* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
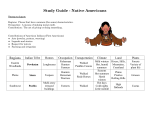
Download Study Guide Colony Table
Colonial American bastardy laws wikipedia , lookup
St. Mary's City, Maryland wikipedia , lookup
Colony of Virginia wikipedia , lookup
Jamestown supply missions wikipedia , lookup
Slavery in the colonial United States wikipedia , lookup
Dominion of New England wikipedia , lookup
Shipbuilding in the American colonies wikipedia , lookup
Province of Massachusetts Bay wikipedia , lookup
Massachusetts Bay Colony wikipedia , lookup
Province of Maryland wikipedia , lookup
Province of New York wikipedia , lookup
London Company wikipedia , lookup
Thirteen Colonies wikipedia , lookup
Colonial South and the Chesapeake wikipedia , lookup
English overseas possessions in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms wikipedia , lookup
CHAPTER 3 REVIEW STUDY GUIDE – PAGE 39 Region Colony Reasons for settlement New England Colonies Massachusetts Puritans escaping religious persecution Rhode Island Middle Colonies Geography & Climate Sandy coast/ports/pastu res/forest Harsh winters, warm summers Settlers/Founders Religion Government Economy William Bradford (Pilgrims) John Winthrop (Puritans) Puritan Crop/live-‐ stock farming, lumbering, shops, shipping People seeing religious freedom Coastal lowlands; flat, rocky woodlands Hot, humid summers, snowy winters Roger Wiliams and Anne Hutchinson Various faiths Self-‐governing (strong religious influence) a government that required everyone in the colony to worship as they did. Self-‐governing (elected assembly) Connecticut Puritans seeking new settlement Forested hills/sea coast Cold winters, mild summers Thomas Hooker (drew up the first written plan of government for any of the colonies) Puritan Written constitution (Fundamental Orders -‐ right to vote!) Self-‐governing New York Dutch and English seeking new lives Wetlands along the coast and Hudson River/Forested mountains to the North, cold, snowy winters; hot, humid summers Dutch West India Company/James Duke of York (The duke gave huge chunks of his colony to two friends, Sir George Carteret and Lord John Berkeley. These men (then established the colony of New Jersey to the south of New York. Various faiths British appointed governer and council alternating with an elected assembly (charter of rights as English citizens. - right to elect their own lawmakers, trial by jury, to worship as they pleased. They did not get these rights until 1691, along with the right to pass laws and set taxes for the colony) Farming (cattle, dairy farms) lumberingsh ipbuilding, fishing, whaling, trade (including slave trade) Farming (cattle/livest ock), shipbuilding, fishing, whaling Fur-‐ trapping, lumbering, shipping slave trade, merchants and tradesmen, farming, iron mining Region Colony Reasons for Settlement Middle Colonies Pennsylvania Southern Colonies Maryland English Quakers and other Europeans seeking freedom and equality Quakers believed in a simple lifestyle and in treating all people equally. They refused to bow before the king, fight in wars, or pay taxes to the Church of England. Catholics/Protestants seeking religious and political freedom Geography Climate Rolling hills, tress, and fertile soil Cold winters; hot, humid summers. Settlers/Founders Religion Government Economy William Penn (wrote great documents of government that made Pennsylvania the first democracy in America.) Various faiths Self-Governing Great Law of 1682, he promised that people of all faiths would be treated equally. Farming (crops/dair y), merchants and tradesmen, lumbering, and shipbuilding Low, fertile land surrounding Chesapeake Bay Cold, rainy winters; hot, humid summers Sir George Calvert (Lord Baltimore – Cecil’s father) Cecil Calvert (Lord Baltimore) Leonard Calvert (governor – brother) Various faiths, particular ly Catholic Self-‐Governing (influenced by Catholics and Protestants) Farming and ranching (crops, beef, dairy), lumbering, shipping, fishing, iron mining Farming (plantations and independent farms) – tobacco! Slavery Farming (plantations and independent farms, trade, skilled labor Virginia English landowners, skilled laborers (shoemakers, bricklayers, tailors), people seeking profit Coastal lowlands, wooded mountains Mild winters; hot, humid summers Sir Walter Raleigh and the Virginia Company Church of England Self –governing with elected assembly (House of Burgesses) Georgia Debtors (poor people) from English prisons, Europeans seeking religious freedom (Protestants, Catholics, & Jews) and cheap land Wetlands/red-‐ clay plains; forested mountains Short, mild winters; long hot, humid summers George II and James Oglethorpe Various faiths Self-‐governing (eventually an elected assembly – colonists did not like Oglethorpe’s laws against drinking alcohol and owning slaves.) Chapter 3 Review Study Guide (page 40 in ISN) II. Similarities (1 pt each) 1. The U.S. Constitution is similar to the Mayflower Compact. 2. The New England colonies were alike because they were self-‐governing. 3. The elected Colonial assembly made the laws in most of the colonies. 4. Separatists were Puritans who wanted to separate from the Church of England in order to form their own congregation and practice their faith in peace. The shared the same religious beliefs. 5. Events that were similar to Quaker’s actions and beliefs include: The American Revolution, The Civil War, Women’s Suffrage (women’s rights), Civil Rights Movement, etc. 6. The Appalachian Mountains restricted colonist’s growth, acting as a Western border; impacted ability to travel West and trade, settle land; barrier that kept them near to the coast. III. Differences (1 pt each) 1. Providence, Rhode Island differed from Puritan Massachusetts because it welcomes people with different religious beliefs. 2. Pennsylvania offered the most freedom. 3. Cash crops, like tobacco plantations, made the Southern colonies unique. 4. People in all three of the regions adapted to different ways of life because they had different geographies, climates, and resources. 5. The colony most motivated to make a profit was Virginia. 6. The region most dependent upon the ocean for its economy was New England. 7. The colony founded to hopefully prevent the Spanish from attacking other colonies was Georgia.