* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exam Name___________________________________
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
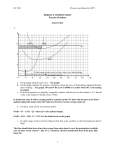
Exam Name___________________________________ MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Perfect competition is an industry with A) a few firms producing goods that differ somewhat in quality. B) many firms producing goods that differ somewhat. C) a few firms producing identical goods. D) many firms producing identical goods. Quantity sold 5 6 7 1) Price $15 $15 $15 2) In the above table, if the firm sells 5 units of output, its total revenue is A) $30. B) $90. C) $15. 2) D) $75. 3) In the above table, if the quantity sold by the firm rises from 6 to 7, its marginal revenue is A) $15. B) $105. C) $90. D) $30. 3) 4) In the above table, if the quantity sold by the firm rises from 5 to 6, its marginal revenue is A) $15. B) $90. C) $75. D) $30. 4) 5) Which of the following characterizes a perfectly competitive industry? A) Each firm sets a different price. B) The industry demand curve is vertical. C) The demand for each individual firmʹs product is perfectly elastic. D) Each firm produces a product slightly different from that of its competitors. 5) 6) A competitive firmʹs total revenue minus its total opportunity cost equals its ________. A) economic profit B) marginal revenue C) opportunity cost D) normal profit 6) 7) At a firmʹs break-even point, definitely its A) marginal revenue equals its average variable cost. B) marginal revenue exceeds its marginal cost. C) marginal revenue equals its average fixed cost. D) total revenue equals its total opportunity cost. 7) 1 8) In the above figure, the firm will produce A) 15 units B) 5 units. 8) C) 0 units. D) 20 units. 9) In the above figure, the marginal cost of the last unit produced by the profit maximizing firm is A) $15. B) $10. C) $20. D) $5. 10) In the above figure, the firmʹs total economic profit is equal to A) $150. B) $50. C) $200. 10) D) MR - MC. 11) 11) In the short run a perfectly competitive firm will A) shut down if P > AFC. C) shut down if P < AVC. Output (tons of rice per year) 0 1 2 3 4 5 9) B) shut down if P < ATC. D) never shut down. Total cost (dollars per ton) $1,000 $1,200 $1,600 $2,200 $3,000 $4,000 12) Based on the table above which shows Chipʹs costs, if rice sells for $600 a ton, Chipʹs profit-maximizing output is A) less than one ton. B) between one and two tons. D) between two and three tons. C) between three and four tons. 2 12) 13) Based on the table above which shows Chipʹs costs, if rice sells for $600 a ton, Chip will A) stay open because the price is above his minimum average variable cost. B) stay open because he earns an economic profit. C) shut down because the price is below his minimum average variable cost. D) shut down because he incurs an economic loss. 13) 14) Based on the table above which shows Chipʹs costs, if rice sells for $600 a ton, Chip A) incurs an economic loss and should shut down in the short run. B) earns an economic profit and should stay open in the short run. C) incurs an economic loss, but should stay open in the short run. D) earns an economic profit, but should shut down in the short run. 14) 15) Consider the perfectly competitive firm in the above figure. The profit maximizing level of output for the firm is equal to A) 17 units. B) 0 units. C) 14 units. D) 19 units. 15) 16) Consider the perfectly competitive firm in the above figure. At the profit maximizing level of output, the firm is earning A) an economic loss equal to $187.00. B) a normal profit. C) an economic loss equal to $119.00. D) an economic loss equal to $123.50. 16) 17) Consider the perfectly competitive firm in the above figure. The shutdown point occurs at a price of A) $11.00. B) $16.00. C) $22.00. D) $12.00. 17) 18) Consider the perfectly competitive firm in the above figure. At what price will long-run equilibrium occur? A) $23 B) $22 C) $12 D) $11 18) 3 19) A perfectly competitive firmʹs short-run supply curve is the same as its A) MR curve. B) AVC curve. C) ATC curve. D) MC curve above the minimum of the AVC curve. 19) 20) In the above figure, below what minimum price will the firm shutdown rather than produce? A) for any price less than $12 per unit B) for any price less than $4 per unit C) for any price less than $8 per unit D) for any price less than $16 per unit 20) 21) A perfectly competitive firm is definitely earning an economic profit when B) MR < MC. C) P > AVC. A) P < ATC. 21) D) P > ATC. 22) In the short run, perfectly competitive firms ________ but in the long run, perfectly competitive firms make ________. A) make economic losses; economic losses B) can incur economic losses; zero economic profit C) must positive economic profits; positive economic profits D) can incur economic losses; positive economic profits 4 22) Quantity (coats per day) 7 8 9 10 11 Total cost (dollars per coat) 1,410 1,640 1,910 2,210 2,560 23) The table above shows the total cost incurred by Sueʹs Coat Shop, a perfectly competitive firm. If the market price of a coat is $285, Sueʹs will maximize economic profit by selling ________ coats a day. A) 8 B) 11 C) 9 D) 7 23) 24) Tammy sells woolen hats in a perfectly competitive market. The marginal cost of producing 1 hat is $24. The marginal cost of producing a second hat is $26 and the marginal cost of producing a third hat is $28. The market price of a hat is $26. To maximize profit, Tammy produces ________ a day. A) as many hats as possible B) 3 hats C) 1 hat D) 2 hats 24) 25) If perfectly competitive firms exit an industry, the A) profits of the remaining firms decrease. C) industry supply curve shifts leftward. 25) B) price of the good or service falls. D) output of the industry increases. 26) In the long run, a perfectly competitive firm can A) earn an economic profit. B) earn a normal profit. C) earn an economic profit, earn a normal profit, or incur an economic loss. D) incur an economic loss. 26) 27) A firm is producing the profit-maximizing amount of output when it is producing where its ________ curve intersects its ________ curve. B) MC; AVC C) MC; MR D) MC; TR A) MC; ATC 27) 28) The profit maximizing condition for a perfectly competitive firm is A) TR = TC. B) P = ATC. C) MR = P. 28) D) P = MC. 29) When marginal revenue equals marginal cost, a perfectly competitive firm is A) maximizing its profit. B) establishing its shutdown point. C) maximizing its revenues. D) determining the price it will set. 5 29) 30) Fast Copy is a perfectly competitive firm. The figure above shows Fast Copyʹs cost curves. If the market price is 4 cents per page, what is Fast Copyʹs profit maximizing level of output? A) 16 pages per hour B) 64 pages per hour C) 48 pages per hour D) 32 pages per hour Quantity 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Total fixed cost, TFC (dollars) 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 30) Total variable cost, TVC (dollars) 0 100 180 220 300 390 500 640 800 1000 1250 31) The table above shows some of the costs for a perfectly competitive firm. The firm will produce 9 units of output if the price per unit is A) $200. B) $1750. C) $300. D) $500. 31) 32) In a perfectly competitive market in the short run, as the market demand increases, the firms ________ their output and their profit ________. A) decrease; decreases B) decrease; increases C) increase; decreases D) increase; increases 32) 6 Answer Key Testname: UNTITLED1 1) D 2) D 3) A 4) A 5) C 6) A 7) D 8) A 9) B 10) B 11) C 12) D 13) A 14) C 15) A 16) C 17) A 18) B 19) D 20) D 21) D 22) B 23) C 24) D 25) C 26) B 27) C 28) D 29) A 30) C 31) A 32) D 7