* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geography and History Detailed Overview with objectives
Early world maps wikipedia , lookup
History of cartography wikipedia , lookup
Cartography wikipedia , lookup
Department of Geography, University of Kentucky wikipedia , lookup
Cartographic propaganda wikipedia , lookup
Iberian cartography, 1400–1600 wikipedia , lookup
Royal Geographical Society wikipedia , lookup
Children's geographies wikipedia , lookup
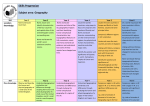
St Anne’s Catholic Primary School Geography and History Coverage Overview Year Subject Autumn Term Spring Term My Local Area ‘Incredible Me’ LK,PK,H&P- Subject Year Weather/ Seasonal Changes ‘Walk on the Wild Side’ H&P- Identify seasonal and daily weather patterns in the united kingdom and the location of hot and cold areas of the world in relation to the equator and the North and South Poles. Pupils should develop knowledge about the United Kingdom and our locality. Geography Summer Term S&F - Use simple fieldwork and observational skills to study the Geography of their school and the key human and physical features of its surrounding environment. H&P- Use basic Geographical vocabulary to refer to: key physical features including; beach, coats, forest, hill, mountain, ocean etc. S&F - Use compass directions and locational language to describe the location of features and routes on a map. Geography Seaside ‘Summer Holiday’ (Comparison to a non-European country) PK - Understand Geographical similarities and differences through studying the human and physical geography of a small area of the United Kingdom and of a contrasting non-European country. 1 1 Great Fire of London / Gateshead ‘Hot & Cold!’ George Stephenson ‘Full Steam Ahead’ Events beyond living memory that are significant nationally or globally. Wide vocabulary of everyday historical terms. The lives of significant individuals in the past who have contributed to national and international achievements. Some should be used to compare different aspects of lives in different periods. Significant historical events, people and places in their locality. They should know where people and events they study fit within a chronological framework. Wide vocabulary of everyday historical terms. The lives of significant individuals in the past who have contributed to national and international achievements. History Toys – Past & Present Events beyond living memory that are significant nationally. Changes within living memory, used to reveal aspects of changes in national life. Wide vocabulary of everyday historical terms. Understand some ways in which we find out about the past. History Geography Continents and Oceans ‘Over the Seas and far away…’ UK ‘There’s no place like home…’ LK - Name and locate the World 7 continents and 5 oceans Use world maps, atlases and globes to identify the United Kingdom and its countries, as well as the countries, continents and oceans studied at this key stage. Pupils should develop knowledge about the United Kingdom. LK - Name, locate and identify characteristics of the 4 countries and capital cities of the United Kingdom and its surrounding seas. H&P - Identify seasonal and daily weather patterns in the united kingdom. 2 Captain James Cook / Christopher Columbus / Modern Explorer ‘Famous Explorers’ History The lives of significant individuals in the past who have contributed to national and international achievements. Some should be used to compare different aspects of lives in different periods. Significant historical events, people and places in their locality. They should know where people and events they study fit within a chronological framework. Wide vocabulary of everyday historical terms. Using stories and sources so that they know and understand key features of events. ‘Wonderful World’ LK - World map – Continents & Africa Geography 3 Locate the world’s continents using maps to focus on Africa, concentrating on their environmental regions, key physical & human characteristics (including coasts), countries & major cities. H&P – Types of settlement & land use UK and Abroad ‘Home and Away’ H&P- Use basic Geographical vocabulary to refer to: key human features including city, town, village, island, farm, house, office, shop etc. Geography S&F - Use aerial photographs and plan perspectives to recognize landmarks and basic physical features; devise a simple map and use and construct basic symbols in a key. Travel ‘Planes, Trains & Automobiles’ Seaside – Past & Present ‘Oh I do Like to be beside the seaside’ How holidays and travel has changed over the years. Some should be used to compare different aspects of lives in different periods. Similarities and differences between ways and lives of different periods. Wide vocabulary of everyday historical terms. Understand some ways in which we find out about the past. Similarities and differences between ways and lives of different periods. Wide vocabulary of everyday historical terms. Understand some ways in which we find out about the past. 2 History ‘Volcanoes & Earthquakes’ LK – Revisit Countries & Oceans Revise countries & oceans through looking at where volcanoes & earthquakes take place. PK – Volcanoes in the news Locate the world’s countries using maps to focus on Europe & N&S America, concentrating on their environmental regions, key physical & human characteristics (including coasts), countries & major cities. ‘Local Settlements’ H&P – Types of settlement & land use Ongoing with History Topic Geography 3 H&P – Volcanoes & Earthquakes Describe and understand key aspects of physical geography e.g. volcanoes & Earthquakes. History ‘The Stone Age’ Stone Age to the Iron Age ‘The Ancient Egyptians’ The achievements of the earliest civilisations – an overview of where and when the first Anglo-Saxons / Northern Saints ‘Settlements & Saints’ Britain’s settlements by Anglo Saxons and History Changes in Britain from the Stone age to the Iron Age. Late Neolithic hunter gathers, Bronze age religion, technology and travel e.g. Stonehenge, Iron age hill forts. civilisations appeared and an in depth study of one of the following: Ancient Egypt Scots. (Before Alfred the Great and the creation of the Kingdom of England) Northern Saints significant to local area and school. ‘Living in the UK’ LK - UK map – Name & locate counties/cities Name and locate countries and cities of the United Kingdom, geographical regions and their identifying human and physical characteristics including hills, mountains, cities, rivers and land use patterns and understand how some of these have changed over time. ‘Europe’ LK – Map of Europe – Northern Europe Geography Locate the world’s countries using maps to focus on Northern Europe concentrating on countries and major cities. ‘World Biomes’ H&P - Biomes Describe and understand key aspects of physical geography e.g. biomes. Geography H&P – Settlement, land use, economic Describe & understand key aspects of economic activity including trade links, the distribution of natural resources including energy, food, minerals & water. Use