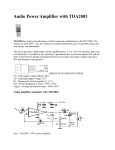
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Feedback in Amplifiers
Oscilloscope types wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Tektronix analog oscilloscopes wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Phase-locked loop wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Instrument amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Distortion (music) wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
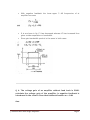
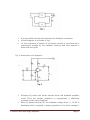
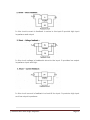
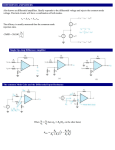
Chapter 4 : Feedback in Amplifiers Contents Types of feedback, effect of negative feedback on gain, bandwidth, stability, distortion and frequency response etc. voftage series, current series, voltage shunt, current shunt feedback circuits and their analysis. POINTS TO PONDER Feedback amplifiers are those in which a fraction of the output energy is fed back to the input of the same circuit. If the feedback signa[ is in phase with the input signal then it is a positive feedback or direct feedback. In this case the signal is additive. If the feedback signal is 180° out of phase with the input signal then it is a negative feedback. In this case the signal opposes the input signal. Amplifier without feedback gives gain: Where Is the output voltage and is the nput voltage. Amplifier with feedback i.e. negative feedback give gain: Where, A is the amplifier gain without feedback and f is the feedback fraction. Negative feedback amplifiers as used because: It improves gain stability. Reduce the distortion or noise. Decreases the output impedance. Increases the input impedance. Increases bandwidth. Due to reduced noise and distortion and increase bandwidth, the negative voltage feedback is used in radio receivers, public address J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 1 system etc. For perfect impedance matching negative current feedback is used at the output stage. An emitter follower circuit is widely used in electronic instruments because of its input. impedance is high and output impedance is low. Series feedback connections generally increases the input impedance where as shunt feedback connection decreases the input impedance Voltage feedback generally decreases the output impedance and the current feedback generally increases the output impedance. The series-voltage feedback are used in negative feedback amplifiers. Q 1. Why is negative feedback employed in high gain amplifiers? Ans If A is the gain of an amplifier, then the gain bandwidth product is given by A x BW Where BW= f2—f1 Now when negative feebback is applied the amplifier gain is reduced But at the same time bandwidth increases If A is gain of amplifier and A be the gain of an amphfier with negative feedback then where, is the feedback fraction. Gain reduces. Thus, high gain amplifiers are used in case of negative feedback so as to maintain the jain to a specific level. J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 2 Q 2.Why is —ye feedback provided in Wein- bridge oscillator ? Ans. A negative feedback ensures stability and constant output In case of Wein bridge oscillator the negative feedback is provided through the voltage divider circuit in the output amplifier through resistances (say R3 and R4) in Wein bridge. Basically, a temperature sensitive tungsten lamp is used in place of R4 Its resistance increases with current As soon as, the amplitude of output tend to increase, more current would provide more negative feedback. This brings back the output to its original value A reverse action would take place if the output tends to decrease. Q 3. How does. negative feedback increase bandwidth of an amplifier ? Ans. The bandwidth of an amplifier circuit without feedback is equal to the separation between the 3 db frequencies f1 and f2 When f1 = lower 3 dB frequency f2= upper 3-dB frequency BW = f2 — f1 Let A be its gain, then the gain bandwidth product is A x BW. Now, when negative feedback is applied, the amplifier gain reduced. Since the gain bandwidth product has to remain the same in both cases. J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 3 With negative feedback the lower upper 3 dB frequencies of ai amplifier becomes It is as shown in fig. f’1 has decreased whereas t’2 has increased thus gives a wider separation or bandwidth. Since gain bandwidth product is the same in both cases Q 4. The voltage gain of an amplifier without feed back is 3000. calculate the voltage gain of the amplifier is negative feedback is introduced in the circuit. Given that feedback fraction m = 0.01 Ans. J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 4 Voltage gain with negative feedback is given by Q 5. How that negative teed back changes the impedances? (Explain with mathematical experssion) Ans. Following fig.. shows the typical feedback (negative) connection: Effect of negative feedback on. input impedance J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 5 • Thus, series voltage negative feedback increases the input impedance of an amplifier by a factor • Effect of negative feedback on output impedance: The output