* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CHEM 107
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
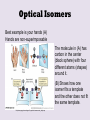
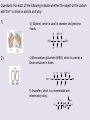
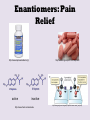
Part 2 • Chapter 14- aldehyde and ketone – Predicting reactions. • Chapter 14- Stereoisomerism • • • • structural isomers stereoisomers chiral / achiral enantiamers Frequency: BB Structural isomers and Stereoisomers http://www.studyvilla.com/isomerism.aspx Structural Isomers and Stereoisomers Structural isomers- same molecular formula, but different structural formula. CH3CH2CHO propanal C3H6O CH3COCH3 propanone C3H6O H H C H O O H C C H Same molecular formula C H H C H H C HH different structural formula H Structural Isomers and Stereoisomers •Stereoisomers – the same structural formula, but different arrangement of the atoms in space. two types: –Geometrical isomers (already have seen with alkenes) • Butene H H C H H C H C H H C CH3 C H CH3 C CH3 C H CH3 C H H H trans- cis- –Optical isomers – have non-superimposable mirror images Optical Isomers Best example is your hands (A) Hands are non-superimposable The molecule in (A) has carbon in the center (black sphere) with four different atoms (shapes) around it. (B) Shows how one isomer fits a template and the other does not fit the same template. http://www.google.com/imgres?q=optical+isomers main_body.asp Optical Isomers • Non-superimposable mirror images are called chiral. • The hands and feet are chiral. • The glass, bat and ball are all Superimposable and are Called achiral. • Chiral molecules are also called enantiomers. • In order for a carbon atom to be chiral it has to have four different atoms or groups http://www.creation-science-prophecy.com/amino of atoms attached to it. Gum Drop Isomers • Pair up • Get a bag of gum drops, 8 toothpicks. Questions: For each of the following indicate whether the object or the carbon with the * is chiral or achiral and why: 1) 3) Glycerol, which is used to sweeten and preserve foods. HO 2) H OH H C C* C H H H OH 4) Monosodium glutamate (MSG), which is used as a flavor enhancer in foods. Na+ -O O H H NH2 O C C C C H H H * C OH 5) Ibuprofen, which is a nonsteroidal antiO infammatory drug. CH3 H H C OH C C C* CH3 CH3 H H Enantiomers : Your Nose Knows. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Spearmint http://www.bojensen.net/EssentialOilsEng/Essential Oils05A/EssentialOils05A.htm Caraway seeds used in rye bread Olfactory receptors in the nose detect these enantiomers as two defferent odors. Taste buds in the tougue can also detect the difference. http://butane.chem.uiuc.edu/cyerkes/Chem104ACSP08/Lecture_Notes_104/lect21c.html Enantiomers: Pain Relief http://www.naproxensodium.org/ active http://www.drugs-expert.com/naproxen/ inactive http://www.chem.moravian.edu http://www.google.com/imgres?q=optical+isomers main_body.asp Represent Compounds with Chiral Carbons • 3-D models: COOH eye Lactic acid HO H CH3 http://www.3dchem.com/molecules.asp?ID=415 • 3-D to 2-D dash and wedge model COOH HO C H CH3 Remove the chiral C COOH H HO CH3 Fischer Projection Enantiomers • 3-D: COOH HO COOH H H OH CH3 • 2-D: CH3 COOH COOH H HO CH3 OH H mirror CH3 Acetals and Hemiacetals Hemiacetals • are carbon atoms that contain a hydroxyl group –OH and an alkoxy group –OR. • are formed when an alcohol adds to an aldehyde or ketone in the presence of an acid catalyst. • react with a second alcohol molecule to produce an acetal, a carbon with two alkoxy groups –OR. Acetals from Aldehydes Alcohol adds to the aldehyde carbonyl producing a hemiacetal. When a second alcohol adds, it forms an acetal. Acetals from Ketones Ketones are less reactive than aldehydes because the carbonyl carbon is more positive in aldehydes. react with one alcohol molecule to form a hemiacetal, and react with a second alcohol molecule to form an acetal. Cyclic Hemiacetals In glucose, a cyclic hemiacetal between the C═O group and the –OH group on carbon 5, forms a stable, six-atom ring. Cyclic Acetals Cyclic acetals • form when an alcohol adds to a cyclic hemiacetal. • are very important in carbohydrate chemistry. It is the type of linkage that bonds glucose molecules to other glucose molecules in the formation of disaccharides and polysaccharides. Glucose + Glucose = Maltose Maltose • is a disaccharide consisting of two glucose molecules linked by an acetal bond (shown in red). • is produced from the hydrolysis of starch from grains. • has one glucose that retains the cyclic hemiacetal bond (shown in green). Maltose Maltose, a disaccharide, is produced from the hydrolysis of the starches in grains, such as barley.