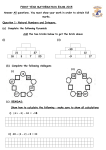
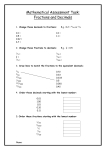
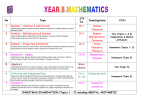
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download curriculum objectives
Group action wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
CURRICULUM OBJECTIVES
PROBLEM
SOLVING WITH
WHOLE NUMBERS
Types of Problems
1
2
3
Strategies
FRACTIONS
Terms
Fractions
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
any combination of mathematical operations with whole
numbers
any combination of mathematical operations with
averages, medians, modes, factors, prime numbers
any combination of mathematical operations with
exponents, squares of numbers, square roots
develop good work habits
read all parts of question carefully
determine what is asked for or required
separate information given from question being asked
record information given and solution required separately
decide what arithmetic process will solve the problem
work neatly and arrange work in rows where possible
label the answer in terms of values given in question
estimate an answer
check every step and compare with estimated answer
compare estimated answer with answer found
translate English statements into mathematical expressions
draw pictures of problem
supply missing information if necessary
write full statements to answer questions
develop calculator skills
use clue words to solve word problems; e.g. total, sum,
how much, how many, increased, altogether, less, fewer,
more, difference, left, remains, times, at, divide, and each
define fraction, numerator, denominator
define mixed number, proper fraction
define improper fractions
define common denominator
the proper way to write fractions
compare and reduce fractions
write equivalent fractions
add fractions: like and unlike denominators
add fractions: find common denominators
subtract fractions: like and unlike denominators
subtract fractions: find common denominators
reduce fractions to lowest terms
cancelling fractions
14
15
16
17
18
19
DECIMALS
Terms
Decimals
PERCENT
Terms
Percent
INTRODUCTION
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
multiply fractions
divide fractions
use division rule: cancel, invert 2nd fraction, then multiply
change mixed numbers to improper fractions, as
appropriate
change improper fractions to mixed numbers, as
appropriate
report answer in lowest terms or mixed numbers, as
appropriate
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
define: decimal, decimal system
define mixed decimal
define terminating decimals
define repeating decimals
define lowest common multiple (LCM)
use of the decimal point
convert mixed numbers to decimals
multiply and divide by powers of 10
zero as a place holder
add and subtract decimals
place decimal points under each other
borrowing and carrying decimals
multiply decimals and placement of decimal in final
answer
divide decimals and placement of decimal in final answer
expressing remainders as decimals
round off decimals
estimate when working with decimals
work with money
compare decimals and fractions
convert decimals to fractions
convert fractions to decimals
convert repeating decimals to fractions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
define percent
use of the “%” sign
add and subtract with percents
multiply and divide with percents
convert fraction to percent
convert percent to fraction
convert decimals to percents
convert percents to decimals
convert fractions to decimals to percents
TO RATIO,
PROPORTION, AND
PERCENT
Percent
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Ratio
Proportion
LINES AND
ANGLES
Terms
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Construction
Angles
11
12
13
14
definition and calculation of percent
use formula “r/100 = P/W” to find percent of a number
use formula “r/100 = P/W” to find what percent one
number is of another
use formula “r/100 = P/W” to find a number when a
percent is given
discuss other terms: “r” represents Percent rate
discuss other terms: “P” represents part of the number
discuss other terms: “W“ represents the whole (entire)
number
define ratio
how to write ratios
reduce ratios
distinguish between equivalent and non-equivalent ratios
compare and write equivalent ratios
define proportion
explain relation between ratio and proportion
how to write proportions
discuss proportional
discuss mean
discuss extreme
discuss product
discuss true proportion
discuss direct proportion
define lines: point, line, line segment, ray
define lines: vertex, angle, perpendicular, parallel lines
define angles: acute, right, obtuse, straight, complete,
reflex
define transversal lines
define alternate angles
define corresponding angles
define interior angles
define angle relations: complementary, supplementary
define angle relations: adjacent, vertical, opposite, exterior
investigate angle relations when transversal intersects two
parallel lines
draw perpendic ular lines and 90 degree angles
construct parallel lines
label angles: 3 capital letters, middle one is vertex
find relation of angles when transversal cuts parallel lines
Protractor
15
16
17
18
19
INTRODUCTION TO
GEOMETRIC
FIGURES
Definition
1
Circles
2
3
4
5
6
Polygons
Three-dimensional
Working with
Geometric Figures
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
CHARACTERISTICS
discuss angles, using circle as a base for measuring angles
discuss degree as unit of measure for angles
use protractor to measure angles
classify angles and angle relation
use three step approach to measuring an angle: center
point of protractor on vertex of angle, one arm of angle on
base line of protractor, and decide on measurement
units/scale
define geometry
define and/or diagram: circle, radius , diameter
define and/or diagram: circumference, chord, arc,
