* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reproductive system
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
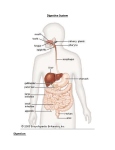
The REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM I. Vocabulary Ovum, sperm, foetus, vas deferens, progesterone, labia majora, coitus, labia minora, spermatogenesis, ovaries, maturation, clitoris, release, vestibule, ejaculation, fallopian (or uterine) tubes, vulvovaginal glands, epididymis, sustains, erectile, premenstrual syndrome (PMS), hymen and Bartholin's glands, seminal vesicles, vagina (sheath), urethra, graafian follicles, acid, oestrogen, prostate gland, endometrium, fimbriae, puberty, labour (delivery), cross-section, epithelium, hormones, testes (testicles), excretory ducts, penis, accessory glands, scrotum, testosterone, mons veneris, development of sperm, glans penis, Cowper's glands (bulbourethal glands), uterus (womb), alkaline, ripe, nourish, cramping, abortion, infertility, miscarriage II. Label the pictures III. On the basis of the acquired vocabulary depict the anatomy and functions of the reproductive system IV. Read the text and fill in the gaps The purpose of sexual reproduction is perpetuation of the species, by the creation of a new individual. This is achieved by the union of the nuclei of the ……………. and the ……………. The specific role of the female is to provide the best possible conditions for the development of the ………… , in addition to providing the female germ cell. THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM. The female reproductive and the endocrine systems are interrelated. Pituitary hormones regulate some functions of the reproductive system and one organ – the ovary, is part of both systems. The external genitals (collectively called the vulva) include the following structures:………….., …………….., ……………………. , ………………, …………………………. , ……………………….., ……………………………, ……………... The internal genitals consist of two …………., two ………………………………., the …………. and the ………, all situated in the pelvis which gives their excellent protection from accidental injuries and are located in intimate contact with the bladder and the rectum. The ovaries are oval shaped organs, about 4 cms long, though their size may vary in different people. They are located in the lower abdomen, one on each side of the uterus near the pelvic wall and close to the outer end of the fallopian tube. In structure, the adult ovary is simply a collection of ova, or microscopic eggs. Within each ovary are thousands of small sacs called ………………….. Each contains an ovum and a section through a ……………… would show an ovule in a stage of development. When the ovum is mature, the graafian follicle ruptures to the surface and the ovum leaves the luteum functions as an endocrine organ and secretes two hormones, ……………… and …………………. Fertilization can occur during the 4-5 days needed for the ovum to travel the length of the tube if sperm are present. If fertilization does not occur, the corpus luteum in the ovary stops producing progesterone and oestrogen and regresses. At this time — owing to the lowered levels of progesterone and oestrogen some women have symptoms of depression, breast tenderness and irritability, prior to menstruation. These symptoms are known as ……………………………….. About five days after the fall in hormones, the uterine ………………….. breaks down and the menstrual period begins. The ……………………….are two small muscular tubes. The egg, after its ………… from the ovary, is caught up by the finger-like ends of the uterine tube. These ends are called …………. The tube itself is lined with small hairs that, through their motion, sweep the ovum along. The ………… is a strong, muscular organ located in the pelvis, between the bladder and the rectum. It is freely moveable. After receiving the fertilized ovum, the uterus ………… and protects it through the various stages of growth and expels the developed child at term. It is capable of enormous enlargement during pregnancy and returns to nearly its former size afterwards. The ………….. is a musculomembranous tube extending from the exterior of the body to the uterus. It is the female organ of sexual intercourse and also serves as a passage for the foetus during ………….. Its size and shape are variable and it is also capable of great expansion, to facilitate the birth of a child. Normally the anterior and posterior vaginal walls lie in contact and on …………………. the cavity takes the shape of the letter H. The anterior wall is in contact with the urethra and the base of the bladder. The cyclic changes of the vaginal …………………. are under the control of the ovarian ……………………... THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM. The male reproductive system consists of two ………….., four types of …………….., a ……….. and three different …………………... The two ……………… are located in a sac called the …………….. They have two functions: the production of sperm (…………………….), and the production of the male hormone, …………………….. The scrotum lies between the thighs, exposing the testicles to a lower temperature than the rest of the body, this is necessary for the adequate ………………… and ……………………... © Veronika Srchová, Jozef Gémeš Sperm production begins at puberty and throughout adulthood millions of sperm cells are continuously produced. Somewhat resembling a tadpole, sperm are microscopic in size less than 1/100,000th the size of the female ovum. It only needs to live long enough to travel from the point of release the female uterine tube. Approximately 300 million sperm cells are released during a single …………….. Testosterone is the hormone that gives secondary male sex characteristics. At ……………….. testosterone causes voice changes, increased body hair and increased muscular development. The ……………………are where sperm are collected and carried, forming a long tube beginning with the ……………... Here the sperm mature and are temporarily stored. The tube runs down the length of the testicle turning upwards again where it becomes a narrow straight tube called the ……………... It carries the sperm into the pelvic region around the urinary bladder and into the ejaculatory duct, leading towards the ……………. The penis is composed of three layers of …………… tissue and at its tip expands to form a soft sensitive region called the …………………. In an erection, the spaces between the layers fill with blood becoming enlarged and rigid, which facilitates …………….. During an erection the urinary sphincter closes to prevent urine from mixing with semen. The accessory glands of the male reproductive system consists of: …………………, the ……………and the two pea-sized …………………. Two sets of seminal vesicles are located at the back of the bladder. The secretions produced by these glands enter the ejaculatory ducts. The prostate gland surrounds the ejaculatory ducts and upper portion, of the urethra. Prostate secretions assist in maintaining motility of the sperm. Below the prostate gland are the two Cowper's glands. These glands secrete an ………….. mucus that helps protect sperm from the …………… environments of the male urethra and female vagina. Ducts of the glands enter the urethra below the prostate. V. Diseases of the reproductive system Disorders of the female reproductive system: - Premenstrual tension - Dysmenorrhoea - Amenorrhoea - Metrorrhagia - Menorrhagia - Cervicitis - Endometriosis - Fibroids - Mastitis - Ectopic pregnancy - Carcinomas: cervical endometrial ovarian Disorders of the male reproductive system: - Orchitis - Cryptorchidism - Hydrocele - Hyperplasia of prostate - Penis: epispadia hypospadia phimosis Peyronie´s disease priapism - Carcinoma of: testes prostate penis Sexually transmitted diseases: - bacterial: Gonorrhoea (clap) – Neisseria gonorrhoeae Lymphogranuloma venereum – Chlamydia trachomatis Syphilis (lues) – Treponema pallidum Chancroid – Haemophilus ducreyi Chlamydia – Chlamydia trachomatis - viral: HIV/AIDS Herpes genitalis – HSV Human papilomavirus – HPV Molluscum contagiosum – MC Hepatitis B, C – HBV, HCV - protozoal/parasitic: Trichomoniasis Scabies Pubic lice genitals – private parts, crotch penis – phallus, member, prick, dick, peter, cock, tool, shaft testis – testicle, orchis, bollock, ballock, egg, ball, nut, family jewels coitus – copulation, intercourse, carnal knowledge © Veronika Srchová, Jozef Gémeš