* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dental Terminology: Periodontology - CSUF Pre
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
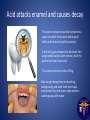
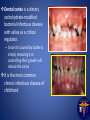
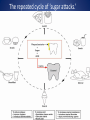
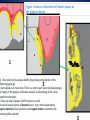
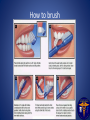
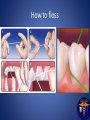
CSUF Pre-Dental Society Dental Outreach Program Commonwealth Elementary Fullerton, CA TODAY!! 12:45pm – 2:00pm Outreach Points: 3 points Why is this important? • Oral health is apart of your body’s health as well. If there is infection in your mouth it can spread to the rest of your body through your blood stream. • If severe enough, infection can lead to your BRAIN!! • This can all be prevented by taking care of your teeth and gums • It is your job to educate the public on oral health because not many people know about these facts! Teeth Importance • Baby teeth (primary teeth) o Eating!! o Speech development o Holds position for permanent teeth • Adult teeth (permanent teeth) o Eating o Speech o Self Esteem/ Appearance We would like to keep our teeth for all these reasons so we need to keep them healthy!! Oral health and nutrition • Decay is formed by a number of things such as amount of saliva a person has, bacteria, and the foods we eat. • High amounts of carbohydrates and sugars encourage bacteria to become more acidic. • More acid means leads to decay and infection sugar Bacteria Acid Acid attacks enamel and causes decay This picture shows decay that turned into a cavity into both the enamel (white part/ shell) and the dentin (yellow section) If the decay gets deeper into the tooth, the pulp (middle section with nerves), then the patient will need root canal This patient will only need a filling Kids can get decay from not brushing, eating candy, and even from their baby bottles that they drink over night without washing away with water. Dental caries is a dietary carbohydrate-modified bacterial infectious disease with saliva as a critical regulator. – Since it is caused by bacteria simply removing it or controlling their growth will reduce the caries It is the most common chronic infectious disease of childhood How we can prevent decay • Brushing off the plaque which is bacterial biofilm resting on the surface of your teeth. (recommended 2-3 brushing a day along with flossing once a day and rinsing after every brush) • Plaque can harden into tartar/calculus that can only be removed with regular cleanings at a dental office called prophylaxis (recommended every 6 months) Before cleaning : tartar build up After dental office cleaning: no more tartar…notice spaces between teeth More prevention • Applying fluoride to kid’s teeth in the dental office will help harden the enamel and reverse early decay • Over the counter rinse called ACT has a lot of fluoride that dentists recommend as well • Sealants for kids prevent decay • Sealants is a plastic material that flows into the grooves of teeth and prevents decay from hiding in those grooves; easier for kids to clean and prevents cavities Saliva The role of saliva is to clean out and reduce oral bacteria, helps to chew, to speak, and to swallow Flow rate Increased by: – gustatory stimulants (sugar-free candy) – masticatory stimulants (sugar-free chewing gum) Reduced by: – – – – – medications (antihistamines, anti-asthmatics, others) disease dehydration radiation age The repeated cycle of ‘sugar attacks.’ People who consume sugars frequently in their diet increase the levels of streptococci and lactobacilli The two bacteria species thought to be responsible for caries. These bacteria continue to thrive as the pH drops. If the plaque is not removed, eventually, the enamel starts to decalcify and an incipient ‘white spot’ lesion ensues. Caries results when all of the factors that contribute to caries overlap (red color, center). Figure shows an illustration of dental plaque at the gingival margin. 1) The enamel (e) has plaque biofilm (b) growing at the border of the nflamed gingival (g). 2) Same plaque at closer look. There is a ‘white spot’ lesion (w) developing at he margin of the gingiva, and brown calculus (c) developing in the sulcus ttached to the tooth. 3) Close-up view of plaque. Biofilm bacteria, which onsists of several species of bacteria (cocci, rods, motile spirochetes), organic material (salivary proteins) and organic matter secreted by the acteria (yellow-stained) Gingivitis= moderate gum disease that has symptoms of swollen gums and deep pockets; leads to more serious disease (periodontitis) if not treated Periodontitis can lead to bone loss and loses support for teeth which leads to your teeth falling out!!! How to brush How to floss Steps in cleaning teeth • Recommended to floss before brushing then rinse • BUT, dentists will probably say it doesn’t matter the order of brushing and flossing as long as you do it!! • As you know there are a ton of dental products out there so as long as you have a soft tooth brush, tooth paste with fluoride, floss, ADA certified rinse then you are good to clean!! Dental Outreach Event Today!! 12:45pm – 2:00pm Commonwealth Elementary School 2200 East Commonwealth Ave Fullerton, Ca 92831