* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Solutions To Worksheet 7
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of the function concept wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Function (mathematics) wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard calculus wikipedia , lookup
Volume and displacement indicators for an architectural structure wikipedia , lookup
Weber problem wikipedia , lookup
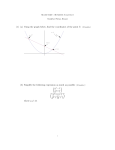
Names Date Math 10550 Worksheet 7 1. One of the following functions has a slant asymptote, and one has a horizontal asymptote. Identify both functions and find the equation of the slant asymptote and horizontal asymptote respectively. h(x) = 6x2 + x + 2 , x2 + 4 7x3 + x2 + 1 , 7x2 + 2 t(x) = r(x) = x6 + x + 3 . x3 + 2x Solution: For rational functions, slant asymptotes occur when the degree of the numerator is one more than the degree of the denominator. This means t(x) has a slant asymptote. Doing long division, we have x + 17 7x2 + 2 7x3 + x2 +1 3 − 7x − 2x 2 x − 2x + 1 − x2 − 27 − 2x + 57 which yields the slant asymptote y = x + 1 7 . We compute 6 + x/x2 + 2/x2 6x2 + x + 2 = lim =6 x→∞ x→∞ x→∞ x2 + 4 1 + 4/x2 6x2 + x + 2 6 + x/x2 + 2/x2 lim h(x) = lim = lim =6 x→−∞ x→−∞ x→−∞ x2 + 4 1 + 4/x2 lim h(x) = lim Thus h(x) has a horizontal asymptote, namely the line y = 6. 2. A box with no top, with square base, and with a volume of 8 cubic feet is needed. Material for the base costs $2 per square foot, and material for the sides costs $1 per square foot. Determine the dimensions of the box that will minimize the cost of materials. Justify that your answer is a minimum. Solution: Let x be the length of the base, and y be the height of the box. We require the volume, x2 y = 8. We have the cost of each square foot of base, is $2, and the cost of each square foot of siding is $1. We want to minimize the total cost, i.e. minimize C(x, y) = 2x2 + (4 × 1)xy. Using the equation for volume, we substitute y = 8 x2 to get the new relation we wish to minimize C(x) = 2x2 + 4·8 . x Now, to find the critical numbers we take the derivative C 0 (x) = 4x − 32 . x2 The critical numbers must satisfy 4x − 32 = 0 =⇒ x = 2. x2 We know this is a minimum, since C 0 (x) < 0 for all 0 < x < 2 and C 0 (x) > 0 for all 2 < x. So each side should have length 2 feet and it should have a height of y = 282 = 2 feet. 3. Determine the dimensions of the rectangle of the largest area that can be inscribed in a right triangle with base 3 units and height 6 units. Justify that your answer is a maximum. Solution: We want to maximize the area, A = xy of the rectangle with base x and height y. Clearly, this rectangle will have one of its corners on the hypotenuse of the triangle. Therefore, the lower right triangle (pictured) is similar to the whole triangle, which implies the relation 6 y = . 3 3−x Thus, y = 2(3 − x). To maximize the area, A = xy = 2(3 − x)x = −2x2 + 6x, we compute the first derivative 3 A0 (x) = −4x + 6 =⇒ A0 (x) = 0 when x = . 2 00 This is a maximum, since the second derivative A (x) = −4 is negative, meaning the graph of A is concave down. To find the dimension of y, we use the equation y = 2(3 − x), so y = 2(3 − (3/2)) = 3. 2x2 + 9 . Indicate the x and y intercepts, if relevant, and 2x all horizontal, vertical and slant asymptotes. Also include local extrema (i.e. local max’s and local min’s) and points of inflection along with the intervals where the function is increasing, decreasing, concave up, and concave down. 4. Sketch the graph of the function f (x) = Solution: We’ll determine some properties of the graph by algebraic methods so that we get a sense of how to sketch it. There are no x-intercepts. This is because the numerator of f (x) is always positive, and so the quotient f (x) is never zero. There are no y-intercepts, since x = 0 is not in the domain of the function because x = 0 gives . x = 0 is a vertical asymptote. By considering the signs of the an undefined expression 9/2 0 numerator and denominator near x = 0, we see that limx→0+ = +∞ and limx→0− = −∞ The power of x in the numerator is one more than that in the denominator, so this is the situation in which we look for a slant asymptote. x x 2 x + − x2 9 2 so we find that the slant asymptote is y = x. To find critical points we find the derivative, f 0 (x) = Thus critical points are x = ± q x2 − 9/2 2x2 − x2 − 9/2 = . x2 x2 9 . 2 The second derivative is f 00 (x) = x2 (2x) − (x2 − 9/2)(2x) 9x = 4. 4 x x This shows that the graph is concave down for x < 0 and concave up for x > 0. q q 9 The second derivative information then let us classify x = 2 as a local minimum and x = − 92 as a local maximum; x = 0 is not an inflection point since it is not in the domain of the function. q S q Finally, we have f 0 (x) < 0 in the intervals (− 92 , 0) (0, 92 ) and f 0 (x) > 0 in the interq Sq vals (−∞, − 92 ) ( 92 , ∞), and therefore, the function is decreasing and increasing on those intervals respectively. We can then sketch the graph. 15 10 5 -4 -2 2 -5 -10 -15 4