* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1-Light and Polarization Problem Set TE
Survey
Document related concepts
Speed of light wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Diffraction wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
History of optics wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
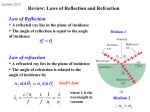
IB-Light and Polarization Problem Set Please answer the following questions on a separate sheet of paper: 1. List the electromagnetic spectrum from longest wavelength to smallest wavelength. 2. How do the speeds of these different electromagnetic waves compare? 3. How do their frequencies compare? 4. What exactly is oscillating in an electromagnetic wave? 5. What evidence is there that light is a wave? 6. What evidence specifies that light is a transverse wave? Explain how/why. 7. Explain polarization. 8. What is Brewster’s Angle? 9. Unpolarized light passes through two Polaroid filters; the axis of one is vertical and that of the other is at 60° to the vertical. What is the orientation and intensity of the transmitted light? a. First polarizer cuts intensity by ½ (as is true when unpolarized light goes through a polarized filter). The second polarizer is at 60 degrees which cuts it further by ¼ (using the equation) for a total Intensity = 1/8 original intensity. It is plane polarized at 60° to the vertical. 10. At what incident angle is reflected sunlight fully plane-polarized from a piece of glass (n = 1.5)? What would be the angle of refraction in this case? a. Tanθ = 1.5, so θ = 56.3° b. Reflected + Refracted = 90° for full plane-polarization, so Refracted = 9056.3 = 33.7° (this can be verified with Snell’s Law) IB Questions: 1. Unpolarized light of intensity I0 is incident on a polarizer. The transmitted light is then incident on a second polarizer. The axis of the second polarizer makes an angle of 60 to the axis of the first polarizer. The cosine of 60 is 1 . The intensity of the light transmitted through the second 2 polarizer is A. I0 . B. I0 . 2 C. I0 . 4 D. I0 . 8 (1) 2. This question is about polarization and liquid crystals. (a) A liquid crystal has the property of being able to rotate the plane of polarization of light. Explain what is meant by the expression “able to rotate the plane of polarization of light”. ................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) The diagram below is a representation of a liquid crystal display. P1 is a polarizer and P2 is an analyser. The transmission axis of P2 is at right angles to that of P1. E is an electrode. G is a glass plate upon which a shaped electrode is etched. Unpolarized light is incident on P1. (i) State, and explain, what the observer would see if the liquid crystal were not present. ......................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................... (2) (ii) Outline how the application of a potential difference between E and the electrode etched on G enables the observer to see the shape of the electrode. ......................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 7 marks) 3. This question is about polarization. (a) State what is meant by polarized light. ................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Polarized light of intensity I0 is incident on an analyser. The transmission axis of the analyser makes an angle with the direction of the electric field of the light. (i) Calculate, in terms of I0, the intensity of light transmitted through the analyser when = 60. ......................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) On the axes below, sketch a graph to show the variation with angle of the intensity of the transmitted light. (2) (c) Outline how polarizing sunglasses reduce glare from a reflecting surface. ................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 7 marks) IB Answers 1. D [1] 2. (a) polarized light is light in which the (electric) field vector vibrates in one plane only / OWTTE; the liquid crystal changes the plane in which (electric) field vector rotates; (b) (i) (ii) 2 nothing / whole area black; since the optical axes of P1 and P2 are at right angles / OWTTE; 2 since the liquid crystal rotates the plane of polarisation light is now transmitted by P2 / OWTTE; the electric field across the parts of the liquid crystal in the shape of the electrode on G no longer rotates the plane of polarization; the field of view of the observer will now contain a black area corresponding to the shape of the electrode on G / OWTTE; 3 [7] 3. (a) (b) light where the direction of the (electric) field is always / predominantly in the same plane; (i) I I 0 cos 2 60 I0 ; 4 1 1 (ii) general cos2 shape; max at = 0 and curve touches horizontal axis at = 90; (c) 2 light is (partially) horizontally polarized by reflection; sunglasses have a transmission axis at 90 to the plane of reflected light; intensity of reflected light is reduced; Award full marks for a clearly labelled diagram. 3 [7]