* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mythology - WordPress.com
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
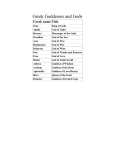
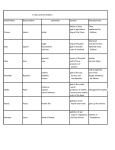
Quick write Your first entry in your interactive notebook! Be sure to add it to the table of contents with today’s date and the page number. TOPIC: Brainstorm some ideas to create your own modern god or goddess to add to the Greek pantheon. The new god or goddess should fall into the hierarchy of the Greek pantheon but rule an aspect of modern life (think about things that didn’t exist in ancient Greece, such as cars and electronic devices). Might the modern world need a new god or goddess to control highway traffic, prevent cyber-bullying, influence fashion trends, promote human rights, or promote healthy eating? Jot down ideas about the following: name; what s/he rules; what her/his primary symbol might be; what special abilities s/he might have; how/why s/he came into being, and how does s/he help in the modern world Mythology Introduction and Recap What are myths? Stories that use fantasy to express ideas about life that cannot easily be expressed in realistic terms At the heart, they are religious stories that deal with and explore the relationship between human beings and the unknown/spiritual world Once believed to be true (no matter how wild or strange they seem to be) Purposes of myths Scientific: explanation of things in nature Literary: entertaining; good storytelling Religious: give meaning to things in life; explain role of the gods in everyday life Myths seek to explain all those unexplainable or unknowable aspects of life… Where do we go after we die? How was the world created? water? Why can we see our reflection in Why are there four separate seasons? Why do we fall in love? How is lightning created? Greek Mythology Earliest people to give their gods human forms (fully developed by about 700 B.C.) Gave gods human qualities and emotions Man was not created in the image of the gods; rather, the gods were in the image of man Were able to determine proper behavior based on what would “anger the gods” or “please How did we learn these stories? First passed down through storytelling, songs, and poetry We learned the stories from written versions, mainly Homer’s epic poems The Iliad and The Odyssey, which tell of the great deeds of heroes (stories of Achilles and Odysseus) Also, the Roman poet Virgil and his epic poem The Aeneid (story of Aeneas) The Greeks were polytheists Today, many people believe in one god (monotheism) Many centuries ago, when the stories of mythology began, people believed in many gods (polytheism) and each god had authorities over certain powers Origin of the Gods From Chaos emerged… Gaea (mother earth) and Ouranos (father heaven) Had children: monsters with 50 heads and 100 arms The monsters were so ugly that Ouranos threw the monsters into Tartarus, the pit at the bottom of Hades Then, Ouranos and Gaea had a new group of children called Titans One Titan, Cronus, rebelled against Ouranos and chopped his father into Clash of the Titans vs. the Olympians Cronus was now ruler of the Universe He feared that his children would one day kill him, so as they were born, he swallowed them whole His wife, Rhea grew tired of her husband eating her children, so when the youngest son Zeus was born, she fed her husband a rock and hid Zeus on an island When Zeus was grown, Rhea poisoned her husband Cronus who vomited up Zeus’s brothers and sisters Zeus led his brothers and sisters in a war against the The Olympians A group of 12 gods who ruled after the overthrow of the Titans All related in some way Named after their dwelling place, Mount Olympus, which could have either been: the physical mountain in Thessaly OR a mountain in a mysterious region above the Earth. (Olympus was NOT HEAVEN) Led by Zeus, the god of the other gods Zeus and his brothers split territory (Zeus: earth/sky; Poseidon: the seas; Hades: the underworld) The Twelve Olympians Aphrodite: goddess of love and beauty Hades: god of underworld Apollo: god of the sun and of music Hephaestus: god of fire and of the forge Ares: god of war Hera: queen of the gods Artemis: goddess of the hunt and of the moon Hermes: messenger of the gods Athena: goddess of wisdom and war Dionysus: god of wine and revelry Poseidon: god of the sea Zeus: king of the gods Ancient Greek Beliefs and Characteristics Death is inevitable and final, so the goal was to become a legend through great deeds Greeks were tough, relentless, ambitious, hard-living, and imaginative Honor was extremely important, and the Greeks were very vengeful if wronged Gods mirrored human feelings and physical form Flaws were pride, cruelty, stubbornness, impulsiveness, lust for power, and desire to be like the gods