impedance is determined by applying a voltage V resulting in a current I with Thus, series voltage negative feedback reduces the output impedance of an amplifier by a factor J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 6 Q6. What do you understand by bandwidth of an amplifier? Ans. For each amplifier system, there is a band of frequencies in which the magnitude of the gain is either equal or relatively close to the midband value. To fix the frequency boundaries of relatively high gain, O.7O7Av mid choosen to be the ‘gain at the cut 6ff levels. The corresponding frequencies f1 and f2 are generally called the corner, cut off, break or half- power frequencies. The bandwidth (or passband) -of this system is determined by f1 and 2, i.e. Bandwidth (BW) = f2 — f1 Q 7. Explain in brief the effect of changing Q of the coil used in tank circuit, on its bandwidth. Ans Higher the value of Q, the smaller is the bandwidth. J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 7 It also concluded that Q is a measure of ability of a tank circuit to select a band of frequency. The higher the Q of a circuit, the greater is its ability as a frequency select or as its bandwidth is inversely proportional to the quality factor. Q 8. Compare the negative feedback and positive feedback. Ans. Q 9. Define: Phase Margin. Ans. Phase margin: It is designated by PM. It is used in feedback amplifiers and is defined as the angle of 1800 minus the magnitude of the angle at which th value l3Al is unity 1(0db). J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 8 Q 10. Name the feedback amplifier topologies. Ans. There are basic four types of feedback amplifier topologies: (a) Voltage — series feedback amplifier (b) Voltage — shunt feedback amplifier (c) Current series feedback amplifier (d) Current — shunt feedback amplifier Q 11. The gain and distortion of an amplifier are 150 and 5% respectively without feedback If the stage has 10% of its output voltage applied as negative feedback, find the distortion of the amplifier with feedback Ans. Given: Gain without feedback, Av = 150 Distortion without feedback, D 5% J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 9 Thus, distortion reduces from 5% to 0.313% by using —ye feedback. Q 12. Explain a current shunt feedbackcircuit and perform a suitable analysis. OR Write short note on Current shunt feedback ? Ans. Current shunt feedback circuit It is also called as series derived shunt fed feedback. It is a parallel-series (PS) prototype It is as shown in fig (a). Here, feedback network shunts the input but is in series with the output Hence the output resistance of the ampIifer is increased whereas its input resistance is decreased by a factor of loop gain The two stage amplifier using a current shunt negative feedback is as shown in fig (b) J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 10 The feedback circuit consisting ‘of CF and RF samples the. output current and develops a feedback voltage is parallel with the input voltage. The unbypassed emitter resistor of Q2 provides current sensing. Q.13. Calculate the gain of a —ye feedback amplifier with an internal gain Av = 75 and feedback fraction Av doubles? . What will be the gain if Ans. Gain of a —ye feedback amplifier is given by: J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 11 Thus, it is clear from the above calculation that if 0% doubles, the gain of the amplifiOr increases. Q 14. With circuit diagram explain current-series feedback. OR Explain the current series teedback circuit in detail with a neat diagram and perform a”suitable analysis. Ans. Following figure shows the block diagram current-series feed back: J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 12 It is also called a series-derived series-fed feedback connection. A block diagram is as shown in fig 1. In this connection a fraction of the output current is converted into a proportional voltage by the feedback network and then applied in series with the input Fig. 2 shows the circuit diagram: Following fig shows the series derived series fed feedback amplifier circuit Since the emitter resistance is unbypassed, it effectively provides current series feedback. When 1E passes through RE, the feedback voltage drop V = 1E RE is developed which is applied in phase opposition to the input voltage V, J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 13 This negative feedback reduces the output voltage V0. This feedback can, however, be eliminated by either removing or bypassing the emitter resistor. In case an input signal is applied, the resulting collector current IC develops output voltage across the collector load and emitter current 1E develops ac voltage equal to ‘E RE (1E Ic) across the emitter. The input voltage to amplifier, which is equal to VSE, is given by Q 15. With negative feedback voltage gain reduces, explain why? Ans. The overall gain with negative feedback is ie. Voltage gain reduces by the factor of Let take a care of voltage series feedback as shown below. J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 14 From this eq. it is clear that with feedback the amplifier gain reduced as the factor Q 16. Explain the effect of negative feedback on