segment, sector
define and/or diagram: tangent, semi- circle
measure radius, diameter, and circumference
investigate relation between radius, diameter,
circumference
explain and use
use compass to construct circle, given radius and diameter
define polygon
types of polygons: triangle, quadrilateral, pentagon
types of polygons: hexagon, octagons
recognize that polygons are named by number of sides
distinguish between polygons and non-polygons
distinguish between regular and irregular polygons
identify concave, convex, and regular polygons
types of triangles: scalene, isosceles, equilateral
types of triangles: acute, obtuse, right triangles;
hypotenuse
explain Pythagorean Theorem
types of quadrilaterals and characteristics: trapezoid
parallelograms (rectangle, square, rhombus)
define polyhedron
explain relation between polyhedrons and polygons
types: cube, prism, pyramid, cones, spheres, cylinders
circle: find radius/diameter, given circumference
circle: find circumference, given radius/diameter
triangle: use Pythagorean Theorem to find length of one
side of a triangle
triangle: use Pythagorean Theorem to confirm that triangle
is right triangle
OF GEOMETRIC
FIGURES
Terms
Symmetry
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
Congruence
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
Similarity
CONSTRUCTION
30
31
32
33
define symmetry
define line symmetry
define line of symmetry
define plane of symmetry
define axis of symmetry
define congruence
identify point segment
identify ray
identify plane
identify vertex (vertices)
identify hypotenuse
identify side
define similarity as it applies to geometric figures
find more than one line of symmetry in certain shapes
draw lines of symmetry, using compass and straight edge
complete symmetrical figure, given area and line of
symmetry
in paper, construct shapes with more than 1 line of
symmetry
draw diagrams to illustrate planes of symmetry for
cylinder, prism, cone, and sphere
Determine number of planes of symmetry for cylinder,
prism, cone, and sphere
identify congruent figures (same size and shape)
match vertices, segments and sides
check congruence by comparing figures in various
positions
use slides, flips, and turns
test for congruence: superimpose tracing of one figure
over another figure
use a compass to mark congruent segments
congruent angles
importance of congruence: i.e. congruent stairs are safer
congruent three-dimensional objects
triangle: axioms of congruence: SSS, SAS, ASA: all
triangles
right triangle: axioms of congruence: RSA and RSS
similar figures have equal corresponding angles
similar figures have proportional corresponding sides
use similarity relations to calculate unknown values
OF GEOMETRIC
FIGURES
Terms
Drawing Figures
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
PROBLEM
SOLVING WITH
GEOMETRIC
FIGURES
Types of Problems
Strategies
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
define: vertex, ray, arms of an angle, degree, and rotation
define: right angle, acute and obtuse angles, and straight
angle
define complementary and supplementary angles
drawing instruments: ruler, compass, divider, pencil,
protractor, set square of triangle 30 degrees/60 degrees or
45 degrees
construct line segments, using ruler and compass
construct an angle equal to another angle, using ruler and
compass
right bisect a line segment, using ruler and compass
construct and measure angles, using ruler, compass, and
protractor
designate angles: 3 capital letters – middle letter at vertex
review triangles: acute, obtuse, right
review triangles: equilateral (equiangular), isosceles,
scalene
construct and measure parallel lines
construct and measure triangles
construct and measure equivalent angle s
construct and measure squares
construct and measure rectangles
construct and measure parallelograms
bisect angles, using ruler and compass
construct altitudes and perpendiculars, using ruler and
compass
construct a triangle congruent to a given triangle, using
ruler, compass, and protractor
practical constructions and applications
requiring any combination of mathematical operations
involving whole geometric figures
develop good work habits
read all parts of question carefully
determine what is asked for or required
separate information given from question being asked
record information given and solution required separately
decide what arithmetic process will solve the problem
work neatly and arrange work in rows where possible
label the answer in terms of values given in question
THE METRIC
SYSTEM
Metric System
AREA, PERIMETER,
AND VOLUME
Perimeter
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
estimate an answer
check every step and compare with estimated answer
compare estimated answer with answer found
translate English statements into mathematical expressions
draw pictures of problem
supply missing information if necessary
write full statements to answer questions
develop calculator skills
use clue words to solve word problems; e.g. total, sum,
how much, how many, increased, altogether, less, fewer,
more, difference, left, remains, times, at, divide and each
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
explain metric system and its base of ten
explain International System (SI Units)
fundamental units: length – metre (m)
fundamental units: mass – gram (g)
fundamental units: capacity – litre (L)
fundamental units: time – second (s)
fundamental units: temperature (degrees C)
metric prefixes and abbreviations
milli, ( m ) e.g. mm, mg mL
centi, ( c ) e.g. cm, cg, cL
deci, ( d ) e.g. dm, dg, dL
unit (metre, gram, litre) m, g, L
deka, ( da ) e.g. dam, dag, daL
hecto, ( h ) e.g. hm, hg, hL
kilo, ( k ) e.g. km, kg, kL
derived units such as area (square m.)
