* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Infertility 101 - kusm
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
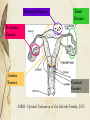
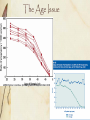
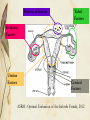
Infertility 101 Laura L. Tatpati, MD Division of Reproductive Endocrinology & Infertility Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Kansas School of Medicine - Wichita No disclosures Objectives Understand key historical and clinical findings which can aid in assessment of gynecologic conditions which affect fertility Review diagnostic testing options and their appropriate usage Understand how to utilize these for enhanced efficiency/efficacy of treatment of the patient Infertility A disease defined by the failure to achieve a successful pregnancy after 12 months or more of appropriate, timed unprotected intercourse or therapeutic donor insemination Early evaluation and treatment: Medical history and physical findings After 6 months if female partner is > 35 y http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2012.09.023 Fertility 80% will conceive w/in 6 mo Monthly fecundibility is highest in the 1st 3 mo Relative fertility is about ½ for women in their late 30s vs. early 20s http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2013.07.011 Peritoneal Factors Tubal Factors Ovulatory Factors Uterine Factors Cervical Factors ASRM : Optimal Evaluation of the Infertile Female, 2012 The History History is essential Menarche Periods…everything you ever wanted to know Ovulation/pre-menstrual symptoms Pregnancy history / how long TTC? Contraception history Coital frequency/dyspareunia/lubricants Q 1-2d Hydroxyethylcellulose-based, canola or mineral oil STIs Pap smears/mammogram Patient Goals and methods they’ve tried Goals: When do they want to conceive? How many children are they considering? Methods: Temperature charting Ovulation testing Method for timing of intercourse Other medical interventions General Medical History Current diseases Chronic diseases Medications & herbal preparations Allergies Surgeries ROS Headaches Vision problems Breast discharge Hair growth Acne Thyroid disease sx Dyspareunia Pelvic pain Bowel/bladder complaints Family history DM, CAD, HTN Cancer: breast, ovarian, uterine, colon, thyroid, pancreatic Other diseases in family Infertility issues, RPL Birth defects Learning delay, Autism, MR Social history Tobacco, EtOH, drugs Tobacco 40% reduction in IVF LBR Moderate alcohol 1-2/d Mixed data 500mg caffeine daily Occupation Exercise Exam Vitals (BP, BMI) HEENT Skin CV/Lungs Breasts Abdomen Pelvic Case Study 31 yo G1P1001 3 year history of infertility She reached menarche at age 12 She had a term delivery at age 18 Menses “like clock-work” No premenstrual symptoms She has acne and denies having any problems with excessive hair growth Ovulatory factors Up to 40% of female factor infertility Can be subtle dysfunction Underlying condition should be sought due to risk for health implications Evaluating ovulation Likely ovulatory if: q 25-35d Moliminal sx Consistent flow < about 45 years old Testing for ovulation BBT Abnormal if: Monophasic <10d luteal phase temp elevation Limitations Less reliable for defining ovulation timing Occ ovulatory w/ mono-phasic Peak fertile about 7d prior Luciano. Obstet Gynecol 1990; 75: 412-6 Mid-Luteal serum progesterone >3ng/ml – presumptive Mid-luteal is a retrospective diagnosis! Urinary LH kits Indirect evidence Likely ovulation in 1-2d Most reliable for ovulation prediction Testing for ovulation cont. Endometrial biopsy >2 days Lacks accuracy and precision Cannot distinguish fertile/infertile Should be utilized for those in whom abnormal pathology is a concern (neoplasia or chronic endometritis) TVUS Costly Reserved for those that simpler methods are ineffective for (primarily used in treatment) Diagnosis of Ovulatory factors Lab evaluation TSH Prolactin FSH/E2 (any day if amenorrheic, day 3 if cyclic) Ovarian failure, hypothalamic dysfunction (LH if this is a concern), diminished ovarian reserve Clomid challenge test Testosterone ?AMH Clinical suspicions of ovulatory dysfunction History, History, History Pubertal disturbances Menstrual history Secondary oligo- or amenorrhea Pregnant #1 Ovarian disease — 40 percent Hypothalamic dysfunction — 35 percent Pituitary disease — 19 percent Uterine disease — 5 percent Other — 1 percent Diagnostic approach to secondary amenorrhea ©2007 UpToDate® • www.uptodate.com Licensed to Mayo Foundation Treatment of Ovulatory Factors: PCOS If obesity related – First-line treatment is diet modification and exercise May proceed with inexpensive treatment modalities (CC +/IUI) 3-6 cycles w/o success indicates need for complete evaluation SA if oligo rather than amenorrhea 6 mo LBR 20–40% ½ who do conceive do so on 50mg, 20% on 100mg 10% risk of twins, 0.5% risk of triplets or more What about metformin? CC 3x as effective Metformin is not recommended as 1st line agent Alone – 1-2 additional ovulatory events / yr Adding metformin to clomiphene may enhance PR in obese patients OR, 2.67; 95% CI, 1.45–4.94; NNT 4.6 Creanga. Obstet Gynecol 2008;111:959–68. Treatment of Ovulatory Factors: Other endocrine/hypothalamic Other endocrine disorders Treat this first Hypogonadotrophic Hypogonadism Gonadotropins (hCG/FSH likely best) IVF The Age Issue ASRM Practice Committee. Optimizing natural fertility. Fertil Steril 2008 Dx of Ovulatory Factor: DOR/POF/AMA Ovarian reserve testing >35 FH early menopause Single ovary or hx ovarian surgery Chemotherapy or pelvic radiation therapy Unexplained infertility Prior poor response to gonadotropins Planning ART Dx of Ovulatory Factor: DOR/POF/AMA FSH > 10-15, AFC <5 (?3), AMH < 1?? Gonadotropins vs IVF vs Egg donation Age is independent variable >42 = < 5% chance success with non-donor IVF Consider REI referral Peritoneal Factors Tubal Factors Ovulatory Factors Uterine Factors Cervical Factors ASRM : Optimal Evaluation of the Infertile Female, 2012 Uterine factors Relatively uncommon cause of infertility Malformation Synechiae Polyps Myomata Pelvic radiation Cervical - ? Chronic cervicitis Tubal Factor: Diagnosis History Tubal ligation Ectopic/Torsion Ovarian surgery or oophorectomy STDs or PID Hx Complicated Appendectomy/Bowel surgery Uterine/Tubal Evaluation Methods of evaluation HSG Ultrasound/3D US Sonohysterography Hysteroscopy - definitive Reserved for further evaluation/treatment or If laparoscopy planned for evaluation Endometriosis or Pelvic adhesions Diagnosis Suspicious history or prior diagnosis Suspect if diagnostic tests are negative or negligible Infertility vs Tubal ligation at laparoscopy 38% vs 5% 1/3 w/endometriosis - asymptomatic Ultrasound: endometriomas, fluid collections Laparoscopy: definitive Laparoscopy to Enhance Fertility Benefits with advanced endometriosis Unclear with early stage disease 2 RCTs Canadian collaborative trial 29% vs 17% PR > 20wks (Tx vs No Tx) Italian study 20% vs 22% LBR after 1 yr (Tx vs No Tx) Combined NNT 12 (CI 7-49) New patient 24 yo female, regular cycles No dysmenorrhea, acne, hirsutism Nothing concerning in history Completed 9 cycles of clomid Had one ER visit for pain after ovulation in 4th cycle Normal HSG What about him? Male factor 13% 5% Ovulatory 14% 20% Tubal Peritoneal Uterine/Cervical 18% Male Unexplained 30% Additional 30-50% likely due to combined factors I’m good. Things to watch for… His “mom” had some trouble getting pregnant, but had 2 children 4 years apart Healthy, goes to the gym daily for 1-2 hrs daily No smoking (but does he chew???) Goes out w/ buddies on weekends “I only drink during KU games” Had to see Dr. for varicocele, but didn’t change, so left alone Had some kind of “hernia” repaired as an infant, but I don’t know details… Male Factor Evaluation Current Physical Hernias, varicoceles BMI Elevated Increased estrogen levels, feedback to LH, decr testosterone? Decreased Counts Reduced (acute/chronic illness) Decrease GnRH Male Factor Evaluation Semen Analysis 2-3 days abstinence >7 days – senescence/debris X 2 (1 month apart) Reference values are not minimum values needed & normal values do not prove male is fertile Semen Analysis Volume 1.5-5ml Count (Concentration) - >20 million/mL and Motility >50% >5M TMC for inseminations Also, morphology, WBC, agglutination Male Factor Infertility Treatments GnRH pump FSH/LH Clomiphene Sperm banking Donor sperm Testicular aspiration/biopsy (MESA/TESE) ICSI w/ IVF Conclusion Complete history for both partners Think in stepwise fashion Initiate testing per history Don’t forget 30-40% risk of combined infertility Referral to REI &/or Urologist as clinically indicated Questions? References ASRM. Practice Committee Report. Optimal evaluation of the Infertile Female. Doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2012.05.032 AUA and ASRM. Report on Optimal Evaluation of the Infertile Male. 2001 Optimizing Natural Fertility. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2013.07.011 ACOG. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome. Clinical Management Guidelines for Obstetrician-Gynecologists. Number 108, October 2009 References Marcoux S, Maheux R, Berube S. Laparoscopic surgery in infertile women with minimal or mild endometriosis. Canadian Collaborative Group on Endometriosis. N Engl J Med 1997 Jul 24;337(4):217-22.