* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download - Pcpolytechnic
Stage monitor system wikipedia , lookup
Studio monitor wikipedia , lookup
Electronic paper wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope types wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Stereo display wikipedia , lookup
Surface-conduction electron-emitter display wikipedia , lookup
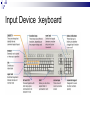
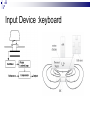
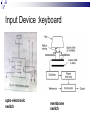
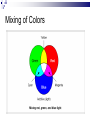
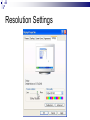
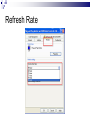
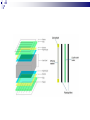
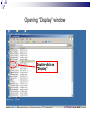
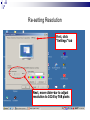
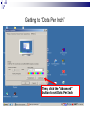
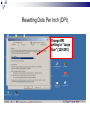
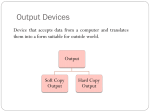
Input & Output devices Input Device :keyboard a keyboard is an input device, partially modeled after the typewriter keyboard, which uses an arrangement of buttons or keys, to act as mechanical levers or electronic switches. A keyboard is also used to give commands to the operating system of a computer. Connectors to keyboard AT(DIN-5) PS2 andUSB. XT with 83 keys,At with 84 keys, 104 keys by adding window keys. Keys includes: Typing keys numeric keypad,function keys,control keys Virtual Laser Keyboard(sensor,Signalsto computer) Input Device :keyboard Components of Keyboard Keyboard switches Keyboard processor or circuitry Key matrix Types of keySwitches Capacitive switch Hall effect switch Opto electronic switch Membrane switch Mechnical switch Input Device :keyboard Key matrix: keyboard matrix is the arrangement of circuit connections between the keyboard controller and all the keys. Key switch: The main component of any keyboard is the key switch. These switches generate typical codes of signal when they are depressed and it is used for interfacing with computer system Input Device :keyboard Input Device :keyboard Input Device :keyboard Key matrix: keyboard matrix is the arrangement of circuit connections between the keyboard controller and all the keys. each key is placed at the intersection of a matrix row and a matrix column. The keyboard repeatedly applies current to each column in turn, and checks to see which rows output current. From this, the keyboard can deduce which keys in that column have been depressed. Input Device :keyboard Capcitive switch:two plates of the capacitor are brought closer when the key is pressed. Change in capacitance of switch changes and change in capacitance is detected in terms of voltage. Basedon the switch open/close voltage is recived thisvoltage is converted into proper signals to inform CPU. Lifespan 20 millonkey strokes. Hall effect switch: magnetic field is applied to any device the resistance of device will be increases or decresed(current starts flowing) This allow current flow Lifespan 100 million keystrokes Input Device :keyboard Input Device :keyboard opto-electronic switch: have LED light generate light when electric power is applied.uses photo- transistor which allow current to flow in the circuit. When key is pressed not pressed the light from LED falls onto photo-transistor When key is pressed the value will be produced at the ouput Vout membrane switch:it is multi layered plastic or rubberuses the row and colum conductor sheets. Mechanical switch: it uses two metal pieces or contacts . Rubber dome:madeup of polyester domes Refered as direct switches. Input Device :keyboard opto-electronic switch membrane switch Input Device :keyboard Mechanical switch Keyboard Interfaces Connects to PC – KEYBOARD – KEYBOARD CONNECTOR Inside keyboard a processor and circuit which carry information to or from that processor. Keyboard controller is single chip contains memory RAM, processor ROM(control operations of keyboard) Key matrix: row and columns made up wires and each key act like switch Key matrix is grid of circuits when key is pressed the row wire makes contact with colmn wire and completes the circuit . KM passes current to keyboard controller . Keyboard controller will detects the closed circuit and registers the key press and controller read the key pressed. Keyboard Interfaces KEYBOARD CONNECTOR Interface between keyboard and pc – AT keyboard connector(DIN5) – PS2 keyboard connector or(MIN-DIN6) – USB connector AT keyboard connector(DIN5) – Uses 5 pins: KBDCLK(provide clock pulse), KBDAT(send/recive data),KBRST (reset