the gain, bandwidth, frequency, response of an amplifier. Ans. J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 15 Effect of negative feedback on: (i) Gain :The gain is stable by using negative feedback. As voltage gain with negative feedback is given by So it is independent of internal gain i e stable ii) Bandwidth:With negative feedback the gain reduces but gain bandwidth product is remain constant So the bandwidth increases to compensate the reduction in gain (iii) Frequency: Response With negative feedback bandwidth increases and due to which the frequency response is improved. Q 17. Draw and design a series transistor voltage regulator circuit to provide output of 9 V for a maximum load current of 1 0 A, when the input voltage variation is 15 to 18 V and transistor gain is 50 Ans. J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 16 It is known as emitter follower because voltage at the emitter follows the base voltage In this the transistor behaves like a variable resistor whose resistance is determined by the base current. It is also called pass transistor because all the load current must pass throughit. J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 17 Q 18. Explain the concept of feedback. Ans. Feedback concept is widely used in any system either electrical, electronics or mechanical. In any system, main aim is to maintain output parameters stable with time inspite variation of environment change or system parameter variations. Feedback concept is used to maintain system stable. Feedback is used in daily life process. Feedback is essential to maintain performances Of the system. The electronics, feedback is used in amplifiers, oscillators by taking a part of or fraction of output mixed with input. The gain of amplifiers may change due to shift in operating point. ft can be due to change in temperature and change in components of amplifier. The feedback in amplifier keep gain constant inspite of above said variations. J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 18 Q 19. What are the different types of negative feedback? Explain each with block and diagram. Ans. Different types of negative feedback are 1. Voltage feedback 2. Current feedback The combination of both may also be present in a circuit. At the same, time, both voltage current can be feedback to the input either in series or parallel, then they named as: 1. Series — Voltage feedback 2. Series — Current feedback 3. Shunt — Voltage feedback 4. Shunt — Current feedback In this circuit voltage is feedback to the input in series This employed high input impedance and low output impedance and invanably employed in negative feedback amplifies. J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 19 In this circuit current is feedback in series to the input.It provide high input impedance and output In this circuit voltage is feedbackin shunt to the input. It provides low output impedance input and high. In this circuit current is feedback in shunt t6 the input. It provicies high input and low output impedance. J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 20 Q 20. Find (a) feedback ratio (b) feedback factor (C) voltage gain without feedback (d) voltage gain with feedback for a circuit given below. J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 21 (d) Voltage gain with feedback: Q 21. An amIifier has a midband gain of 125 and a bandwidth of 250 KHz.If 4% negative feedback is introduced, find the new bandwidth and gain J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 22 Q 22. Draw a voltage-series feedback circuit How are its input and output resistances calculated? OR Draw the circuit diagram of voltage series feedback amplifier and derive the expressions for input and output impedances . Ans. Voltage series feedback circuit J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 23 Q 23. Describe with necessary derivations, the effect of negative feedback on the bandwidth and distortion in an amplifier. J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 24 Ans. 1. Effect of negative feedback on the distortion in an amplifier : Distortion reduces when a negative feedback is used in amplifiers. The following diagram clears the reduction of distortion In the figure let amphfier ‘A’ gives distortion ‘d’ without any feedback. When feedback path is provided the gain ‘A’ becomes ‘Af’ and the distortion becomes df at the output. It is clear from figure that if ‘d’ is the distortion at the input then, ‘di’ is the distortion at output due to negative feedback. It is because a part of distortion ‘di’ i.e. ‘df’ is fed back to the input. This is added in reverse direction because of negative feedback including gain ‘A’. 1.From this expression distortion is reduced by because of negative feedback. 