* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Triangle origami
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Toilet paper orientation wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
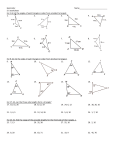
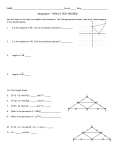
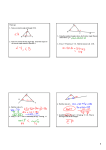
MATH 212 Spring 2008 Name____________________________________ Origami Constructions: Triangles Follow these instructions carefully. They are based on the Hands On activity on pp. 670-671 of MR. The Basic Folds 1. On a blank sheet of white paper, draw a line segment CD; label the endpoints. Measure its length with a ruler and record it below. Now fold C onto D and make a crease to produce a line l ; mark the point M where l intersects CD. Measure € record the values below. Finally, the lengths of both segments CM and MD and using your protractor as accurately as you can, find the exact measure of one of the angles made between CD and l ? Record it below. Is €l really the € of CD?€ perpendicular €bisector € € € € € 2. Use a new sheet of paper to draw an angle made up from two rays with vertex at a point A; use a straightedge. Measure the angle you have drawn with a protractor and record it below. Now fold one of the rays onto the other, making a crease that produces the angle bisector. Then use the protractor to find the exact measures of both of the angles made between the arms of the angle you drew and the folded line; record them both below. According to your measures, is the folded line really a bisector? 3. Use a third sheet of paper for this next item. Draw a bold pencil line and label it l , then mark a point P not on this line. Fold a strong crease into the paper to construct the perpendicular line to l that passes through P. Using your protractor as accurately as you can, what is the exact measure of one of the angles made between the line l and the folded “perpendicular”? Record it below. € € Exploring Properties of Triangles 1. On a fourth sheet of blank paper, draw a large triangle ABC. Use paper folding to construct the three angle bisectors of the interior angles of the triangle. What is interesting about how these three lines intersect? 2. On a fifth sheet of paper, draw a large acute triangle ABC. Use paper folding to construct the three perpendicular bisectors of the sides of the triangle. What special property do you observe? 3. Repeat the instructions for #2 above, but for an obtuse triangle. What do you notice here? 4. If you were to repeat the instructions for #2 with a right triangle, what do you think would happen? Explain. (You may want to carry out the procedure to verify your conjecture, but this is not required.) 5. On a seventh sheet of paper, draw a large acute triangle ABC and use paper folding to construct the three altitudes of the triangle; what do you discover? What would have happened if the triangle were a right triangle? an obtuse triangle? 6. On an eight sheet of paper, draw a large acute triangle ABC and make very short creases to locate the three midpoints of the sides of the triangle; mark these three points L, M, N. Then use stronger creases to construct the three medians of the triangle. Does any special phenomenon occur? Finally, staple all 8 sheets with your origami constructions behind this page and turn in the whole packet.