keyboardinternal buffer),GND(ground),VCC(+5v provides power to keyboard) PS2 keyboard connector or(MIN-DIN6): With 6 pins USB keyboard connector: USB keyboard connector : uses 4 pins VDC(+5V),DATAcarries -ve data signal,DATA+it carries +ve data Signal, Keyboard working:key is pressed it pushes down the rubber dome Dome tuches a pair of conductive lines on circuit Allow current flow Mouse: Mechanical Mouse : Mechanical Mouse uses ball for the movement of cursor on thecomputer screen. When the ball is rolled in any direction, a sensor of the mouse detects it and also moves the mouse pointer in the same direction. Optical Mouse : Optical Mouse uses Laser rays for the movement of cursor on the computer screen. It is an advanced pointing device. Movement is detected by sensing changes in the reflected light rather than the motion of a rolling sphere. Cord-Less Mouse : Cord-Less Mouse is battery driven and does not need any wire for the physical connection with the motherboard. It transmits data through infrared or radio signal. Mechanical mouse Mouse types 1.Mechanical mouse: a rubber ball rolls as the mouse is moved across table top or mouse pad. The wheels are referred as encoders have tiny metal contact points on rims Location of mouse is identified by how many times the contact points have touched the bars. mouse moved across flat surface. As balls rotate it touches and turns two rollers inside the mouse Two rollers are used for vertical and horizontal movements of cursor 19 Mouse types Each roller attached to encoder. Each time a contact bar touches a point an electrical signal. Signals generated are sent to PC over the mouse cables And number of mouse time mouse button is clicked. 2. Optical-mechanical mouse: When mouse moves the ball of mouse moves and two separate rollers fixed at 90 degree to each other one roller is for vertical and horizontal movement of cursor. Each roller connected to wheel these rollers are rotated by movement of rollers. Wheel rotate pair of LED and photo detectors Signals sent to PC through mouse connectors 20 Mouse types Optical mouse: LED produces a red light that is emitted onto surface the light reflected back to CMOS sensor then to DSP(digital signal processor) for analysis DSP analysis the signal and and patterns and determines mouse movements. Along with coordinates are received by computer and will show mouse movement on screen. Monochrome Monitor Monochrome Monitors Monochrome Monitors Video processing unit: contains video signals from display adopter card to video Amplifier Circuit. Video signal controls brightness of beam only two levels to set brightness ON and OFF. Vertical Sync Processing: Grayscale Monitors A special type of monochrome monitor capable of displaying different shades of gray. They are also known as black-and-white, are composed exclusively of shades of gray, varying from black at the weakest intensity to white at the strongest. Early grayscale monitors can only show up to sixteen different shades Grayscale Monitor Color Monitors A display monitor capable of displaying many colors. Color Monitors works like a monochrome one, except that there are three electron beams instead of one. The three guns represent additive colors (red, green and blue) although the beam they emit are colorless. Each pixel includes three phosphors, red, green and blue, arranged in a triangle. When the beam of each of these guns are combined and focused on a pixel, the phosphors light up. Color Monitors The monitors can display different colors by combining various intensities of three beams. Mixing of Colors What is being used today? The most popular display today remains Color monitors CRT. It has been available for more than 70 years. CRT is used. Cost less than LCD monitors. History of the Cathode Ray 1855- Heinrich Geissler creates the mercury pump, the first good vacuum tubes. Sir William Crookes uses these to produce the first cathode rays. 1858- Julius Plücker bends cathode rays using a magnet 1869- J.W. Hittorf establishes that the “rays” travel in straight lines 1883- Heinrich Hertz concludes incorrectly that cathode rays are not made up of particles because they are not deflected by electrically charged metal plates 1895- Jean-Baptiste Perrin shows that cathode rays are particles because they deposit a negative charge where they impact 1897- J.J. Thomson discovers electrons using cathode rays How Monitor Works? Most use a cathode-ray tube as a display device. CRT: Glass tube that is narrow