field work to observe, measure and record the human and physical features in the local area using a range of methods, including sketch maps, plans and graphs and digital technologies 4/5 A Anglo-Saxons & the Vikings ‘Vicious Vikings and Savage Saxons’ History 4/5 B PK – Area in UK to study Understand geographical similarities and differences through the study of human and physical geography of a region of the UK. Geography The Viking and Anglo Saxon Struggle for the Kingdom of England to the time of Edward the Confessor. (After Alfred the Great and the creation of the Kingdom of England) LK –Equator & tropics Locate the world’s countries using maps to focus on N & S America. Understand geographical similarities and differences through the study of human and physical geography of a region of the UK and a region within N or S America. PK – South American Rainforest Use maps, atlases, globes, digital computer mapping to locate countries and describe features. Identify and position the significance of 4 Benin/Mayan Civilisation A non-European society that provides contrast with British History – One study chosen from: Early Islamic civilisation, including a study of Baghdad; Mayan civilisation Benin (West Africa). History ‘Europe’ LK – Map of Europe – Countries Locate the world’s countries using maps to focus on Europe concentrating on their environmental regions, key physical and human characteristics, countries and major cities. PK – Area in Europe to study Understand geographical similarities and differences through the study of human and physical geography of a region of Europe. H&P – Water cycle Geography 5 latitude, longitude, equator, Northern hemisphere, Southern hemisphere, the tropics of cancer and Capricorn, the prime Greenwich meridian and time zones. Describe and understand key aspects of physical geography e.g. the water cycle. H&P Climate zones, biomes, vegetation belts Understand geographical similarities and differences through the study of human and physical geography of a region of the N or S America. Describe and understand key aspects of physical geography e.g. climate zones, biomes, vegetation belts. Extended chronological study History Geography ‘The Battle of Britain’ A study of an aspect or theme in British history that extends pupils’ chronological knowledge beyond 1066: The Battle of Britain ‘Rivers’ LK - World map PK – Compare Tyne, Amazon, Nile H&P – Rivers Describe and understand key aspects of physical geography e.g. rivers Ancient Greece ‘Groovy Greeks’ Ancient Greece – A study of Greek life and achievements and their influence on the Western World. ‘Mountains’ LK - World map locate main mountains PK –Kathmandu, Alps, Ben Nevis H&P – Mountains Describe and understand key aspects of physical geography e.g. mountains. 6 History Local History Study over time: Local Innovations (Stephenson/Swan/Parsons/Armstrong) ‘It’s Great Up North!’ A local History study. A study of an aspect of History or a site dating from a period beyond 1066 that is significant in the locality. Romans ‘The Rotten Romans’ Roman Empire impact on Britain History LK – Name & location of counties & cities in UK linked to History Name & locate counties & cities of the United Kingdom, geographical regions and their Identifying human & physical characteristics, key topographical features and land-use patterns and understand how some of these aspects have changed over time. Local History Industrial Revolution ‘Everything’s Changing’ A study of an aspect or theme in British History that extends pupils chronological knowledge beyond 1066. Geography 6 History Geography LK – Locational knowledge PK – Place knowledge H&P – Human and physical geography S&F – Geographical skills and fieldwork Collective Fieldwork objectives KS1 – These should be covered progressively in every topic/year group through field work and map skills work. use world maps, atlases and globes to identify the United Kingdom and its countries, as well as the countries, continents and oceans studied at this key stage use simple compass directions (North, South, East and West) and locational and directional language [for example, near and far; left and right], to describe the location of features and routes on a map Collective Fieldwork objectives KS2 – These should be covered progressively in every topic/year group through field work and map skills work. use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied use the eight points of a compass, four and six-figure grid references, symbols and key (including the use of Ordnance Survey maps) to build their knowledge of the United Kingdom and the wider world use fieldwork to observe, measure, record and present the human and physical features in the local area using a range of methods, including sketch maps, plans and graphs, and digital technologies. History - Aims Key stage 1&2 The national curriculum for history aims to ensure that all pupils: know and understand the history of these islands as a coherent, chronological narrative, from the earliest times to the present day: how people’s lives have shaped this nation and how Britain has influenced and been influenced by the wider world know and understand significant aspects of the history of the wider world: the nature of ancient civilisations; the expansion and dissolution of empires; characteristic features of past non-European societies; achievements and follies of mankind gain and deploy a historically grounded understanding of abstract terms such as ‘empire’, ‘civilisation’, ‘parliament’ and ‘peasantry’ understand historical concepts such as continuity and change, cause and consequence, similarity, difference and significance, and use them to make connections, draw contrasts, analyse trends, frame historically-valid questions and create their own structured accounts, including written narratives and analyses understand the methods of historical enquiry, including how evidence is used rigorously to make historical claims, and discern how and why contrasting arguments and interpretations of the past have been constructed gain historical perspective by placing their growing knowledge into different contexts, understanding the connections between local, regional, national and international history; between cultural, economic, military, political, religious and social history; and between short- and longterm timescales. Key Stage 2 Subject content Pupils should continue to develop a chronologically secure knowledge and understanding of British, local and world history, establishing clear narratives within and across the periods they study. They should note connections, contrasts and trends over time and develop the appropriate use of historical terms. They should regularly address and sometimes devise historically valid questions about change, cause, similarity and difference, and significance. They should construct informed responses that involve thoughtful selection and organisation of relevant historical information. They should understand how our knowledge of the past is constructed from a range of sources.