2. Effect of negative feedback on bandwidth : By using negative J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 25 feedback the bandwidth increases As the gain of an amplifier using negative feedback decreases because where ‘A’ is gain of amplifier without feedback Thus, a fraction of the is effect in gain Due to this upper cut oft frequency i e f2 or IJCF and lower cut off frequency i or LCF will be affected Due to negative feedback ‘f1’ i e lower cut off frequency decreases by factor increases by factor SW =(f2 — f1). and ‘f2’ i e upper cut off frequency Hence bandwidth increases. Because, bandwidth Q 24. Derive an expression for the gain of negative voltage feedback amplifier Ans. It is as shown in fig. The gain of amplifier without feedback is Av This then by feeding a fraction of the output voltage J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers back to amplifier input. Thus, the Page 26 actual input to the amplifier is signal voltage minus feedback voltage ie The output V0 must be equal to the input voltage gain Av of the amplifier. But multiplied by is the voltage gain of the amplifier with feedback Thus it is given by Thus using negative voltage feedback the gain reduced by a factor But it does not affect the current gain of the circuit Q 25. What are the different types of feedback? With help of diagram explain a RC coupled amplifier. Discuss its gain response. 0R Explain transistor RC coupled amplifier with special reference to frequency, response, advantages, disadvantages and applications. OR Explain the operation and frequency analysis of RC coupled amplifier. Ans. There are two types of feedback 1. Positive feedback J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 27 2. Negative feedback 1. In positive feedback if the feedback voltage (or current) is so applied as to increase the input voltage (i.e. it is in phase with it),then it is called positive feedback. Other names for it are regenerative or direct feedback. 2. In negative feedback if the feedback voltage (or current) is so applied as to reduce the amplifier input (i.e. it is 1800 out of phase), than it is called as negative feedback. Other names for it are degenerative or inverse feedback. RC Coupled Amplifier A two-stage AC coupled amplifier circuit using identical transistors is as shown In fig. A coupling capacitor C is used to convert the output of first stage to the base (i.e. input) of second stage and so as the coupling from one stage to next is achieved by a coupling capacitor followed by a connection to a shunt resistor, therefore, such amplifiers are called resistance capacitance coupled amplifiers. Operation V is the input signal applied to the base of first transistor Q1 its amplified brm appears across the collector resistor R. J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 28 This amplified signal developed across Rc is ed to the base of the next transistor Q2 through coupling capacitor C, The second stage further amplifies the signal. This is how, the cascaded stages amplify the signal and the overall gain (G = G1 x G2 x G) is considerably increased. It may be noted that the overall ga is always less than the product of gains of individual stages It is because of effect,ve load resistance of each stage decreases due to shunting effect of the input resistance of the next stage. Voltage V frequency response is as shown in fig 1. At low frequencies (< 50 Hz) the gain is small. 2. At mid frequencies (50 Hz to 20 kHz) also called as audio frequency range the gain is almost constant. 3. At high frequencies (> 20 kHz) the gain drops off as shown in fig clearly. Advantages: 1. It is the most convenient and least expensive multistage amplifier. 2. It has a wide frequency response i e its gain versus frequency curve remain constant for a wide frequency range. 3. It gives less frequency distortion. Disadvantages: J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 29 1. Th& overall gain of the amplifier is comparatively small because of the loading effect of number of stages. 2. it bcomes noisy wth the passage of long time 3. It provides poor impedance matching between the stages Applications R-C coupled amplifiers provide excellent audio-fidelity over a wide range of frequencies. Therefore they are widely used as voltage amplifiers e g in the initial stages of Public Address System. Q 26. Explain types of negative feedback in transistor circuits? Ans. Transistor circuit with negative voltage freedback The components and necessary feedback voltage is . J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers act as feedback circuit and provide the to the input. Let the voltage feedback Page 30 This circuit reduces the output impedance and also decreases the gain of the amplifier. all the modern high pass. transistor ampllfier negative feedback is employed. Transistor circuit with negative current feedback 1.Common-emitter circuit with by-pass capacitor When an ac signal v is applied at the input and voftage increases during positive halt the emitter-base junction becomes more forward biased. This develops an ac voltage across the emitter resistor. Thus, a negative voltage is feedback to the input. Since, the ye voltage feedback to the input is proportional to the output current hence the irrent feedback circuit. Emitter follower : J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 31 It has high input impedance and low output impedance. In theon-emitter amplifier circuit, if the collector resistance R is reduced to zero an output is from the emitter terminal, instead of collector terminal. When ac signal Vs is applied at the input, resulting current flows through