at one end and opens to a flat screen at the other end. How Monitor Works? Electrons travel through a vacuum sealed container from the cathode (negative) to the anode (positive). Because the electrons are negatively charged, they are repelled away from the cathode, and move across the tube to the anode. The ray can be affected by a magnet because of its relation to positive and negative charges Some Anatomy of the CRT Anode- Positively Charged, Ray travels towards this Cathode- Negatively Charged, Ray travels away from this Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) Monitors A CRT monitor contains millions of tiny red, green, and blue phosphor dots that glow when struck by an electron beam. Electron beam travels across the screen to create a visible image. In a CRT monitor tube, the cathode is a heated filament. The heated filament is in a vacuum created inside a glass tube. The electrons are negative and the screen gives a positive charge so the screen glows. Basic Cathode Ray Tube Electrons excite phosphor to glow Electrons fired from the back Phosphor is arranged in dots called pixels Dot mask ensures proper pixel is lit Phosphore It is a semi-conducteur material which emits visible radiation in response to the impact of electrons. (i.e. when it absorbs energy from some source such as an electron beam, it releases a portion of this energy in the form of light). In response to a sudden change in the electron beam(from on to off), the light emission does not fall instantaneously, there is a gradual reduction challed ‘fluorescence’ . Scanning Pattern of CRT Electron Gun The electron gun scans from left to right and From top to bottom. Refreshing every phosphor dot in a zig-zag pattern. Advantages of CRT The cathode rayed tube can easily increase the monitor’s brightness by reflecting the light. They produce more colours The Cathode Ray Tube monitors have lower price rate than the LCD display or Plasma display. The quality of the image displayed on a Cathode Ray Tube is superior to the LCD and Plasma monitors. The contrast features of the cathode ray tube monitor are considered highly excellent. Disadvantages of CRT They have a big back and take up space on desk. The electromagnetic fields emitted by CRT monitors constitute a health hazard to the functioning of living cells. CRTs emit a small amount of X-ray band radiation which can result in a health hazard. Constant refreshing of CRT monitors can result in headache. CRTs operate at very high voltage which can overheat system or result in an implosion Within a CRT a strong vacuum exists in it and can also result in a implosion They are heavy to pick up and carry around CRT Monitor Liquid Crystal Display - Monitor It is a flat panel display, electronic visual display, or video display that uses the light modulating properties of liquid crystals (LCs). LCs do not emit light directly . LCD History Liquid crystals were first discovered in 1888 by Austrian botanist Friedrich Reinitzer. RCA, an American Laboratory made the first experimental LCD in (1968). Manufacturers have been developing creative variations and improvements since on LCDs. In 1997, manufactures began to offer full size LCD monitors as alternatives to CRT monitors. Until recently, was only used on notebook computers and other portable devices. LCD Technology Used for displays in notebooks, small computers, pagers, phones and other instruments. Uses a combination of fluorescent-based backlight, color filters, transistors, and liquid crystal to create and illuminate images. Until recently, was only used on notebook computers and other portable devices. From CRT to LCD CRT Bulky, heavy, use vacuum tube technology. Using technology that was developed in the 19th century. LCD First LCD laptop monitors were very small due to manufacturing costs but now are available in a variety of sizes. Light, sleek, energy-efficient, have sharp picture. Liquid Crystal Display There are mainly two categories of LCD. The passive matrix LCD The Active matrix LCD Passive Matrix LCD Monochrome passive-matrix LCDs were standard in most early laptops. Still being used today for applications less demanding than laptops and TVs. It consisting of a grid of horizontal and vertical wires. At the intersection of each grid is an LCD element which constitutes a single pixel, either letting light through or blocking it. Passive matrix LCD Pixels arranged in a grid Pixels are activated indirectly Row and column are activated Animation can