derived units such as volume (cubic cm.)
derived units such as capacity (cubic dm)
concept of place value
convert one metric unit of measure into another
1
2
3
define perimeter
explain that circumference is the perimeter of a circle
formula for finding perimeter of polygons: Perimeter (P) =
sum of length of all sides
formula for finding perimeter of regular polygons:
Perimeter (P) = number of sides (n) x length of sides (s)
practice finding perimeter of a variety of figures: square,
rectangle, pentagon, decagon, equilateral, irregular shapes
define area
measure area in square units
4
5
Area
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
Volume
18
19
20
21
22
formula:
formula:
formula:
formula:
2
area of square: A = side x side = s
area of a rectangle: A = length x width = l x w
area of triangle: A = ½ base x height = ½ x b x h
area of parallelogram: A = base x height = b x h
2
formula: area of circle: A = pi x radius squared = r
area of irregular shapes
surface area of 3-dimensional figures
application of area: e.g. flooring coverings, paint, etc.
practice finding area of rectangle, square, triangle
practice finding area of cube, parallelogram, circle,
irregular shapes
define volume
measure volume in cubic units
3
formula: volume of a cube: V = side x side x side = s
formula: volume of a rectangular prism: V = length x
width x height = l x w x h
formula: volume of a cylinder: V = pi x radius squared x
2
23
INTRODUCTION TO
INTEGERS
Integers
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
INTRODUCTION TO
EQUATIONS:
EQUALITIES AND
INEQUALITIES
Terms
1
2
3
4
5
6
height = x r x h
applications of volume: e.g. amount of gravel to buy,
capacity of fuel tank, etc.
review of thermometer temperature reading
definition of integers
using a number line
standard form of integers: signs of operation
standard form of integers: signs of quantity
use of negative and positive integers: + shows gain
use of negative and positive integers: - shows loss
order integers from least to greatest and vice versa
add, subtract, multiply, divide with integers
practical applications of integers (golf, banking, etc.)
define equation
use and understand: variable, constant
use and understand: algebraic expressions, term, factors,
coefficient
use and understand: replacement and solution
order of operations (BEDMAS)
symbols: +, -, x, ÷, =, and √
Equations
Equalities and
Inequalities
PROBLEM
SOLVING WITH
EQUATIONS AND
EQUALITIES
Types of Problems
Strategies
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
symbols: ( ), [ ], { }
symbols: , >, <, ,
equality and inequality
use of “•
• ” in place of “x” for multiplying
use letters to represent numbers
order of operations
solve equations
use opposite operations to isolate the variable
Principle of Equations: doing same thing on both sides
use distributive property
build equations
solve equations with integers
combine like terms to solve equations
translate English statements into mathematical statements
use mathematical symbols appropriate to grade level
define equality and inequality
23
24
25
using terms equality and inequality correctly
solving inequalities
combine like terms to solve inequalities
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
requiring any combination of mathematical operations
involving equations (equalities) and inequalities
develop good work habits
read all parts of question carefully
determine what is asked for or required
separate information given from question being asked
record information given and solution required separately
decide what arithmetic process will solve the problem
work neatly and arrange work in rows where possible
label the answer in terms of values given in question
estimate an answer
check every step and compare with estimated answer
compare estimated answer with answer found
translate English statements into mathematical expressions
draw pictures of problem
supply missing information if necessary
write full statements to answer questions
develop calculator skills
18
use clue words to solve word problems; e.g. total, sum,
how much, how many, increased, altogether, less, fewer,
more, difference, left, remains, times, at, divide, and each
INCOME
Compute Income
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Deductions
Income Tax
MONEY
MANAGEMENT
Money Management
Credit
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
hourly wages: compute hours worked per week
find weekly wage based on hourly rate
find monthly wage based on hourly rate
weekly wages: find hourly rate from weekly wage and
hours worked
find monthly wages and annual wage
monthly/bi-weekly wages: find hourly rate from monthly
wage and hours worked
find weekly and monthly wages
calculations involving overtime pay
piece work and calculations
commission: define and calculate: given rate and amount
of sales
