* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download database management system
Business intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Data vault modeling wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Versant Object Database wikipedia , lookup
Relational algebra wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
Operational transformation wikipedia , lookup
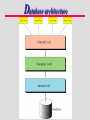
14. Databases 14.1 DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM DBMS components A database is a collection of data that is logically, but not necessarily physically, coherent. A database management system (DBMS) defines, creates, and maintains a database and allows controlled access to users. 14.2 ARCHITECTURE Database architecture Database architecture DBMS users can be humans or application programs. A DBMS has three levels: internal, conceptual, and external. The internal level of a DBMS interacts directly with the hardware and is concerned with low-level access methods and byte transfer to and from the storage device. The conceptual level of a DBMS defines the logical view of the data as well as the data model and schema diagrams. The external level of a DBMS interacts directly with the user. 14.3 DATABASE MODELS Database models A database model defines the logical design of data The model also describes the relationships between different parts of data. Three models: Hierarchical model Network model Relational model Hierarchical model Data are organized as an upside down tree Each entity has only one parent but can have several children. Network model The entities are organized in a graph, where some entities can be accessed through several path. 14.4 RELATIONAL MODEL Relational model Data are organized in two-dimensional tables called relations. The relational database management system (RDBMS) is the only database model in wide use today. The hierarchical and network models are obsolete. Each column in a relation is called an attribute. The number of attributes in a relation is its degree. Each row in a relation is called a tuple. The number of rows in a relation is its cardinality. Relational model Relation 14.5 OPERATIONS ON RELATIONS Insert operation None operations can be performed on relations. An operation that operates on one relation is a unary operator. Unary operators include the insert, delete, update, select, and project operations. Delete operation Update operation Select operation Project operation Join operation An operation that operates on two relation is a binary operator. binary operators include the join, union, intersection, and difference operations. Union operation Intersection operation Difference operation 14.6 STRUCTURED QUERY LANGUAGE SQL The Structured Query Language (SQL) is the language standardized by ANSI and ISO for use on relational databases. For example: Fig 14.10 select * 整個tuple都抓出來 from COURSES where Unit = 5 SQL- cont’s For example: select Name from where CourseCOURSES Unit = 5