* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
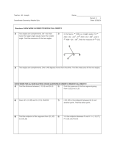
Name: __________________________________________ Date: __________ Period: _____ Geometry w/ Trig Review for Unit 2 Test: PART 2 You must know how to …. 1. Identify the hypothesis and conclusion of a conditional statement. 2. Write the converse of a conditional statement. 3. Give a counterexample of a false conditional statement. 4. Identify and apply the Symmetric Property & Transitive Property. 5. Use the Segment Addition Postulate and Angle Addition Postulate. 6. Write algebraic/geometric proofs or logical explanations. 7. Apply and know all postulates and theorems from Sections 2.1, 2.3, 2.6-2.8. 8. Apply and know all vocabulary from Chapters 1 and 2, such as complementary, perpendicular, bisect, etc. PART 1: Use the property to complete each statement. 1. Transitive Property of Congruence: If XY AB and AB MN , then ____________________. 2. Symmetric Property of Equality: If MN = QR, then ___________________. 3. Multiplication Property of Equality: If ½ AB = 11, then ___________________. 4. Segment Addition Postulate: If O is between D and G, then _________________________________. (Sketch a diagram!) PART 2: Name the property or reason that justifies each statement. Each property is used only once! 5. If mA 42 and mA mG , then mG 42 . 5. ________________________________ 6. If 2(XY) = 25, then XY = 12.5. 6. ________________________________ 7. If 2(3x – 7) = x + 5, then 6x – 14 = x + 5. 7. ________________________________ 8. If JK LM , then LM JK . 8. ________________________________ 9. If 1 2 and 2 3 , then 1 3 . 9. ________________________________ PART 3: Complete each definition or theorem. 10. If two angles form a linear pair, then ____________________________________________________________. 11. If two angles form a right angle, then ____________________________________________________________. 12. If a ray bisects an angle, then __________________________________________________________________. 13. If two angles are complementary, then ___________________________________________________________. 14. If two angles are vertical angles, then ____________________________________________________________. 15. If two segments are congruent, then ______________________________________________________________. 16. If a point is the midpoint of a segment, then _______________________________________________________. 17. If two lines are perpendicular, then ______________________________________________________________. PART 4: Use the statement below to answer the questions that follow. If 2 angles form a linear pair, then they are adjacent angles. 18. What is the hypothesis of the statement? Underline it. What is the conclusion of the statement? Circle it. 19. What is the converse of the statement? ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 20. Is the converse true or false? ________________ . If false, sketch a counterexample: PART 5: Fill in the blanks to complete the explanation that proves why x = 34 from the given information. 21. Given: mABC 100 mABD (2 x 12) Prove: x 34 From the diagram, _____________ and _____________ form a linear pair. Therefore, since the angles form a linear pair, then the angles are _______________________________________. If angles are supplementary, then their measures ___________________________________________________ , so _______________ + ________________ = __________. By the _________________________________________ Property, ___________ + ___________ = ________. 2x + 112 = 180 by ______________________________________________________________. ______________________________________________________ by the Subtraction Property. x = 34 by the ___________________________________________________________________. PART 6: In complete sentences, write a clear and logical explanation for the proofs below. 22. Given: MA HT MA 6 x 24 HT 4 x 34 Prove: MA = 54 ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ 23. Given: mSOX = (4x + 4)° m1 = (x + 14)° m2 = 107° Prove: x = 39 S W 1 2 O X ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ 23. Given: l bisects MN at P Prove: P is the midpoint of MN ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________