* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1.1 radian and degree measure
Rotation formalisms in three dimensions wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
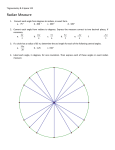
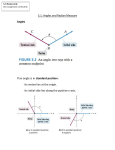
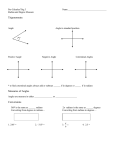
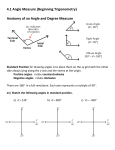
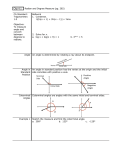
1.1 RADIAN AND DEGREE MEASURE Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Angles The starting position of the ray is the initial side of the angle, and the position after rotation is the terminal side. Angle The endpoint of the ray is the vertex of the angle. Angles When the origin is the vertex and the initial side lies on the positive x-axis, the angle is in standard position. Angles Positive angles - counterclockwise Negative angles - clockwise Radian Measure The measure of an angle is determined by the amount of rotation from the initial side to the terminal side. One way to measure angles is in radians. To define a radian, you can use a central angle of a circle, one whose vertex is the center of the circle. Arc length = radius when = 1 radian Radian Measure Definition of Radian One radian is the measure of a central angle θ that intercepts an arc, s, equal in length to the radius, r, of a circle. 𝑠 𝜃= 𝑟 𝜃 is measured in radians Since the circumference of a circle is 2 r, it follows that a central angle of one full revolution corresponds to an arc length of s = 2 r. Radian Measure Since 2 6.28, there are just over six radius lengths in a full circle. Radian Measure Since one full revolution is 2 Radian Measure These are additional common angles. What Quadrant do the following angles lie in? a) b) c) 𝜋 5 11𝜋 8 𝜋 − 4 Radian Measure Two angles are coterminal if they have the same initial and terminal sides. To find coterminal angles, we add or subtract multiples of 2. A given angle has infinitely many coterminal angles. For instance, = / 6 is coterminal with 𝜋 + 2𝑛𝜋 6 where n is an integer. Example 1 – Sketching and Finding Coterminal Angles For the positive angle 13 / 6, we can subtract 2 to obtain a coterminal angle Example 1 – Sketching and Finding Coterminal Angles cont’d For the negative angle –2 / 3, add 2 to obtain a coterminal angle Determine two coterminal angles (one positive, one negative) Radian Measure Two positive angles and are complementary if their sum is / 2. Two positive angles are supplementary if their sum is . Complementary angles Supplementary angles Degree Measure A second way to measure angles is in terms of degrees, denoted by the symbol . Degree Measure A full revolution corresponds to 360 Since 2 radians corresponds to one complete revolution 360 = 2 rad or 180 = rad. Which gives us the following conversions: Degree Measure Example 3 – Converting from Degrees to Radians a. Multiply by / 180. b. Multiply by / 180. c. Multiply by / 180. Applications The radian measure formula, = s / r, can be used to measure arc length along a circle. Example 5 – Finding Arc Length A circle has a radius of 4 inches. Find the length of the arc intercepted by a central angle of 240. Example 5 – Solution To use the formula s = r, first convert 240 to radian measure. Example 5 – Solution Since the radius, r = 4 inches s = r cont’d Applications A sector of a circle is the region bounded by two radii of the circle and their intercepted arc. Area of the sector 1 𝐴 = 2 𝑟 2 𝜃 (where 𝜃 is in radians)