* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The water cycle has no beginning or
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
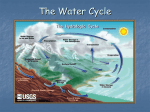
Key Understandings and Guiding Questions: Human activity can affect groundwater and surface water in a watershed. — What happens to precipitation when it reaches the Earth? — Why are aquifers and ground water important to life on Earth? Human activity can either positively or negatively impact Earth systems. — How does human activity contribute to the pollution of ground water? — What are some actions humans can take to reduce or eliminate pollution to our water sources? Vocabulary of Instruction: watershed - _________________________________ ____________________aquifer - ____________________________________________________ ground water - _________________________________________________ porosity - ___________________________________________________ permeability - __________________________________________________ pollution- ___________________________________________________ percolation - ___________________________________________________ infiltration - _________________________________________________ Background Information: The water cycle has no beginning or ending point. The Sun plays a major role in the water cycle. The Sun drives the water cycle. Evaporation, condensation, and melting all occur in the water cycle, and none of them can occur without the addition or removal of energy. The Sun’s energy heats the upper ocean causing evaporation on liquid water into water vapor. This water vapor rises in the atmosphere and cools. Upon cooling to the dew point, the water vapor condenses around a condensation nucleus (particle) to form millions of water droplets called clouds. Clouds become heavy with water droplets. When clouds become too heavy, water droplets fall to the Earth as precipitation: rain, snow, sleet, hail, etc. Once water reaches the Earth’s surface, it either infiltrates (goes down into) the ground or runs along the surface. Surface waters erode the Earth’s features and end up in ponds, rivers, and eventually oceans. Water soaks into the ground or goes through percolation – The downward movement of water from the land surface into soil or porous rock caused mainly by gravity. Water that soaked into the ground can be pulled into plants, pulled into the water table or aquifers. The process of transpiration in plants will eventually put water back into the cycle. An aquifer is a storage container for groundwater that is made up of different sediments. The various sediments can store different amounts of groundwater within the aquifer. The amount of water that it can hold is dependent on the porosity and permeability of the sediment. Porosity is the amount of water that a material can hold in the spaces between the pores, while permeability is the material’s ability to pass water through these pores. Surface water sources include reservoirs, rivers, streams, lakes or ponds. The alternative to surface water is groundwater obtained from wells. Most large cities in the United States rely on surface water, while many smaller towns or individual homes depend on wells. These two sources are quite different with regard to biological contamination. Surface water carries some bacteria; groundwater from properly constructed and maintained wells is free of them. Rain may encounter animal waste on the surface, but as it seeps into the ground, microbes are filtered out by soils, sand and gravel before the water reaches the water table. When it is pumped to the surface, it has undergone nature's filtration. Water on Earth is a finite source. Protecting the water means protecting all forms of the water found on Earth including water at the surface, under the ground, in vapor form, and as precipitation. Pollution from using fossil fuels such as from crude oil leaks to acid rain generated from coal burning can impact all forms of water. Acid rain falls onto the land and flows into the surface water, back into the ground, and back into the air. It can be an endless cycle. As contamination infiltrates the water cycle, more water will be impacted. Most of the water on Earth is saline (salty). Fresh water is and will be in demand and become a very valuable resource. Care must be taken to prevent overuse of potable water sources as well as to protect the earth’s waters from contamination.