* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Utility
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
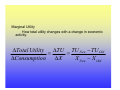
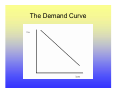
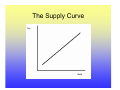
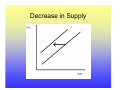
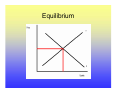
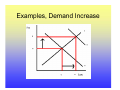
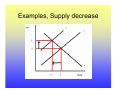
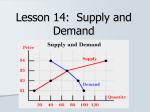
Utility Utility A quantitative measure of satisfaction that consumers from engaging in economic activity. • Utility is a useful fiction • Utility is ordinal; its cardinal measure is meaningless. Marginal Utility How total utility changes with a change in economic activity. ∆Total Utility ∆TU TU New − TU Old = = X New − X Old ∆Consumptio n ∆X Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility states that with each additional consumption unit, the consumer enjoys less satisfaction than the previous consumption unit. i.e., you like ice cream, but you don’t want a tone. Demand Law of Demand There is a negative relationship between quantity and price. This negative relationship between price and quantity reflects the law of diminishing marginal utility. With each additional unit, the consumer is willing to consume only at lower prices. Price- Quantity Space The Demand Curve Change in Quantity Demand Notes for Change in Quantity Demand Demand Function: Quantity=f(Price, Pc+s, Income, Tastes) • When there is a change in the quantity demanded, only price changes. • Pc+s, Income and Tastes remain constant. Increase in Demand Decrease in Demand Notes on Changes in Demand • A change in demand holds price constant and changes Pc+s, Income and Tastes. • A change in demand shifts the curve. • There is a complex relationship between the direction that the demand curve shifts and Pc+s and Income. • An increase in demand shifts the demand curve the right, a decrease to the left. Supply • The supply curve rests on the assumption that producers will produce more at higher prices. • The supply curve also indicates that for producers to produce more, they must pay higher costs to draw resources away from alternative activities. Therefore, at higher quantities, it is more expensive to produce. Law of Supply • The supply curve has a positive slope. Q=f(price, price of inputs, resources, technology) The Supply Curve Change in Quantity Supplied Notes on Changes in Quantity Supplied • When there is a change in the quantity supplied, only price changes. • Price of inputs, resources and technology remain constant. Increase in Supply Decrease in Supply Notes on Supply Changes • A change in supply holds price constant and changes the price of inputs, resources and technology. • A change in supply shifts the curve. • An increase in supply shifts the supply curve the right, a decrease to the left. • Note: Do not think of shifting the supply or demand curve up or down, only right and left. Equilibrium Equilibrium represents: • A point of rest • Market clears • No tendency to change unless an exogenous factor changes. • Exogenous factors: Pc+s, Income, Tastes and preferences, price of inputs, resources and technology. The Process 1. 2. 3. 4. Exogenous change Which curve is influenced? Which direction is the curve influenced? What happens to price and quantity? Examples, Demand Increase Results of an increase in demand? • Price increases • Quantity increases Examples, Demand Decrease Results of an decrease in demand? • Price decreases • Quantity decreases Examples, Supply Increase Results of a supply increase? • Price declines • Quantity Increases Examples, Supply decrease Results of a supply decrease? • Price increases • Quantity Decreases