* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
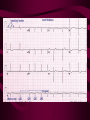
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Linda A. Snyder, MSN, CRNP Definition: • A common arrhythmia characterized by chaotic, rapid, discontinuous atrial depolarizations resulting in rapid oscillations that are recorded as irregularly formed “f” waves in contrast to uniform P waves of sinus or other distinct supraventricular rhythms. Ventricular responses become irregular. Rate may be rapid. Classification • • • • Paroxysmal Persistent Permanent or Chronic Lone EKG Characteristics • Rate: Atrial rate – 400 – 600 bpm Ventricular rate – Rapid – 110 – 160 bpm Controlled – 60 – 100 bpm • Rhythm: Irregular • P- Waves: Not present • P-R Interval: Not measurable EKG Characteristics, cont. • QRS Complex: Usually normal • Conduction: Intra-atrial conduction is disorganized and irregular. Ventricular conduction is usually normal. Conditions Frequently Associated with AF Age HTN CAD Cardiomyopathy ETOH/Drug Intox. CVA Hyperthyroid Valvular Hrt. Disease PVD Inflam/infiltrat. Processes Post Op OHS DM Pulm. Embolus COPD Pulm. HTN Metabolic disorders Symptoms None Palpitations Lightheadedness SOB Diaphoresis Anxiety • • • • Syncope Dizziness Chest pain / pressure Abnormal Sensation in throat / neck • Frequent urination • Altered cognition. Implications • Can lead to decrease in cardiac output • Danger of thromboemboli Treatment Goals • • • • Eliminate cause Control ventricular rate Restore and Maintain Sinus Rhythm Prevent Thromboembolism Eliminate Cause • • • • Post- op Electrolyte Imbalance Thyroid Function Pneumonia Rate Control • Calcium Channel Blockers • Beta Blockers • Digitalis • A-V Node Ablation and Pacemaker Restoring and Maintaining Sinus Rhythm • Cardioversion • Antiarhythmia Drugs • Ablation Procedures Antiarrhythmia Drugs • • • • Vaughan Williams Classification Issues with tolerability and efficacy Toxicity concerns, esp. with Amiodarone Some require in-patient stay for initiation Surgical/Ablation Procedures Considered when--• Medical therapy does not effectively control or correct AF • Medications are not tolerated • Anticoagulants can not be taken • Symptoms of AF continue, despite medical therapy • Blood clots, including stroke, occur • Surgery is needed for coexisting heart condition Goals of Surgical Procedures • Produce lesions and ultimately scar tissue to block the abnormal electrical impulses from being conducted through the heart. • Promote the normal conduction of impulses through the proper pathway. Procedures for AF • Catheter-based Posterior Left Atrial Radiofrequency Ablation • Keyhole Approach • Maze Procedure • Modified Maze Alternative Energy Sources • • • • Radiofrequency Cryothermy Microwave Lasers Preventing Thromboembolism • • • • • *** COUMADIN *** Aspirin Plavix New Anticoagulants Left Atrial Appendage Occlusive Device Indications for Hospital Admission with an Initial Diagnosis of AF • Significant symptoms • Hemodynamic intolerance • High risk for thromboembolic complications • To facilitate prompt cardioversion • Concomitant condition that mandates admission (i.e. acute MI, acute PE, acute TIA or stroke, thyroid storm) “The End” ?’s