* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download K channel blockers
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
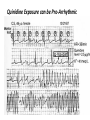
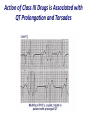
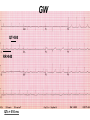
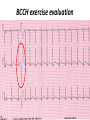
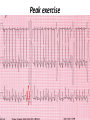
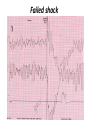
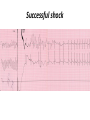
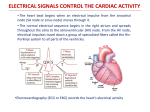
Drugs Controlling Myocyte Excitability and Conduction at the AV node Singh and Vaughan-Williams Classification Class III K channel Blockers Dofetilide , Dronedarone, Amiodarone Class I Na Channel Blockers Flecainide Propafenone Class II Beta Blockers Propranolol Metoprolol Class VI Ca Channel Blockers Diltiazem Class V Other Digoxin Two Strategies for Drugs Directly Treating AFib • Rhythm Control – True antiarrhythmic drugs – designed to restore sinus rhythm by affecting ion channels during the action potential – Na channel blockers • Flecainide and propafenone • Inhibits……… – K channel blockers • Dofetilide, • Inhibits……. – Multi ion channel blockers • Amiodarone and dronedarone • All-in-one Na, K, Ca and beta blockers (has rate control properties) • Vernakalant, Na and K channel blocker Antiarrhythmic Drugs Antiarrhythmic compound Cardiac Myocyte Membrane Effects route of administration Presumable indications Propafenone/flecainide/vernakalant: PO/IV Parox AF (AFI) Amiodarone PO and (?IV) Persist AF Dronedarone (AFI) multiple effects PO Persist AF Dofetilide blocks .... PO Parox and Persistent AFl and AF PO AF/Afl: rate control Verapamil/Beta blocker History of Antiarrhythmic Therapy Beta blockers Class II Amiodarone Class I 1960s 1950s 1990s 1999 1967 Class Ic Tree extracts Quinidine From China 1918 1700 1980s 1989 CAST ? 2005 Selective SWORD Class III compounds DIAMOND AFFIRM • Clinical trials: failure, failure, failure..... Vaughan-Williams Classification.. CLASS DRUGS ACTIVE IN EFFICACY TOXICITY Potential for PROARRHYTHMIA IA Moderately slow conduction Moderately prolong action potential Quinidine Procainamide Dispyramide Atria, Ventricles 2+ 3+ 2+ IB Minimally slow conduction Shorten action potential duration Lidocaine Mexilitine Phenytoin Ventricles 1+ 1+ 1+ IC Markedly slow conduction Minimally prolong action potential duration Flecainide Propafenone Encainide Atria, Ventricles 3+ 1+ 3+ II Beta Blockers AV node Ventricles 1+ 1+ 0 III Prolong action potential duration Amiodarone Bretylium Sotalol Ibutilide Atria, Ventricles 2+ 1+ 2+ IV Calcium Channel blocking drugs AV node 1+ 1+ 0 Red = drug effect on action potential. Blue = normal action potential. (Purkinje fiber) Treatment of ventricular arrhythmias – Drugs are generally used with a great deal of care due to potential for pro-arrhythmia (CAST trial in 1980s). – Ectopic activity arising from DADs/EADs: Not considered serious unless more than 4-10 beats in a row. Potentially treat with beta blockers, amiodarone or Na or K channel blockers in a healthy heart. – Re-entry arrhythmias: e.g. Ventricular tachycardia. Can attempt suppression in a healthy heart, with Na channel blockers, amiodarone, dofetilide; otherwise use implantable defribillators (ICD) + Beta blockade. – Inherited arrhythmias in children/adults: The long QT interval syndromes. Tendency for torsades de pointes due to repolarization instability. Treat with beta blockade to suppress EADs. If recurrent insert ICD. Brugada syndrome. Right ventricular disease, due to loss of function of Scn5A (Na channel). Treat with ICD, or quinidine. Catecholaminergic Paroxysmal Ventricular Tachycardia (CPVT). Beta blocker or ICD Quinidine Exposure can be Pro-Arrhythmic Implantable cardiac defribrillator Evolution Number of Worldwide ICD Implants Per Year (Ref: Corporate Market Share Database) ICD Evolution ICD Components Action of Class III Drugs is Associated with QT Prolongation and Torsades GW • Unusual spells since age 6 • Almost 20 years later, syncope during an argument • Fell off a balcony in 1994 • August 2002: cardiac arrest during an argument at a sporting event • Managed with implanted defibrillator GW QT=500 RR=940 QTc = 510 ms Brugada syndrome What you might want to know • • • • • • • • Flecainide Propranolol Amiodarone Diltiazem Dofetilide Digoxin (digitalis) Atrial fibrillation, Rate and Rhythm control Treatment of ventricular arrhythmias including LQTS, Brugada, CPVT Johnny’s Case • Previously well 13 year old • Midst of running, eyes became fuzzy, felt dizzy and then he fell over • 1-2 seconds of warning • Down perhaps 20-30 seconds • Back to normal within a very brief period • Doesn’t eat or drink much before being active Johnny’s Case (cont’d) • • • • • No family history of similar Paternal grandfather died of MI at 59 yrs Normal physical exam Local ECG showed PVCs Local exercise test showed PVCs and couplets Benign fainter or not? BCCH exercise evaluation Peak exercise Early recovery Failed shock Successful shock Catecholaminergic Polymorphic VT • CPVT is a familial arrhythmogenic disorder characterized by adrenergically mediated polymorphic ventricular tachyarrhythmias • Important cause of syncope and SCD in individuals with a structurally normal heart • First description CPVT by Reid et al in 1975 CPVT • Direct relation between adrenergic activation (physical or emotional stress) and the onset of arrhythmias • Exercise test: Typical pattern of bidirectional VT (reproducible) • Resting ECG: Normal • Echo: Normal • MRI: Normal • Autopsy: Normal CPVT • Average age at first event: 8 ± 2 years • Syncope triggered by exercise or emotion • Family history premature sudden deaths in up to 30 % of patients CPVT- Natural History • CPVT highly lethal disease; if left untreated; – By age 40: 80% of CPVT patients will develop symptoms (syncope, VT or VF) – Overall mortality is 30%-50% Johnny’s Case (cont’d) • Started on nadolol • Underwent MRI, blood for genetic testing • ICD implant