* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dot map of the World
Ordnance Survey wikipedia , lookup
History of geography wikipedia , lookup
Scale (map) wikipedia , lookup
Contour line wikipedia , lookup
Iberian cartography, 1400–1600 wikipedia , lookup
History of cartography wikipedia , lookup
Mercator 1569 world map wikipedia , lookup
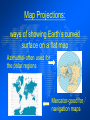
Map Elements Map Projections Scale Bar Political, Physical, and Thematic Maps Map Elements: • Title-subject of the map • Symbols-represent information (natural resources & economic activities) Map Elements: • Labels-names of places (cities, countries, rivers, mountains, etc.) • Colors-represent different kinds of information (blue=water, etc.) Map Elements: • Lines of latitude-imaginary horizontal lines measuring distance n or s of the equator • Lines of longitude-imaginary vertical lines measuring distance e or w of the prime meridian Map Elements: • Scale-shows how much distance on Earth is represented by distance on the map • Legend (key)-explains what the symbols and colors on the map represent Map Elements: • Compass roseshows directions north (N), south (S), east (E), and west (W) • Locator globeshows the specific area of the world that is shown on a map Which map elements do you see below? Map Projections • The world is a sphere but maps are flat, so all maps distort the shapes, areas, distances, and directions found in the real world. Map Projections: ways of showing Earth’s curved surface on a flat map Azimuthal-often used for the polar regions Mercator-good for navigation maps Map Projections Homolosineaccurately shows the shape and area of landmasses Robinson-shows the shape and area of continents & oceans with reasonable accuracy Map Projections Winkel Tripel-modified version of the Robinson projection, with less distortion of area and shape. Scale Bar • shows how much distance on earth is shown on the map • usually shown in both inches and centimeters Political Maps • shows features that humans have created (countries, states, provinces, and cities) • features are labeled, and lines show boundaries Physical Maps • shows natural features of physical geography (mountains, plains, valleys, deserts, oceans, lakes, rivers, etc.) • can also show elevations (height of a physical feature) and relief (change in elevation from one place to another) Physical Maps Thematic Map: • a map that shows a type of geographical information (economic activity, natural resources, population density, etc.) • common types-point symbol map, dot density map, proportional symbol map Thematic Map: Point Symbol Map-shows location of activities at different points using symbols Thematic Map: Dot Density Map-uses dots to show how something is distributed in a country or a region Thematic Map: Proportional Symbol Map-uses symbols of different sizes to show the size of an event