be blurry Passive Matrix Display Active Matrix LCD Active-matrix LCDs depend on thin film transistors (TFT). TFTs are tiny switching transistors and capacitors. They are arranged in a matrix on a glass substrate. Each pixel is activated directly Pixels have 4 transistors One each for red, green, blue One for opaqueness Animation is crisp and clean TFT LCD Screen Advantages of LCD The sharpness of a LCD display is at maximum tweak ness. High peak intensity produces very bright images. Best for brightly lit environments. Screens are perfectly flat. Thin, with a small footprint. Consume little electricity and produce little heat The LCD display unit is very light and can be put anywhere or moved anywhere in the house. Lack of flicker and low glare reduce eyestrain. Disadvantages of LCD After a while the LCD display the some of the pixels will die you will see a discoloured spot on a black spot on the display. The cost of a LCD is considerably at a high price. The LCD display will have slow response times. The LCD display has a fixed resolution display and cannot be changed. The viewing angle of a LCD display is very limited. Other types of Monitors Paper-white displays High contrast between fore and background Electro-luminescent displays (ELD) Similar to LCD Uses phosphor to produce light Plasma monitor Gas is excited to produce light Paper White Display NASA -Electroluminescent displays Plasma Monitors Monitor Specifications Monitor Specifications can be judged through, Size Resolution Refresh rate Dot pitch Size A monitor’s size affect how well we can see images. With a larger monitor, we can make the objects on the screen appear bigger. Monitors are measured diagonally, in inches, across the front of the screen. A 17 inch monitor measures 17 inches from the lower left to the upper right corner. CRT monitors viewing area is smaller than the monitor’s overall size. Resolution The images you see on your monitor are made of tiny dots called pixels. The term resolution refers to the sharpness and clarity of an image. A monitor resolution is determined by the number of pixels on the screen. It is expressed as a Matrix. The more pixels a monitor displays, higher will be its resolution. Clearer will be images appear. For example 640 X 480 resolution means that there are 640 pixels horizontally across the screen and 480 pixels vertically down the screen. Resolution Actual resolution is determined by the video controller. Most monitors can operate at several different resolutions. They are 640 X 480 800 X 600 1024 X 768 1152 X 864 1280 X 1024 As the resolution increases, image on the screen gets smaller. Resolution Settings Standards There are various standards for monitor resolution. Video Graphics Array standard is 640 X 480 pixels. Super VGA is 800 x 600 and 1024 x 768. Today, nearly all color monitors can be set to higher resolution. Refresh Rate Monitor refresh rate is the number of times per second that the electron guns scan every pixel on the screen. Refresh rate is important because phosphor dots fade quickly after the electron gun charges them with electrons. If the screen is not refreshed, it will appear to flicker. Refresh rate is measured in Hz or Cycles per second. If the monitor refresh rate is 100 Hz, it means that it refreshes its pixels 100 times every second. Refresh Rate Dot Pitch It is the distance between the same color dots Ranges between .15 mm and .40 mm Smaller creates a finer picture Should be less than .22 Dot Pitch Touch screen technologies It is visual display that can detect the presence and location of touch with in the display area Touch screen senses the passive object,finger,etc.. Components of touch screen – Touch sensor – Controller – Software driver Touch sensor: Touch screen detects the location of touches with in display area. It is touch sensor panel with a touch responsive surface over display Sensor have electric current or signal which produces voltage or signal to determine touch to screen. Touch screen technologies Controller: It is printed circuit board connects sensor and display, it carries information from touch screen and translates to computer. Software Driver: a program which allows communication between OS and controller . Different TS Technologies – – – – Resistive capacitive Surface acoustic wave Infrared Resistive Touch screen technology Flexible top layer polyethylene bottom layer of glass both layers are coated with Indium Tin Oxide(ITO)Electric current flows between the two