ? Explain. 19 ID: A Geometry - Review for Final Chapters 5 and 6 Answer Section 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. C C D D C D B A B, C, D, E C, D B, C, E 26°, 64° B B A A C B C C B A B A D B, C, D F D E A B STATEMENTS 1. J is the midpoint of KM . 2. KJ ≅ MJ 3. JL⊥KM REASONS 1. Given 2. Definition of midpoint 3. Given 4. ∠LJM and ∠LJK are right angles. 4. Definition of perpendicular lines 5. ∠LJM ≅ ∠LJK 6. LJ ≅ LJ 7. JKL ≅ JML 5. Right Angles Congruence Theorem 6. Reflexive Property of Congruence 7. SAS Congruence Theorem 1 ID: A 33. STATEMENTS 1. DF ≅ DH REASONS 1. Given 2. FG ≅ HG 2. Given 3. DG ≅ DG 4. DFG ≅ DHG 3. Reflexive Property of Congruence STATEMENTS 1. B is the midpoint of AE . 2. AC Ä DE REASONS 1. Given 2. Given 3. AB ≅ EB 4. ∠ABC ≅ ∠DBE 5. ∠CAB ≅ ∠DEB 6. ABC ≅ EBD 3. Definition of midpoint 4. SSS Congruence Theorem 34. 4. Vertical Angles Congruence Theorem 5. Alternate Interior Angles Theorem 6. ASA Congruence Theorem 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. STATEMENTS REASONS 1. Given 1. ST ≅ UV , RS Ä TU , ∠RTS and ∠TVU are right angles 2. ∠RTS ≅ ∠TVU 2. Right Angles Congruence Theorem 3. ∠SRT ≅ ∠UTV 3. Corresponding Angles Theorem 5. AAS Congruence Theorem 5. RST ≅ TUV no; The congruent angles are not the included angles. yes; Two pairs of sides and the included angles are congruent. By the Linear Pair Postulate and the definition of supplementary angles, m∠BCA = 180° − 140° = 40° . Because m∠A = 40° = m∠BCA, by definition of congruent angles, ∠A ≅ ∠BCA. So, by the Converse of the Base Angles Theorem, AB ≅ BC . So, AB = BC = 15 feet. 12 ft; Using the Exterior Angle Theorem, m∠PFY = m∠ZPF − m∠PYF = 60° − 30° = 30°. Because m∠PYF = 30° = m∠PFY, by the definition of congruent angles, ∠PYF ≅ ∠PFY. So, by the Converse of the Base Angles Theorem, PF ≅ YP. So, PF = YP = 12 feet. 40. You are given that JK ≅ LM and that the triangles are right triangles. So, one pair of corresponding legs is congruent. By the Reflexive Property of Congruence, JL ≅ JL . So, by the HL Congruence Theorem, JLM ≅ LJK . 41. a. true; Because the triangles are congruent, the corresponding side lengths are congruent. The side lengths have the same measures by the definition of congruence. So, the triangles will have the same perimeter. b. false; Sample answer: ABC with AB = 3 meters, BC = 4 meters, and AC = 6 meters has a perimeter of 13 meters, and DEF with DE = 4 meters, EF = 5 meters, and DF = 4 meters has a perimeter of 13 meters. ABC is not congruent to DEF . ÊÁ 3n ˆ˜ 5n 42. Using the Midpoint Formula, M ÁÁÁÁ 0, ˜˜˜˜ and P ÁÊË 2n,0 ˜ˆ¯ . Using the Distance Formula, MP = and BC = 5n . 2 2 Ë ¯ So, MP = 1 BC . 2 43. B 2 ID: A 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. C C B A D B no; You would need to know that either LN = MN or LP = MP . 51. yes; Because point P is equidistant from L and M , point P is on the perpendicular bisector of LM by the Converse of the Perpendicular Bisector Theorem. Also, LN ≅ MN , so PN is a bisector of LM . Because P can only be on one of the bisectors, PN is the perpendicular bisector of LM . 52. The firefighter will walk the same distance to connect the hose to either fire hydrant; Point P is on the perpendicular bisector of AB, so AP = BP by the Perpendicular Bisector Theorem. 53. The pet owner can copy the positions of the three places, connect the points to draw a triangle, and draw three perpendicular bisectors of the triangle. The point where the perpendicular bisectors meet, the circumcenter, should be the location of the stake. 54. You should drill the hole at the incenter of the birdhouse because the incenter is equidistant from the sides of the triangle by the Incenter Theorem. 55. yes; Point P is in the interior of ∠ABC and it is equidistant from sides AB and BC . So, P lies on the bisector of ∠ABC . 3 Geometry - Review for Final Chapters 5 and 6 [Answer Strip] D __________ 3. C __________ 5. C __________ 1. D __________ 4. D __________ 6. C __________ 2. ID: A Geometry - Review for Final Chapters 5 and 6 [Answer Strip] B __________ 7. B, C, D, E 9. __________ B __________13. A __________ 8. C, D __________10. B __________14. B, C, E __________11. ID: A Geometry - Review for Final Chapters 5 and 6 [Answer Strip] A __________15. B __________18. B __________21. C __________19. A __________22. A __________16. B __________23. C __________17. C __________20. ID: A Geometry - Review for Final Chapters 5 and 6 [Answer Strip] B __________43. A __________24. D __________25. C __________44. F __________27. D __________28. E __________29. A __________30. B __________31. B, C, D __________26. ID: A Geometry - Review for Final Chapters 5 and 6 [Answer Strip] C __________45. B __________46. D __________48. A __________47. B __________49. ID: A