* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt slides
Oracle Database wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft SQL Server wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
ContactPoint wikipedia , lookup
Versant Object Database wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
Keyword Searching and Browsing in
Databases using BANKS
Gaurav Bhalotia
Arvind Hulgeri
Soumen Chakrabarti
Charuta Nakhe
S. Sudarshan
18th International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE'02), 2002
Kushal Bansal
1
Outline
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Introduction
Database and Query Model
Searching for the Best Answers
Interface and Templates of BANK System
Experiment and Performance
Conclusion
2
Introduction
Web Search engines make use of unstructured queries
Users have to type in keywords and follow hyperlinks
Relational databases use structured query languages like
SQL
Users need to know the schema of the database
Difficult for naïve users
For data stored in databases, keyword based techniques is not
much useful
Data often splits across the tables due to normalization
3
Introduction
BANKS (Browsing And Keyword Searching)
It is a system which provides search engine type
interface to search and browse relational databases.
Allows interaction with controls on the displayed
results.
No query language or programming required.
4
Outline
Introduction
2. Database and Query Model
1.
Informal Model
b) Formal Model
c) Query and Answer Model
a)
3. Searching for the Best Answers
4. Interface and Templates of BANK System
5. Experiment and Performance
6. Conclusion
5
Database and Query Model
Informal Model
1. Each database is modeled as a directed graph
2. Each tuple in the database is modeled as a node in
the graph.
3. Every Primary – Foreign key relation is modeled as a
directed edge.
6
Database and Query Model
Informal Model
4. An answer to a query is a subgraph connecting nodes
matching the keywords.
5. The importance of a link depends upon the relations
it connects and on its semantics
7
Database and Query Model
The Schema
8
Database and Query Model
Fragment of the Database
9
Database and Query Model
Formal Database Model
Node Weight
• Each node u in the graph is assigned a weight N(u)
• Node weight is also known as the node prestige
• N (u) = Indegree of the node
Node score N = Root node weight + Sum of leaf node
weights
10
Database and Query Model
Formal Database Model
Edge Weights
Weight of the directed edge (u,v) given by
a)
(u,v) exists but (v,u) does not = s (R(u), R(v))
b)
(v,u) exists but (u,v) does not = IN(u) s (R(v),R(u))
c)
If both exists = min [ s(R(u),R(v)), IN(u) s (R(v),R(u)) ]
11
Database and Query Model
Formal Database Model
Edge Weights
Escore(e) of an edge = w(e)/w min
Escore overall = 1/ (1 + ∑ Escore(e))
Escore overall is in the range [0,1]
12
Database and Query Model
Formal Database Model
Overall relevance score
= Node weights + Edge Weight
Using weighting factor
Additive: (1- ) E + N
multiplicative: E * N
13
Database and Query Model
Query and Answer Model
Query
Query consists of search terms t1 ,t2, ……tn
For each term ti we find set of nodes Si that are relevant to ti
S = {S1,S2,…Sn}
Answer Model
An answer to a query is a rooted directed tree connecting
keyword nodes
Relevance score of an answer tree
Relevance scores of it nodes and its edge weight
14
Database and Query Model
Result of query “soumen and sunita”
15
Outline
Introduction
Database and Query Model
Searching for the best answers
Backward expanding search algorithm
Interface and Templates of BANKS
Experiment and Performance
Conclusion
16
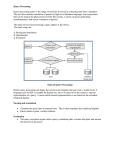
Searching for the Best Answer
Backward expanding search algorithm
Assumes that the graph of the database fits in memory
Starts at leaf nodes each containing a query keyword
Run concurrent single source shortest path algorithm from
each such node
Traverses the graph edges in reverse direction
Common vertex along the backward paths identify answer tree
roots
Tree formed is a connection tree and root of tree is
information node.
17
Outline
Introduction
Database and Query Model
Searching for the best answers
Interface and Templates of BANKS
Experiment and Performance
Conclusion
18
Interface
BANKS system provides
A rich interface to browse data stored in a relational
database
Schema browsing and data browsing
Hyperlink to the referenced tuple
Columns can be projected away (dropped)
Selections can be imposed on any column
Tuples can be sorted by a specified column
19
Templates
BANKS system provides several predefined templates
Cross – tabs
Group by
Folder Views
Graphical Interface for display in bar, line or pie chart
20
Outline
Introduction
Database and Query Model
Searching for the best answers
Interface and Templates of BANKS
Experiment and Performance
Conclusion
21
Experiment and Performance
Computed absolute value of the rank difference of the
ideal answer and answer for each parameter setting.
Sum of the rank differences gives the raw Error score
Setting = 0.2 with log scaling of edge weights did
best, with an error score of 0.0
22
Error scores vs. parameter choices
23
Outline
Introduction
Database and Query Model
Searching for the best answers
Interface and Templates of BANKS
Experiment and Performance
Conclusion
24
Conclusion
BANKS system
Provides an integrated browsing and keyword querying
system for relational databases
Allows users with no knowledge of database systems or
schema to query and browse relational database with
ease
Reduces the effort involved in publishing relational data
on the web and makes it searchable.
25