and produces an output voltage across it This voltage opposes the signal voltage thus provides negative feedback. Q 27. Find the loop gain and overall gain for negative feedback if A = 200 and B = 0 02 Ans. Loop gain of feedback amplifier is A x M 200 x 0.02=4 and gain with feedback J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 32 Q 28. The gain of an amplifier without feedback is 100 and with negative feedback is 50. If due to ageing the amplifier gain falls to 60, find the %age reduction in stage (i) without feedback and (ii) with negative feedback. Ans. (i) %age reduction in stage gain without feedback (ii) %age reduction in stage gain with feedback As, negative feedback J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 33 Q 29. The input impedance of an amplifier is 4 Ks2 and voltage gain is 2000. If negative feedback of m 0.006 is employed than what will be the input impedance of a circuit 25%. Q 30. The voltage gain of an amplifier is 100 and with negative feedback circuit m= 006. Calculate the %age change in the gain with feedback if A falls as 10. J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 34 Ans. Gain of the amplifier with negative feedback, And now absoftite gain of the amplifier without negative feedback after ageing is say A1. A1 = A—A’ = 100—20 =80 And gain with negative feedback after ageing Now, %age change in system gain Q 31 The gain of amplifier is 200 with its bandwidth as 20 KHz If 20% of negative feedback is applied in amplifier then determine the feedback gain and new bandwidth of amplifier J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 35 Ans. Feedback fraction m=20%=02 gain with negative feedback Q 32. An frequency output is frequency amplifier has gain = 200 without feedback the cut off = 20 KHz and input resistance is 20 K If one percentage of applied as negative feedback, what is the new cut off and input resistance J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 36 Q 33. For emther fouower circuit shown n figure. Measure the input resistance. Ans. The voftage at base terminal of transistor is J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 37 Q 34. Write the amplifier classification, companson signal and output signai for cases of positive (P) and negative (N) voltage series J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 38 current series, voltage shunt and current shunt feedback amplifiers. Ans. 1. Voltage series (Series shunt): Negative and positive feedback (i) Amplifier classification — Voltage (ii) Comparison signal — Voltage (iii) Output signal —* Voltage 2. Current series (Series series): Negative and positive feedback (i) Amplifier classification -+ Voltage to current converter (ii) Comparison signal —* Voltage (iii) Output signal -4 Current 3. Voltage shunt (Shunt shunt) Negative and positive feedback (i) Amplifier classification —+ Current to voltage converter (ii) Comparision signal —+ Current (iii) Output signal —* Voltage 4. Current shunt (shunt series): Negative and positive feedback: (i) Amplifier classification -4 Current (ii) Comparison signal -+ Current (iii) Output signal —* Current – Q 35. Explain the general feedback system arrangement. Ans. J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 39 A feedback system consists of the following blocks 1. Basic amplifier to amplify the signal. 2. Sampling network to obtain current or voltage proportional to the output. 3. Feedback network (usually two part network) comosed of passive components such as resistance, óapacitor and inductor. 4. Mixing network to get the mixed signal of input and feedback signal for the error output. Q 36. Explain how the negative feedback amplifier improves stability, reduces noise and increases the input impedance. Ans. (i) Negative feedback improves stability by making gain of the amplifier independent of change in power supply or change in the parameters of transistor. The gain of an amplifier with negative feedback is J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 40 By taking Am>>1 This gain of feedback is independent of the internal gain A. Hence the negative feedback give, more stability. (ii) Negative feedback reduces noise (or distortion) by employing reverse direction distortion whch is added to the original distortion as Thus, distortion or noise is reduced by factor (1 + Am). (iii) Following fig. shows the typical feedback (negative) connection Effect of negative feedback on input impedance J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 41 Thus, series voltage negative feedback increases the input impedance of an amplifier by a factor Q 37. An amplifier with 60 dB gain without feedback has output impedance equal to 12 k2. It is required to modify its output impedance to 600 2 by the feedback. Calculate feedback factor and percentage change in overall gain for 10% change in the gain of basic amplifier. Ans. Open-loop voltage gain, A = 60 dB or antilog J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 42 Output impedance with feedback, Now, feedback factor is given by For 10% change in openoop gain, we have new open-loop gain as J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 43 J Srinivasa Rao- Multi Stage Amplifiers Page 44