* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 13
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Complex polytope wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
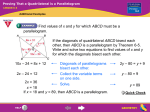
GEOMETRY NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Name________________________ Lesson 13 M4 Period: _____Date______________ Lesson 13: Analytic Proofs of Theorems Previously Proved by Synthetic Means Learning Targets Using coordinates, I can find the intersection of the medians of a triangle that meet at a point that is two-thirds of the way along each median from the intersected vertex. Using coordinates, I can prove a quadrilateral to be a parallelogram showing that diagonals of a parallelogram bisect one another ̅̅̅̅ with 𝐵(−2, −1) and 𝐶(4, 1). Opening Activity Line 𝐴 is the perpendicular bisector of segment 𝐵𝐶 What is the midpoint of ̅̅̅̅ 𝐵𝐶 ? ̅̅̅̅ ? What is the slope of 𝐵𝐶 ̅̅̅̅ .) What is the slope of line 𝐴? (Remember, it is perpendicular to 𝐵𝐶 ̅̅̅̅ . Write the equation of line 𝐴, the perpendicular bisector of 𝐵𝐶 Remember from Module 1…… All triangles have three medians will intersect at one point in the interior of the triangle called the centroid or the point of concurrency. The centroid of a triangle divides the medians into a 2:1 ratio Example 1 Given triangle 𝑨𝑩𝑪 with vertices𝑨(𝟏, 𝟏),𝑩(𝟓, 𝟐), and 𝑪(𝟑, 𝟓), find the coordinates of the point of concurrency. Find point M midpoint of segment AB Find point N midpoint of segment CB Find point R midpoint of segment AC Draw all three medians and label the point concurrency D Use the ratio to find the coordinates of the point of concurrency GEOMETRY Lesson 13 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Name________________________ M4 Period: _____Date______________ Quadrilaterals Properties (Polygons having four sides) Parallelograms Trapezoids 2 sets of parallel sides 2 sets of congruent sides Opposite angles congruent Diagonals bisect each other Kites Have exactly one pair of opposite sides that are parallel 2 pairs adjacent congruent sides Opp. sides not congruent or parallel 2 pairs of opposite sides parallel Opposite sides and opposite angles are congruent Rectangles Rhombuses Diagonals bisect each other All of the properties of the parallelogram PLUS 4 right angles diagonals are congruent All of the properties of the parallelogram PLUS 4 congruent sides diagonals bisect angles diagonals are perpendicular Isosceles Trapezoid One set of parallel sides Base angles and legs congruent Diagonals are congruent Opposite angles are supplementary Squares I have it all! Coordinate Proofs On a parallelogram (including rectangles, squares and rhombuses) diagonals that bisect each other. On the coordinate plane, diagonals have the same midpoints, therefore they intercept each other. A parallelogram is always a trapezoid, with two sets of opposite sides parallel. On the coordinate plane we prove to sides to be parallel if they have the same slope A rectangle is a parallelogram with all four right angles. On the coordinate plane we prove that by showing consecutive sides have slopes that are opposite reciprocals A rhombus is a parallelogram with all four sides equal. On the coordinate plane we prove that by using the distance formula to find the length of all sides GEOMETRY Lesson 13 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM M4 Name________________________ Period: _____Date______________ Example 2. Quadrilateral MATH with vertices M(3,-4) , A(0,2) , T(6,2) and H(9,-4) A. Prove that Quadrilateral MATH is a parallelogram Explanation: Quadrilateral MATH is a parallelogram because two sets of opposite sides have the same slope, meaning that two sets of opposite sides are _________________. B. Prove that Quadrilateral Math is a parallelogram using diagonals i. What is the midpoint of segment MT ii. What is the midpoint of segment AH C. Is quadrilateral MATH a trapezoid? Explain your answer Explanation: Quadrilateral MATH is a parallelogram because the diagonals have the same midpoint, therefore the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect one another D. Is quadrilateral MATH a rhombus? E. Is quadrilateral MATH a rectangle? Explain your answer GEOMETRY Lesson 13 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Name________________________ M4 Period: _____Date______________ Lesson 13: Analytic Proofs of Theorems Previously Proved by Synthetic Means Classwork 1. Let 𝐴(−23, 12), 𝐵(13, 36), and 𝐶(23, −1) be vertices of a triangle. ̅̅̅̅ and label M a) Find the midpoint for segment 𝑨𝑩 b) Find the midpoint for segment ̅̅̅̅ 𝐵𝐶 and label P ̅̅̅̅ and label N c) Find the midpoint for segment 𝐴𝐶 d) Where will the medians of this triangle intersect? (point of concurrency or centroid) 2. Given quadrilateral 𝑱𝑲𝑳𝑴 with vertices 𝑱(−𝟒, 𝟐), 𝑲(𝟏, 𝟓), 𝑳(𝟒, 𝟎), and 𝑴(−𝟏, −𝟑): a. Is it a trapezoid? Explain b. Is it a parallelogram? Explain c. Is it a rectangle? Explain d. Is it a rhombus? Explain e. Is it a square? Explain f. Find the point of interception of diagonals of 𝑱𝑲𝑳𝑴 GEOMETRY NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 13 M4 Name________________________ Period: _____Date______________ 3. Given a quadrilateral with vertices 𝑬(𝟎, 𝟓), 𝑭(𝟔, 𝟓),𝑮(𝟒, 𝟎), and 𝑯(−𝟐, 𝟎): a. Prove quadrilateral 𝑬𝑭𝑮𝑯 is a parallelogram. b. Prove (𝟐, 𝟐. 𝟓) is a point on both diagonals of the quadrilateral. 4. Prove quadrilateral 𝑾𝑿𝒀𝒁 with vertices 𝑾(𝟏, 𝟑), 𝑿(𝟒, 𝟖), 𝒀(𝟏𝟎, 𝟏𝟏), and 𝒁(𝟒, 𝟏) is a trapezoid. Explain your answer. GEOMETRY NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Name________________________ Lesson 13 M4 Period: _____Date______________ Lesson 13: Analytic Proofs of Theorems Previously Proved by Synthetic Means Homework 1) Prove that the quadrilateral whose vertices are the points A(-1,1), B(-3,4), C(1,5) and D(3,2) is a parallelogram. 2) Quadrilateral DEFG has vertices at D(3,4), E(8,6), F(9,9) and G(4,7). Prove that DEFG is a parallelogram using diagonals GEOMETRY NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 13 M4 Name________________________ Period: _____Date______________ 3) Quadrilateral ABCD has vertices 𝐴(2, 3), 𝐵(10, 3), 𝐶(10, −1), 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝐷(2, −1). Prove quadrilateral ABCD is a rectangle 4) Quadrilateral QRST has vertices 𝑄(6, 7), 𝑅(11, 7), 𝑆(8, 3), 𝑇(3, 3). Prove quadrilateral QRST is a rhombus 5) The coordinates of the vertices of quadrilateral ABCD are 𝐴(4,1), 𝐵(1,5), 𝐶(−3,2) 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝐷(0, −2). Prove the quadrilateral is a square.