layers. Change in electrical signal detected and coordinates are calculated by controller and parsed into readable signals to the OS. capacitive Touch screen technology Most durable and coated with capacitive material (ITO) Transmit 90% of light from monitor. Surface CTS technology – Large panels – Transparent electrode film is placed above glass – Voltage is applied to electrodes placed at four corners – Generate low uniform voltage – Simple structure , low cost. – No multi-sense. CTS technology Projective CTS technology – Small touch panels – It includes IC chips over which layer of numerous transparent electrodes are placed SAW technology Surface acoustic wave panels achieve bright touch panels with high levels of visibility which refereed as surface wave Two transducers Waves passes through glass and reflected back to sensors. When it senses touch these waves are absorbed and touch is sensed – High surface durability – Best optical quality Infrared/optical imaging technology Based on infrared image sensors infrared LED on top of panel and image sensor. When touch sensed by image sensor image is captured . The image shadow formed by infrared light hjgh Plasma display gas discharge display Three cells make up one pixel (one cell has red phosphor, one green, one blue). cells are sandwiched between x- and y-axis panels, and a cell is selected by charging the appropriate x and y electrodes. Plasma Pixels Each pixel is made up of three cells full of ionized gas that are lined with red, green and blue phosphors. When charged, the gas emits ultraviolet light that causes the phosphors to emit their colors. Plasma display gas discharge display Plasma display Inside a Plasma unit sit hundreds and thousands of tiny pixels which are cells filled with a mixture of neon and xenon gases These cells are sandwiched between two glass panels running parallel to each other. A single pixel is made up of three colored sub-pixels, one sub pixel has a red light phosphor, one has a green light phosphor and the third has a blue light phosphor. A plasma screen works by controlling each individual phosphor. Visual Display Devices Video Cards Interface between computer and a display device. Unless a computer has graphics capability built into the motherboard, the video card is required. The CPU, working in conjunction with software applications, sends information about the image to the video card. The video card decides how to use the pixels on the screen to create the image. It then sends that information to the monitor through output interface. Parts of Video Card How Video card works? The CPU, working in conjunction with software applications, sends information about the image to the graphics card. The graphics card decides how to use the pixels on the screen to create the image. It then sends that information to the monitor through a cable. It is capable of rendering 3D images. Video Card - GPU Similar to CPU but designed specifically to perform complex mathematical and geometric calculations necessary for graphics rendering. Less congestion on the system bus Reduction in the workload of CPU Graphics GPU Video Card - GPU Operations: bitmap transfers, painting, window resizing and repositioning, line drawing, font scaling and polygon drawing etc. Some GPUs have image enhancement algorithms built-in. Video Card - GPU Some of the latest GPUs have more transistors than average CPU and produce a lot of heat. Heat-sinking and fan cooling are required Video Card - Memory When a video card is connected within the motherboard, it will use the computers random access memory (RAM). If it is not connected to the motherboard though, the video card often has its own memory known as Video RAM (VRAM). The capacity of VRAM in modern video cards ranges from 125 to almost 800 MB. Video Card Memory In 2006, DDR technology was the base of the VRAM. The clock rate of the memory was between 300 MHz and 1.7 GHz. The Z-buffer is an important part of the video memory. It takes care of the depth coordinates in 3D graphics Modern cards have up to 512 MB RAM Changing your computer’s display settings Click Start button Then, click here to open the Control Panel Opening “Display” window Double-click on “Display” Re-setting Resolution First, click “Settings” tab Next, move slider-bar to adjust resolution to 1024 by 768 pixels Getting to “Dots Per Inch” Then, click the “Advanced” button to set Dots Per Inch Resetting Dots Per Inch (DPI) Change DPI setting to “Large Size” (120 DPI)