* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ancient Egypt - Mr. Ellers 6th Grade Social Studies Website
Joseph's Granaries wikipedia , lookup
Thebes, Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Rosetta Stone wikipedia , lookup
Index of Egypt-related articles wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Prehistoric Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Egyptian pyramid construction techniques wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian literature wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian race controversy wikipedia , lookup
Middle Kingdom of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Egyptian hieroglyphs wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian medicine wikipedia , lookup
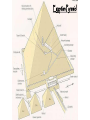
Ancient Egypt Part 2 The Old Kingdom (2700 BCE to 2200 BCE) • People saw their kings as gods • Called a theocracy = same person is the political AND religious leader • King gave many responsibilities to a bureaucracy = groups of government officials • King controlled trade & taxes • King supervised building of canals, dams, grain storehouses The Old Kingdom (2700 BCE to 2200 BCE) • Egyptians built pyramids as burial places for their kings • Great Pyramids in Giza • King’s bodies were mummified for preservation Pyramids The Great Pyramid ∆ The Pyramids were considered "Houses of Eternity“. ∆ Tallest human-made structure until the Eiffel Tower in the 1800's ∆ Took approximately 23 years to build ∆ All pyramids had to have a North-facing entrance, to align with the North Star. ∆ Built by farmers and other laborers during the Inundation (flood season) ∆ Most stones weigh 2.5 tons, but some weigh up to 80 tons ∆ Laborers used mud-slicked ramps to move the stones. Egyptian Pyramid The Great Pyramid Contributions of Egypt • Language: Hieroglyphics • Architecture: Pyramids • Inventions: 365 day calendar, papyrus (paper), irrigation system, mathematics, medicine, weapons, chariots, • Art: statues, paintings, jewelry A System of Writing • The Ancient Egyptians had no separate word for “art”, their word for “art” was the word for “writing”. • This Egyptian “alphabet” was made up of about 800 picturesymbols called HIEROGLYPHS. • The word HEIROGLYPHICS means “sacred writing” Other Symbols of Egypt King Tut Queen Hatputshut amulets Scarab Beetle Eye of Horus The Sphinx Cartouche A System of Writing • The Egyptians considered HIEROGLYPHS sacred and believed that they conveyed the words of the gods. • HIEROGLYPHICS also helped to preserve the memory of deceased people. • In order to keep track of government records, taxes, and the passage of time, the Egyptians developed a system of writing called HIEROGLYPHICS. A System of Writing PAPYRUS: • The earliest form of paper • Made from the papyrus reed that grew in the Nile • The reeds would be criss-crossed and pounded down to a paper-like thickness. A System of Writing Not all Egyptians could read or write hieroglyphics: SCRIBES: ∆ Pharaoh’s record keepers ∆ Very Educated in reading, writing & math ∆ Highly respected ∆ Only boys could become SCRIBES ∆ A SCRIBE’S training started at the age of 10 ∆ SCRIBES used rolls of PAPYRUS to write on Only the SCRIBES used HIEROGLYPHICS. A System of Writing • The Common people of Egypt used a form of writing called “hieratic”, a form of script writing. • Eventually, the responsibility of reading & interpreting the HIEROGLYPHS fell to the priests. Even SCRIBES lost the ability to read the ancient symbols. • By 400 AD, no one could read the HIEROGLYPHS anymore. The Rosetta Stone • The Rosetta Stone was the key that unlocked the mysteries of Egyptian hieroglyphics. • Napoleon's troops discovered it in 1799 • The inscription is written on the stone three times, once in hieroglyphic, once in hieratic, and once in Greek. • Jean Francois Champollion, a French Egyptologist, deciphered the hieroglyphic and hieratic texts by comparing them with the known Greek text. • From this meager starting point, a generation of Egyptologists eventually managed to read most everything that remains of the Egyptians' ancient writings. Return The End of the Old Kingdom • The economy began to be strained by huge government building projects. • People became unhappy with the pharaoh's demands for taxes to pay for these projects. • Pharaoh Pepy III ruled for 92 years, he eventually lost control over the central government - local governors took over. • This period without any pharaohs lasted about 150 years - there were foreign invasions and disorder during this time. The Middle Kingdom (2050 BCE to 1800 BCE) • Old Kingdom ended with violence & a new dynasty reunited Egypt • Capital moved to Thebes • Theben kings = seized new territory & added thousands of acres to their civilization • Built canals and irrigation systems The Middle Kingdom (2050 BCE to 1800 BCE) • Local leaders began to challenge the kings’ power, which threatened peace • At same time = 1st real threat to Egypt = invasion by Hyksos (people from western Asia) • Hyksos swept through with new tools for war --> bronze weapons & horse-drawn chariots • Easily conquered the Egyptians & set up a new dynasty (for about 110 years) The Middle Kingdom 2100BC - 1700BC • Order was restored by Mentohotep: • strong military leader • restored unity to Egypt • moved the capital to Thebes • took control of Nubia • Nubian gold brought increased prosperity (economy improved) The Middle Kingdom 2100BC - 1700BC • Egypt's contact with other parts of the world increased, bringing foreign goods and foreign ideas to the Egyptian civilization. • Egyptian trade increased with Western Asia, creating a new wealthy class of "common people" Middle Class • Outside groups began moving into Egypt - Hyksos REVIEW