* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Great Recession Explained
Austrian business cycle theory wikipedia , lookup
Post–World War II economic expansion wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Nouriel Roubini wikipedia , lookup
Transformation in economics wikipedia , lookup
Great Recession in Russia wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
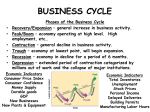
T HE G REAT R ECESSION E XPLAINED The Great Recession Explained The American economy has experienced some major changes over the past several years, and the American people have been closely watching its every move. With an immense amount of media coverage and political discussion surrounding this issue, it can be difficult to extract the basic causes and effects that are associated with this “Great Recession.” The impacts of this recession have indeed been greater than most other recessions, however all recessions are caused by the same downward economic spiral. While politicians disagree about how to escape this recession, the solution can be clearly identified by applying simple macroeconomic theory. P AGE 1 directly correlated to consumer spending behaviors. People generally cut their spending habits in an effort to save as much as possible. As this trend spreads across the country, less and less capital is directly infused into the economy, resulting in a decline in GDP. As the GDP continues to decline, companies tend to lay off workers in order to cut cost, which results in a rise in the unemployment rate. The increase in inflation and unemployment rate coupled with a decline in GDP ultimately causes an economy to fall into a recession. What is a recession? A recession can be classified as any significant decline in economic activity within a country lasting longer than 2 quarters. This decline in activity can be observed in industrial production, employment, real income as well as wholesaleretail trade. A recession generally lasts between 6 and 18 months, with interest rates declining during this time in an effort to stimulate the economy and encourage the borrowing of monies. What causes a recession? Many factors can contribute to an economy’s ultimate decline into a recession, but one major cause is that of inflation. Inflation is described as a rise in the prices of goods and services over an extended period of time. As the rate of inflation increases, the proportion of goods and services that can be purchased with the same amount of money The “downward spiral” of events which cause most declines. When the inflation rate increases, it is recessions. Courtesy of HowStuffWorks.com P AGE 2 T HE G REAT R ECESSION E XPLAINED What caused the American economy to money is being pumped into the country’s economy, so the economic state of our country also fall into “The Great Recession”? improves. This most recent recession that the United States suffered is often referred to as “The Great Recession”. According to National Bureau of Economic Research, the recession began in December 2007 and ended in June 2009. The stock market crash of 2000 set the ground work for the recession. The Federal Reserve lowered the interest rate to help with the economic slowdown created by the crash. This action led to banks giving out loans to individuals and companies that were not truly qualified to pay back their loans. Thus many people defaulted on loans. On the company level, if a certain company could not afford to pay off a debt they had to find a way to cut their costs. The easiest and fastest way to cut costs is to decrease labor, so firms were forced to make massive layoffs. Increased unemployment led to a decrease in consumer spending. How can we recover from this recession? Where do we start? To get this cycle of spending started, This consumer spending can be initiated by either an increase in government spending or a decrease in taxes. Both lead to the same effects and get our nation out of recession. It may seem odd to many Americans that in order to make more money we need to spend more money - but it is a proven theory and a necessity to overcome this Great Recession. What improvements have been made? To help fix “The Great Recession” the government has implemented several forms of legislation to get the country back on track, such the stimulus package and the Recovery Act. The main purpose behind these bills was to get people back to work Macroeconomics teaches us that the only way to get out of a recession is to spend. Economists have and stimulate the economy through spending, whether that was through bailing out big spent years theorizing the solution to a recession companies like the auto industry and saving them and discovered it all comes down to spending. from bankruptcy or funding new government Once spending on goods and services increases, projects in infrastructure, clean energy and inventories of businesses decrease. When firms have less available merchandise they are forced to education. hire more people to produce more goods. This means an increase in labor demanded by companies to keep up with the increase in products demanded. As industries hire more people to keep Many Americans are under the impression that government spending is preventing our economy up with production, those people make more from recovering from “The Great Recession”. money and have more to spend. Consumer Macroeconomic theory proves that this is not the spending then increases, so part of their income case. Both government and consumer based goes back into the goods market, and the cycle starts all over again. As people spend money, more spending are absolutely necessary to pull a nation out of recession. people get jobs so the unemployment rate goes down, which is a definite sign of overall improvement. In addition, GDP goes up since more P AGE 3 T HE G REAT R ECESSION E XPLAINED References Harvey, J. T. (2011.) The Great Recession: How We Got Here (and How to Get Out). Forbes. 07 October 2011. Accessed 22 November 2012. online. http:// www.forbes.com/sites/ johntharvey/2011/10/07/the-greatrecession/ Joint Economic Committee Congress of the United States. (2009). The Challenge of Creating Jobs in the Aftermath of “The Great Recession”(S. HRG. 111523).Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office. Recession. (2012, JANUARY). Investopedia. Retrieved from http:// www.investopedia.com/terms/r/ recession.asp Stiglitz, J. (2009). Interpreting the Cause of the Great Recession of 2008. Retrieved from: http://fcic-static.law.stanford.edu/ cdn_media/fcic-testimony/2009-1020Stiglitz-article-2.pdf What causes a recession?. (2012, JANUARY). Investodpedia. Retrieved from http:// www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/08/ cause-of-recession.asp