define and discuss: fees, tips, pensions, and bonuses
define: net income, take-home pay, gross income
explain and fill in Tax Exemption Return (TD1)
deduction: income tax, Canada Pension, Employment
Insurance
other deductions: union dues, health and life insurance
define terms and become familiar with current forms
read information from T4 slips
read information from General Tax Guide
calculate: Total Income, Net Income, Taxable Income
calculate tax payable: balance due or refund
complete a tax return for a given case
discuss disadva ntages of selling refund to tax preparers
recognizing needs as opposed to wants
setting immediate goals (health, clothing, housing)
setting short-range goals (improving earning)
setting intermediate and long-range goals (financial
independence, travel, luxury items)
putting goals set in order of priority
achieving goals through budget and money management
practice money management with sample net incomes
control spending: use ledgers and journals
define credit
types of credit: installment plans, equalized payments
types of credit: credit cards, bank loans
compare interest rates on overdue payments
contrast credit cards with debit cards
BANKING
Financial Institutions
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
investigate bank interest charges on loans
how to manage credit cards
advantages of credit: taking advantage of sales
advantages of credit: collecting rewards/air miles
disadvantages of credit: overspending
disadvantages of credit: bankruptcy
disadvantages of credit: items cost much more
1
chartered banks, trust companies, mortgage loan, credit
union
contrast bank, trust company, credit union
services: savings, loans, money orders, safekeeping
services: business deposits, travel services, mail service
services: investment services, line of credit
types of accounts: true savings – high interest on small
amounts
types of accounts: checking/savings
types of accounts: personal checking: no interest, monthly
charge
types of accounts: term deposits, GICs: money locked in
at a higher rate of interest
discuss advantages of each type of account
using a banking machine
advantages and disadvantages of using a banking machine
advantages and disadvantages of using telephone or
internet banking
fill out deposit and withdrawal slips
fill out checks, money orders, and traveller’s check
balance a sample account, given a balance, series of
withdrawals, deposits, checks, and bank charges
discuss bank charges/include in calculating bank balance
reading a passbook and bank statement
regular (at least monthly) bank reconciliation
importance of keeping accurate up-to-date records
effect of and charges for overdrafts and NSF checks
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
Bank Forms
Balance Account
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
CALCULATING
INTEREST
Terms
Simple Interest
1
2
3
4
5
6
define simple and compound interest, rate of interest, and
principal
define mortgage and amortization
concept of making money work for you
define and calculate I = Prt
calculate simple interest for various amounts, times, and
rates
calculate value of investment at maturity
Compound Interest
Mortgages
PROBLEM
SOLVING IN
PERSONAL
FINANCE
Types of Problems
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
define compound interest
find compound interest using Compound Interest Tables
calculate value of investment at maturity
discuss advantages/disadvantages of compound interest
define mortgage
read an amortization table
find monthly payments
find total interest paid over the term of a mortgage
find total amount paid at end of term
discuss flexible and fixed mortgages
discuss benefits of weekly or bi-weekly payments
discuss anniversary dates for pay downs
discuss penalties for early repayment
benefits of shopping for the best rate for your purpose
1
Requiring any combination of mathematical operations
involving income, money management, bank ing, or
interest
develop good work habits
read all parts of question carefully
determine what is asked for or required
separate information given from question being asked
record information given and solution required separately
decide what arithmetic process will solve the problem
work neatly and arrange work in rows where possible
label the answer in terms of values given in question
estimate an answer
check every step and compare with estimated answer
compare estimated answer with answer found
translate English statements into mathematical expressions
draw pictures of problem
supply missing information if necessary
write full statements to answer questions
develop calculator skills
use clue words to solve word problems; e.g. total, sum,
how much, how many, increased, altogether, less, fewer,
more, difference, left, remains, times, at, divide, and each
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18