* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 9 - Chemical Quantities: The Mole
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
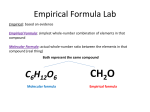
Molecular and Formula Mass • How much does a compound weigh? Unit 9 – Chemical Quantities: The Mole Essential Questions: • What is a mole? • How is the mole used in chemical calculations? • How is an empirical formula different from a molecular formula? • How is a molecular formula calculated? • What is percent composition? The Mole • Avogadro’s Number • A counting number • Like a dozen • 6.02 x 1023 • Named for Amedeo Avogadro • Mole • 1 mole = 6.02 x 1023 particles • Relates atomic mass to grams • 1 atom of 12C – 12 amu • 1 mole of 12C atoms – 12 g Molar Mass • Molar Mass (MM) – Mass of one mole of a substance – Unit is grams/mole • g/mole or g/mol – Same as molecular mass with different unit • molecular mass of water = 18.02 amu • Molar Mass of water = 18.02 g/mol – Add up masses of elements to find out • Molecular Mass – Mass in a molecule – Covalent Bonds • Formula Mass – Mass in a formula unit – Ionic Bonds • Unit is amu for both The Mole 1 Mole = 6.02 x 1023 particles • 1 mole C – 6.02 x 1023 C atoms • 1 mole H2O – 6.02 x 1023 H2O molecules • 1 mole NaCl – 6.02 x 1023 NaCl formula units – 6.02 x 1023 Na+ ions and 6.02 x 1023 Cl– ions Mole – Particle Conversions • Mole to Particle Conversions – Particle could be atom, molecule, or formula unit – Convert using Avogadro’s number – You MUST use dimensional analysis for conversions! – Watch your Exponents!!! • You will NEVER have 1046 particles 1 Mole – Mass Conversions Mass – Particle Conversions • Mole to Mass Conversions – Convert using molar mass of the substance Molar Volume • Mass to Particle Conversions – Find molar mass first – Require 2 step conversion – Mole is intermediate – in the middle Percent Composition • STP Percent Composition – Standard Temperature and Pressure – 0 °C and 1 atm of pressure • Molar Volume – All gases have the same number of molecules present in the same volume • At STP: 1 mole of a gas = 22.4 L of gas –(Element mass) x (# of atoms) Percent Composition Empirical Formula Formula for calculating % composition: Total amu of the element in the compound Total formula mass (amu) Sum of all elements should add up to 100 % – Percentage by mass of each element in a compound – Need: • Mass of compound • Mass of element in compound • Empirical Formula x 100% – Smallest whole number ratio of the atoms in compound – Ionic formulas are always empirical formulas • Molecular Formula – Actual number of each kind of atom found in one molecule of the compound – A multiple of the empirical formula 2 Empirical Formula To Calculate Empirical Formula: 1. Assume the percent is out of 100 grams (change the % to g). 2. Convert each element to moles. 3. Divide each by the smallest answer from step 2. 4. If whole numbers are not obtained in step 3, multiply everything by a factor to make the ratios whole #s. – If .5, multiply everything by 2. If .33, multiply everything by 3. – Empirical/Molecular Formula To Determine Empirical Formula from Molecular Formula: To Determine Molecular Formula from Empirical Formula: CH P4O10 – • 1. Calculate molar mass of the empirical formula 2. Divide molar mass of the Molecular Formula by molar mass of the Empirical Formula Molecular Mass Empirical Mass P2O5 BaCl2 – Percent to Mass Mass to Mole Divide by Small Multiply 'til Whole Empirical/Molecular Formula All you need to do is reduce!! • C6H6 • Empirical Formula 3. Multiply each subscript by answer from step 2 BaCl2 Hydrates • Hydrate – H2O is chemically bonded to compound – Use prefixes to indicate how many H2O are bonded to the compound • Ex: Copper (II) Sulfate Pentahydrate • CuSO4 5 H2O • Anhydrous Hydrates • Hydrate Molar Mass –Include mass of water molecules with compound MM –MM of water – 18.02 g/mol –Ex: MM of Na2CO3 10 H2O • 286.19 g/mol – No water bonded to compound 3 Hydrates • Percent Composition of Hydrates – Use Hydrate Molar Mass – Find percentage of water and anhydrous compound • Add up to 100% Hydrates • Empirical Formula of Hydrates – Same as anhydrous, but include water – Ex: A hydrate is found to contain 48.9 % MgSO4 and 51.1 % water. What is its empirical formula? • MgSO4 ∙ 7 H2O 4