* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5.9—Proportions and Similar Triangles Objective
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
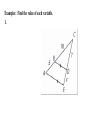
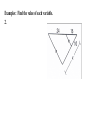
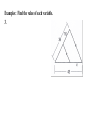
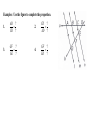
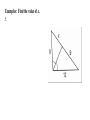
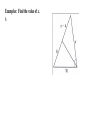
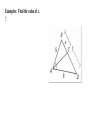
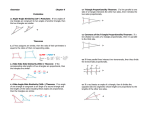
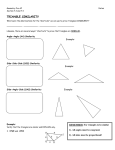
5.9—Proportions and Similar Triangles Write the following biconditional as a conditional statement and its converse. Then determine whether it is true or false. Two angles are supplementary if and only if they form a linear pair. True or False Conditional:________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Converse: __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 5.9—Proportions and Similar Triangles calculate Objective: Use proportionality theorems to ____________________ lengths segment ___________________________. Triangle Proportionality Theorem: parallel intersects If a line _____________ to one side of a triangle ______________ the other two sides, then it divides the two sides ________________________. proportionally RT RU If TU || QS , then R TQ US Converse of the Triangle Proportionality Theorem: divides If a line ___________________ two sides of a triangle proportionally, then it is parallel to the __________________ __________________. third side R RT RU Examples: Find the value of each variable. 1. Examples: Find the value of each variable. 2. Examples: Find the value of each variable. 3. Theorem: three parallel lines intersect If ________ ________ transversals, then they two divide ______________ the transversals proportionally. t Z If r || s || t , then UW WY VX XZ Examples: Use the figure to complete the proportion. 1. AB ? CB ? 3. GF ? GE ? 2. CD ? AD ? 4. GF ? ED ? 5. Use the diagram to find LM and MN to the nearest tenth. Theorem: ray bisects an angle of a triangle, then it divides If a ______ the _____________ side into segments whose lengths are opposite proportional to the __________ of the other two sides. lengths AD CA If CD bisects ACB , then DB CB Examples: Find the value of x. 5. Examples: Find the value of x. 6. Examples: Find the value of x. 7.