* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Culloden way of learning three year topic cycle
Human ecology wikipedia , lookup
Iberian cartography, 1400–1600 wikipedia , lookup
Geopolitics wikipedia , lookup
Environmental determinism wikipedia , lookup
Counter-mapping wikipedia , lookup
Royal Geographical Society wikipedia , lookup
Department of Geography, University of Kentucky wikipedia , lookup
Children's geographies wikipedia , lookup
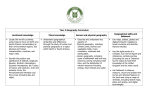
Culloden Way of Learning six-year topic cycle There are 15 discrete topics on the KS2 history curriculum. Some have been combined to fit our cycle. There are eight geography topics. Some have been split to fit our cycle. Pupils will encounter each RE topic twice during the six-year cycle. Early years Autumn term Ourselves Spring term New life Summer term Journeys and holidays Key stage 1 and 2 Y0 first year only (2013-14) Autumn 1: history The Stuart period, including the Union of the Crowns, King versus Parliament, Cromwell’s Commonwealth, the Levellers and the Diggers; the restoration of the monarchy; the Great Plague and the Great Fire of London; Samuel Pepys and the establishment of the Royal Navy; the Glorious Revolution, constitutional monarchy and the Union of the Parliaments Autumn 2: RE Christianity Spring 1: geography Human geography: the distribution of natural resources including energy, food, minerals and water supplies Spring 2: history The later Middle Ages and the early modern period, including Chaucer and the revival of learning, Wycliffe’s Bible, Caxton and the introduction of the printing press, the War of the Roses, Warwick the Kingmaker Summer 1: RE Islam (with comparisons to Christianity) Summer 2: geography Local area study: use fieldwork to observe, measure and record the human and physical features in the local area using a range of methods, including sketch maps, plans and graphs, and digital technologies Y1 (2014-15) Autumn 1: history Early Britons and settlers, including the Stone, Bronze and Iron Ages; Celtic culture and patterns of settlement Autumn 2: RE Hinduism Spring 1: geography Our country: name and locate counties and cities of the UK, geographical regions and their identifying human and physical characteristics, including hills, mountains, cities, rivers, key topographical features and land-use patterns; and understand how some of these aspects have changed over time. Spring 2: history Ancient Greek civilisation Summer 1: RE Buddhism Summer 2: geography Countries of Europe and the world: environmental regions, key physical and human characteristics, countries and major cities. Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied Y2 (2015-16) Autumn 1: history Ancient Roman civilisation focusing on Roman conquest and rule- Caesar, Augustus and Claudius; Britain as part of the Roman Empire; the decline and fall of the Western Roman Empire Autumn 2: RE Sikhism Spring 1: geography Longitude and latitude: equator, northern and southern hemispheres, the tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, Arctic and Antarctic Circles, and time zones (including day and night) Spring 2: history Anglo-Saxon and Viking settlement, including the Heptarchy; the spread of Christianity; key developments in the reigns of Alfred, Athelstan, Cnut and Edward the Confessor Summer 1: RE Judaism Summer 2: geography Countries of North America and the world: environmental regions, key physical and human characteristics, countries and major cities. Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/ computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied Y3 (2016-17) Autumn 1: history The Norman conquest and Norman rule, including the Domesday book; feudalism; Norman culture; the Crusades Autumn 2: RE Secularism Spring 1: geography Physical geography including climate zones, biomes and vegetation belts, volcanoes and earthquakes Spring 2: history Plantagenet rule in the 12th and 13th centuries, including key developments in the reign of Henry II; the murder of Thomas Becket; Magna Carta; de Montfort’s Parliament Summer 1: RE Christianity Summer 2: geography Countries of South America and the world: environmental regions, key physical and human characteristics, countries and major cities. Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/ computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied Y4 (2017-18) Autumn 1: history Relations between England, Wales, Scotland and France including William Wallace, Robert the Bruce, Llewelyn and Dafydd ap Gruffydd, and the Hundred Years War Autumn 2: RE Islam Spring 1: geography Human geography: settlements, land use, economic activity including trade links Spring 2: history Life in 14th century England, including chivalry, the Black Death, the Peasants’ Revolt Summer 1: RE Hinduism Summer 2: geography Regions of the world: understanding geographical similarities and differences through the study of human and physical geography of a region or area of the UK, a region or area in a European country and a region or area within north or south America Y5 (2018-19) Autumn 1: history The later Middle Ages and the early modern period, including Chaucer and the revival of learning, Wycliffe’s Bible, Caxton and the introduction of the printing press, the War of the Roses, Warwick the Kingmaker Autumn 2: RE Buddhism Spring 1: geography Physical geography: rivers, mountains and the water cycle Spring 2: history The Tudor period, including religious strife and reformation in the reigns of Henry VIII, Edward VI and Mary; Elizabeth I’s reign and English expansion, including colonisation of the New World, plantation of Ireland, conflict with Spain Summer 1: RE Sikhism Summer 2: geography Compasses and maps: use of the eight points of a compass, four-figure grid references, symbols and a key (including the Ordnance Survey maps) to build knowledge of the UK and the wider world (choose any areas to focus on) Y6 (2019-20) Autumn 1: history The renaissance in England including the lives and works of individuals such as Shakespeare and Marlowe Autumn 2: RE Judaism Spring 1: geography Human geography: the distribution of natural resources including energy, food, minerals and water supplies Spring 2: history The Stuart period, including the union of the crowns, king versus parliament, Cromwell’s commonwealth, the levellers and the diggers; the restoration of the monarchy; the great plague and the great fire of London; Samuel Pepys and the establishment of the Royal Navy; the glorious revolution, constitutional monarchy and the union of the parliaments Summer 1: RE Secularism Summer 2: geography Local area study: use fieldwork to observe, measure and record the human and physical features in the local area using a range of methods, including sketch maps, plans and graphs, and digital technologies