* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 17 – Urinary System I. The Urinary System consists of 4
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
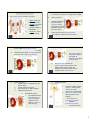
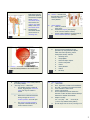
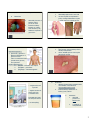
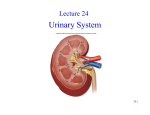
Chapter 17 – Urinary System I. The Urinary System consists of 4 organs: 1. 2. 3. 4. Pg. 454 2 kidneys that filter blood & form urine 2 ureters to transport urine to bladder 1 urinary bladder to store urine 1 urethra to convey urine out of body 17 -1 3. 4. II. Kidneys – are reddish brown, bean-shaped organs 12 cm long & enclosed in a tough, fibrous capsule A. Kidney Structure 1. A medial depression leads to a hollow renal sinus which blood vessels, nerves, lymphatic vessels, & the ureter enter 2. Inside the renal sinus lies a renal pelvis – the widened, superior end of the ureter 17 -2 The renal pelvis is subdivided into smaller tubes, called major & minor calyces (1=calyx) Small elevations called renal papillae project into each minor calyx (pyramid apex) 5. 17 -3 17 -4 Kidney Functions 1. regulate volume, composition, & pH of body fluids 2. remove wastes from blood 3. help control rate of RBC formation 4. regulate blood pressure C. 17 -5 Pg. 456 2 distinct regions are found within the kidney a. b. B. Pg. 455 D. The renal cortex contains the nephrons (the functional units of the kidney) and is found towards the outside of the kidney; it dips into the medulla to form renal columns Nephron Structure 1. 2. Renal Blood Vessels 1. The abdominal aorta gives rise to renal arteries leading to nephrons in the kidneys; renal veins take away CO2 Pg. 455 17 -6 The renal medulla is towards the inside of the kidney, & contains cone-shaped renal pyramids A kidney contains 1 million nephrons, each of which consists of a renal corpuscle & a renal tubule The renal corpuscle is the filtering portion of the nephron it is made up of … glomerulus: ball of capillaries glomerular capsule: receives the filtrate 1 3. 4. Pg. 457 The renal tubule leads away from the glomerular capsule & first becomes a highly coiled proximal convoluted tubule, then leads to the nephron loop, and finally to the distal convoluted tubule Several distal convoluted tubules join to become a collecting duct III. Ureters – muscular tubes that transport urine from kidneys to base of urinary bladder IV. Urinary Bladder A. a hollow, muscular organ lying in the pelvic cavity B. contains the trigone (the openings of the 2 ureters and the urethra) C. neck of urinary bladder at urethra forms an internal urethral sphincter (muscle) 17 -7 17 -8 VI. Pg. 468 V. Urethra – a muscular tube that conveys urine from the urinary bladder to the outside of the body 17 -9 B. C. Muscular peristaltic waves convey urine to the urinary bladder “The Urge to Go” – Micturition 1. The bladder muscles contract & stretch, triggering the micturition reflex & an urge to urinate is sensed http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter27/animation__micturition_reflex.html 17 -11 2. When these contractions become strong enough, the internal urethral sphincter is forced open 3. The external urethral sphincter, composed of skeletal muscle, is under conscious control Urine Elimination A. Urine is formed in nephrons by the glomerulus (in the glomerular capsule within the renal corpuscle), passes through the tubules, and into: 1. collecting ducts 2. renal papillae 3. minor and major calyces 4. out the renal pelvis 5. ureters 6. urinary bladder 7. urethra 8. exit body 17 -10 VII. Urine Composition A. ~95% water B. Urea - byproduct of amino acid metabolism C. Uric acid – byproduct of nucleic acid metab D. Trace amounts of amino acids E. Variety of electrolytes F. Urine composition varies & reflects the amounts of water & solutes that the kidneys eliminate to maintain homeostasis G. Output is usually: 0.6 – 2.5 L/day -OR50-60 mL/hr (<30 mL may indicate kidney failure) H. pH can range from 4.5 to 8.0, but avg is 6.0 17 -12 2 VIII. Urinary System Disorders & Diagnoses A. Bacteriuria 1. 2. 3. abnormal presence of bacteria and/or pus in the urine indicates a kidney infection or urinary tract infection (UTI) antibiotics required to get rid of it 17 -13 C. B. 17 -14 D. Diabetes chemical diagnosis is: 1. glucosuria / glycosuria – abnormal appearance of glucose in urine due to insufficient insulin (breaks down glucose) from pancreas physical diagnoses are: 2. polyuria – excessive urine output 3. polydipsia – great thirst 4. polyphagia – increased appetite 17 -15 Kidney Stones 1. solid “stones” form in kidneys due to diet &/or dehydration 2. causes SEVERE pain as stones pass through the ureters 17 -16 3. World Records E. Largest stone was 3 pounds Highest number of stones was from a Canadian man: Proteinuria 1. albumin (protein) helps regulate water concentration in blood and is not normally found in urine 2. indicates kidney malfunction or kidney (renal ) failure F. Feb 1986 April 2003 he had 4,504 stones (~22 stones/day) 17 -17 Gout 1. abnormally high levels of uric acid 2. uric acid crystals are deposited in joints, causing inflammation & pain usual joints are in hands & feet 17 -18 Hematuria 1. abnormal presence of blood in the urine 2. a symptom of many illnesses 3