* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Measuring Angles PPT
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
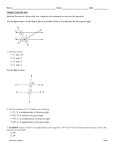
Measuring Angles Chapter 1 Section 4 Common Core Standard: G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a circular arc. Vocabulary Angle: Formed by 2 rays with the same endpoint. Sides: The rays of an angle. Vertex: The endpoint of an angle. Naming angles: there are 3 ways By the letter at the vertex. A letter on each side and the vertex. Vertex letter is the middle letter. By a number inside the angle. A B 1 C Vocabulary The interior of an angle is the region between the two sides. The exterior of an angle is the region outside of the two sides. A B 1 C Vocabulary Acute angle: measures between 0 and 90 degrees Right Angles: Measures exactly 90 degrees Obtuse angle: Measures between 90 and 180 degrees Straight angle: Measures exactly 180 degrees Made of two opposite rays. Congruent Angles: Angles with the same measure Protractor Postulate (1-7) This postulate allows you to measure an angle using a protractor. The measure of an angle is the absolute value of the difference of the real numbers paired with the two rays. IE: Take the number for each ray – subtract them – find the absolute value. Example 1 What is the measure of angle BOC? _____________ What is the measure of angle BOD? _____________ What is the measure of angle COA? _____________ What is the measure of angle DOC? _____________ Angle Addition Postulate (1-8) If point b is in the interior of AOC, then m AOB + m BOC = m AOC Meaning: If you have two adjacent angles you can add the measure of the two angles to find the measure of the large angle. A B O C Example 2 A 4x - 20 If m AOC = 155, find m AOB and m B 3x + 14 O C BOC Checkpoint Turn to page 31. With a partner – answer questions 1 – 5. You will have 8 minutes to complete this before we go over. Homework Pg 31# 6 – 20 even, 22, 23, 28, 29, 30, 42, 43